1. Which of these is reflective of the hierarchical organization of
life from most to least inclusive?
a. Kingdom, order, family,
phylum, class, genus, species
b. Phylum, class, order, kingdom,
family, genus, species
c. Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family,
genus, species
d. genus, species, kingdom, phylum, class, order,
family
e. class, order, kingdom, phylum, family, genus, species
Answer: c
2. Evolution is biology's core theme that ties together all the other
themes.
This is because evolution
a. Explains the unity and
diversity of life
b. Explains how organisms become adapted to
their environment through the differential reproductive success of
varying individuals
c. Explains why distantly related organism
sometimes resemble each other
d. Explains why some organism have
traits in common
e. All of the above
Answer: e
3. A controlled experiment is one in which
a. The experiment is
repeated many times to ensure that the results are accurate
b.
The experiment proceeds at a slow pace to guarantee that the scientist
can carefully observe all reactions and process all experimental
data
c. There are at least two groups, one of which does not
receive the experimental treatment
d. There are at least two
groups, one differing from the other by two or more variables
e.
There is one group for which the scientist controls all variables
Answer: c
4. About 25 of the 92 occurring elements are known to be essential to
life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately 96% of
living matter?
a. carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen
b.
carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, hydrogen
c. oxygen, hydrogen,
calcium, sodium
d. carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
e.
carbon, oxygen, sulfur, calcium
Answer: d
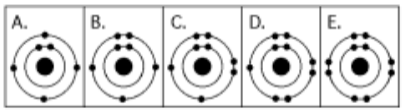
5. Which drawing below depicts the electron configuration of oxygen
(16 8O)
a. A
b. B
c. C
d.
D
e. E
Answer: c
6. What does the reactivity of an atom depend on?
a. Number of
valence shells in the atom
b. Number of orbitals found in the
atom
c. Number of electrons in each orbital in the atom
d.
Presence of unpaired electrons in the outer valance shell of the
atom
e. Presence of hybridized orbitals in the atom
Answer: d
7. A covalent chemical bonds is one in which
a. Electrons are
removed from one atom and transferred to another atom so that the two
atoms become oppositely charged
b. Protons and neutrons are
shared by two atoms so as to satisfy the requirements of both
atoms
c. Outer-shell electrons of two atoms are shared so as to
satisfactorily fill the outer electron shell of both atoms
d.
Outer-shell electrons of an atom are transferred to the inner electron
shells of another atom
e. The inner-shell electrons of one atom
are transferred to the outer-shell of another atom.
Answer: c
8. What results from an unequal sharing of electrons between
atoms?
a. A nonpolar covalent bond
b. A polar covalent
bond
c. An ionic bond
d. A hydrogen bond
e. A
hydrophobic interaction
Answer: b
9. Which bonds must be broken for water to vaporize?
a. Ionic
bonds
b. Nonpolar covalent bonds
c. Polar covalent
bonds
d. Hydrogen bonds
e. Covalent bonds
Answer: d
10. One mole (mol) of a substance is
a. 6.02 x 1023
molecules of the substances
b. 1g of the substance dissolved in n
1 L of solution
c. The largest amount of the substance that can
be dissolved in 1 of solution
d. The molecular mass of the
substance expressed in grams.
e. A and D only
Answer: e
11. One liter of a solution of pH has how many more hydrogen ions
(H+) than 1 L of a solution of pH 6?
a. 4 times more
b. 400
times more
c. 4,000 times more
d. 10,000 times more
e.
100,000 times more
Answer: d
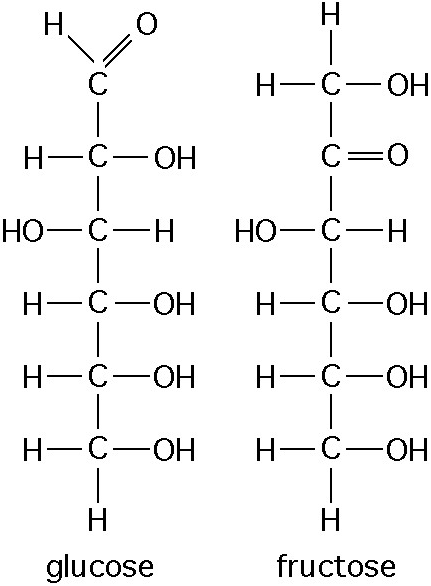
12. Observe the structure of glucose and fructose in the Figure
above
These two molecules are
a. Geometric isomers
b.
Enantiomers
c. Geometric isomers
d. Structural
isomers
e. Nonisotopic isomers
Answer: d
13. Polymers of polysaccharides, fats and proteins are all
synthesized from monomers by which process?
a. Connecting
monosaccharides together (condensation reactions)
b. The addition
of water to each monomer (hydrolysis)
c. The removal of water
(dehydration reactions)
d. Ionic bonding of the monomers
e.
The formation of disulfide between monomers
Answer: c
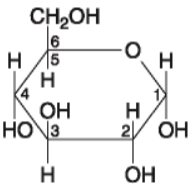
14. If 128 molecules of the general type shown in the figure above
were covalently joined together in sequence, the single molecule that
would result would be a
a. Polysaccharide
b.
Polypeptide
c. Polyunsaturated lipid
d.
Monosaccharide
e. Disaccharide
Answer: a
15. The 20 different amino acids found in polypeptides exhibit
different chemical and physical properties because of
different
a. Carboxyl groups attached to an alpha (α)
carbon
b. Amino groups attached to an alpha (α) carbon
c.
Side chains (R groups)
d. Alpha (α) carbons
e. Asymmetric carbons
Answer: c
16. The tertiary structure of a protein is the
a. Bonding
together of several polypeptide chains by weak bonds
b. Order in
which amino acids are joined in a polypeptide chain
c. Unique
three-dimensional shape of the fully folded polypeptide
d.
Organization of a polypeptide chain into a a-helix or B-pleated sheet
Answer: c
17. What would be an unexpected consequence of changing one amino
acid in a protein consisting of 325 amino acids?
a. The primary
structure of the protein would be changed
b. The tertiary
structure of the protein might be changed
c. The biological
activity or function of the protein might be altered
d. Only A
and C are correct
e. A, B and C are correct
Answer: e
18. Which of the following best describes the flow of information in
eukaryotic cells?
a. DNA → RNA → Proteins
b. RNA → Proteins
→ DNA
c. Proteins → DNA → RNA
d. RNA → DNA →
Proteins
e. DNA → Proteins → RNA
Answer: a
19. All of the following nitrogenous bases are found in DNA
except:
a. thymine
b. adenine
c. uracil
d.
guanine
e. cytosine
Answer: c
20. Which of the following types of molecules are the major
structural components of the cells membrane?
a. Phospholipids and
cellulose
b. Nucleic acids and proteins
c. Phospholipids and
proteins
d. Proteins and cellulose
e. Glycoproteins and cholesterol
Answer: c
21. A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In
an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the
volume of blood lost is transferred directly into one of his veins.
What will be the most probable result of this transfusion?
a. It
will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of
viruses and bacteria
b. The patient's red blood cells with
shrivel up because the blood fluid is hypotonic compared to the
cells
c. The patient's red blood cells will swell because the
blood fluid is hypotonic compared to the cells
d. The patient's
red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood fluid is hypertonic
compared to the cells
Answer: c
22. The movement of a substance across a biological membrane against
its concentration gradient with the help of energy input is
a.
Diffusion
b. Active transport
c. Osmosis
d. Facilitated
diffusion
e. Exocytosis
Answer: b
23. The sodium-potassium is called an electrogenic pump because
it
a. Pumps equal quantities of Na+ and K+ across the membrane
b. Pumps hydrogen ions out of cells
c. Contributes to the
membrane potential
d. Ionizes sodium and potassium atoms
e.
Is used to drive the transport of other molecules against a
concentration gradient
Answer: c
24. Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of
breaking down large molecules into smaller ones?
a.
Catalysis
b. Metabolism
c. Anabolism
d.
Dehydration
e. Catabolism
Answer: e
25. Living organism increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in
a decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the
second law of thermodynamics?
a. Living organism do not obey the
second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy must increase
with time.
b. Life obeys the second law of thermodynamics because
the decrease in entropy as the organism grows is balanced by an
increase in the entropy of the universe
c. Living organism do not
follow the laws of thermodynamics.
d. As a consequence of
growing, organism create more disorder in their environment than the
decrease in entropy associated with their growth
e. Living
organism are able to transform energy into entropy
Answer: d
26. Which of the following statements regarding ATP is (are)
correct?
a. ATP serves as a main energy shuttle inside
cells
b. ATP drives endergonic reactions in the cell by the
enzymatic transfer of the phosphate group to specific
reactants.
c. The regeneration of ATP from ADP and phosphate is a
endergonic reaction
d. A and B only
e. A, B and C
Answer: e
27. Increasing the substrate concentration in an enzymatic reaction
could overcome which of the following?
a. Denaturization of the
enzyme
b. Allosteric inhibition
c. Competitive
inhibition
d. Saturation of the enzyme activity
e.
Insufficient cofactors
Answer: c
28. What is the term used for the metabolic pathway in which glucose
(C6O12H6) is degraded to carbon
dioxide (CO2) and water?
a. Cellular
respiration
b. Glycolysis
c. Fermentation
d. Citric
acid cycle
e. Oxidative phosphorylation
Answer: a
29. In addition to ATP, what are the end products of
glycolysis?
a. CO2 and H2O
b.
CO2 and pyruvate
c. NADH and pyruvate
d.
CO2 and NADH
e. H2O, FADH2, and citrate
Answer: c
30. Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with
glycolysis?
a. An agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its
concentration in the cell
b. An agent that binds to pyruvate and
inactivates it
c. An agent that closely mimics the structure of
glucose but is not metabolized
d. An agent that reacts with NADH
and oxidizes it to NAD+
e. An agent that blocks the passage of
electrons along the electron transport chain
Answer: c
31. The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
a.
Yield energy in the form of ATP as it is passed down the respiratory
chain
b. Act as an acceptor for the electrons and
hydrogen
c. Combine with carbon, forming CO2
d. Combine with lactate, forming pyruvate
e. Catalyze the
reactions of glycolysis
Answer: b
32. In a plant cell, where are the ATP synthase complexes
located?
a. Thylakoid membrane
b. Plasma membrane
c.
Inner mitochondrial membrane
d. A and C
e. A, B, and C
Answer: d
33. Which of the following statements best represents the
relationship between the light reactions and the Calvin Cycle?
a.
The light reactions provide ATP and NADPH to the Calvin Cycle and the
cycle returns ADP, Pi, and NADP+ to the light reactions
b. The
light reactions provide ATP and NADPH to the carbon fixation step of
the Calvin Cycle, and the cycle provides water and electrons to the
light reactions
c. The light reactions supply the Calvin Cycle
with CO2 to produce sugars and the Calvin Cycle supplies the light
reactions with sugars to produce ATP
d. The light reactions
provide the Calvin Cycle with oxygen for electron flow, and the calvin
cycle provides the light reactions with water to split
e. There
is no relationship between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle
Answer: a
34. From the perspective of the cell receiving the message, the three
stages of cell signaling are
a. The paracrine, local, and
synaptic stages
b. Signal reception, signal transduction and
cellular response
c. Signal reception, nucleus disintegration,
and new cell generation
d. The alpha, beta and gamma
stages
e. Signal reception, cellular response and cell division
Answer: b
35. Which of the following is (are) true of ligand-gated ion
channels?
a. They are important in the nervous system.
b.
They lead to changes in sodium and calcium concentrations in
cells
c. They open or close in response to a chemical
signal
d. Only A and B are true
e. A, B and C are true
Answer: e
36. The correct sequence of steps in the M phase of the cell cycle
is
a. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase,
telophase
b. Prophase, metaphase, prometaphase, anaphase,
telophase
c. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase,
telophase, cytokinesis
d. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase,
telophase, cytokinesis
Answer: c
37. Which of the following is true of the process of meiosis?
a.
Two diploid cells result
b. Four diploid cells result
c.
Four haploid cells result
d. Four autosomes result
e. Four
chiasmata result
Answer: c
38. What was the most significant conclusion that Gregor Mendel drew
from his experiments with pea plants?
a. There is considerable
genetic variation in garden peas.
b. Traits are inherited in
discrete units, and are not the results of “blending”
c.
Recessive genes occur more frequently in the F1 than do dominant
ones
d. Genes are composed of DNA
e. An organism that is
homozygous for many recessive traits is at a disadvantage
Answer: b
39. Two characters that appear in a 9:3:3:1 ratio in the F2
generation should have which of the following properties?
a. Each
of the characters is controlled by a single generation
b. The
genes controlling the characters obey the law of independent
assortment
c. Each of the genes controlling the characters has
two alleles
d. Only A and C are correct
e. A, B and C are correct
Answer: b
A woman who has blood type A has a daughter who is type O positive
and a son who is type B negative. Rh positive is a simple dominant
trait over Rh negative.
40. Which of the following is a possible
genotype for the mother?
a. IAIA
b. IBIA
c. ii
d.
IAI
e. IAIB
Answer: d
41. When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyes F1 generation flies
to each other, the F2 generation included both red-and white-eyed
flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the
explanation for this result?
a. The involved gene was on the X
chromosome
b. The involved gene was on the Y chromosome.
c.
The involved gene was on an autosome
d. Other male-specific
factors include eye color in flies
e. Other female-specific
factors influence eye color in flies
Answer: a
42. How could one explain a test-cross involving F1 dihybrid flies in
which more parental-type offspring that recombinant-type offspring are
produced?
a. The two genes are linked
b. The two genes are
unlinked
c. Recombination did not occur in the cell during
meiosis
d. The test-cross was improperly performed
e. Both
the characters are controlled by more than one gene.
Answer: a
43. Which of the following statements does not apply to the Watson
and Crick model of DNA?
a. The two strands of the DNA form a
double helix
b. The distance between the strands of the helix is
uniform
c. The framework of the helix consists of sugar-phospate
units of the nucleotides
d. The two strands of the helix are held
together by covalent bonds
e. The purines form hydrogen bonds
with pyrimidines
Answer: d
44. The leading and the lagging strands differ in that
a. The
leading strand is synthesized in the same direction as the movement of
the replication fork, and the lagging strand is synthesized in the
opposite direction
b. The leading strand is synthesized by adding
nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing strand, and the lagging
strand is synthesized by adding nucleotides to the 5' end.
c. The
leading strand is synthesized continuously, whereas the lagging strand
is synthesized in short fragments that are ultimately stitched
together.
d. Both A and B
e. Both A and C
Answer: a
45. A possible sequence of nucleotides in the template strand DNA
that would code for the polypeptide sequence phe-leu-ile-val would
be
a. 5' TTG-CTA-CAG-TAG 3'
b. 3' AAC-GAC-GUC-AUA 5'
c.
5' AUG-CTG-CAG-TAT 3'
d. 3' AAA-AAT-ATA-ACA 5'
e. 3'
AAA-GAA-TAA-CAA 5'
Answer: e
46. RNA polymerase and DNA polymerase differ in that
a. RNA
polymerase uses RNA as a template and DNA polymerase uses a DNA
template
b. RNA polymerase binds to single-stranded DNA and DNA
polymerase binds to double-stranded DNA
c. RNA polymerase is much
more accurate than DNA polymerase
d. RNA polymerase can initiate
RNA synthesis but DNA polymerase requires a primer to initiate DNA
synthesis.
e. RNA polymerase does not need to separate the two
strands of DNA in order to synthesize an RNA copy, whereas DNA
polymerase must unwind the double helix before it can replicate the DNA.
Answer: d
47. A frameshift mutation could result from
a. A base insertion
only
b. A base deletion only
c. A base substitution
only
d. Deletion of three consecutive bases
e. Either an
insertion or a deletion of a base
Answer: b
48. What is the function of reverse transcriptase in
retroviruses?
a. It hydrolyzes the host cell's DNA
b. It
uses viral RNA as a template for DNA synthesis
c. It converts
host cell RNA into viral DNA
d. It translates viral RNA into
proteins
e. It uses viral RNA as a template for making
complementary RNA strands.
Answer: b
49. What are prions?
a. Misfolded versions of normal brain
protein
b. Tiny molecules of RNA that infect plants
c. Viral
DNA that has to attach itself to the host genome
d. Viruses that
invade bacteria
e. A mobile segment of DNA
Answer: a
50.What does the operon model attempt to explain?
a. The
coordinated control of gene expression in bacteria
b. Bacterial
resistance to antibiotics
c. How genes move between homologous
regions of DNA
d. The mechanism of viral attachment to a host
cell
e. Horizontal transmission of plant viruses
Answer: a
51. Which two functional groups are always found in amino
acids?
a. hydroxyl and aldehyde
b. ketone and
aldehyde
c. carboxyl and amino
d. carbonyl and carboxyl
Answer: c
52. In animal cells, hydrolytic enzymes are packaged to prevent
general destruction of cellular components. Which of the following
organelles function in this?
a. peroxisome
b.
chloroplast
c. lysosome
d. central vacuole
e. glyoxysome
Answer: c
53. A cell has the following molecules and organelles enzymes: DNA,
ribosomes, plasma membrane, and mitochondria. This could be
a. a
bacterial cell
b. a plant or an animal cell
c. an animal
cell, but not a plant cell
d. a plant cell, but not an animal
cell
e. a cell from any kind of organism
Answer: b
54. Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to
which of the following structures in animal cells?
a. gap
junctions
b. peroxisomes
c. tight junctions
d.
extracellular matrix
e. desmosomes
Answer: a
55. Which of the following statements concerning prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells is not correct?
a. DNA or deoxyrinonucleic acid,
is present in both prokayotic cells and eukaryotic cells
b.
Prokaryotic cells contain small membrane-enclosed organelles
c.
Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus
d. Prokaryotic
cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus
e. DNA or deoxyribonucleic
acid is present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells
Answer: b
56. Celery stalks that are immersed in fresh water for several hours
become stiff and hard. Similar stalks left in a salt solution become
limp and soft. From this we can deduce that the cells of the celery
stalks are
a. hypertonic to both fresh water and salt
solution
b. hypotonic to both fresh water ans the salt
solution
c. hypertonic to fresh water but hypotonic to the salt
solution
d. hypotonic to fresh water but hypertonic to the salt
solution
e. isotonic with fresh water but hypotonic to the salt solution
Answer: c
57. The active site of an enzyme is the region that
a. actively
prevents changes in substrate concentration
b. binds to products
of the catalytic reaction
c. is inhibited by the presence of a
coenzyme or a cofactor
d. binds allosteric regulators of the
enzyme
e. is involved in the catalytic reaction of the enzyme
Answer: e
58. When you have a severe fever, what may be a grave consequence if
it is not controlled?
a. Denaturation of the body's
enzymes
b. removal of amino groups from your proteins
c.
destruction of your enzymes' primary structure
d. binding of
enzymes to inappropriate substrates
e. removal of the amino acids
in enzymes active sites
Answer: a
59. Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain
located?
a. Mitochondrial intermembrane space
b.
mitochondrial outermembrane
c. mitochondrial matrix
d.
cytoplasm
e. mitochondrial inner membrane
Answer: e
60. Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which
pathway?
a. citric acid cycle → FADH₂ → electron transport chain
→ ATP
b. citric acid cycle → NADH → electron transport chain →
oxygen
c. electron transport chain → citric acid cycle → ATP →
oxygen
d. pyruvate → citric acid cycle → ATP → NADH →
oxygen
e. glycolysis → NADH → oxidative phosphorylation → ATP → oxygen
Answer: b
61. Which of the following occurs in the cytoplasm of an eukaryotic
cell?
a. Glycolysis and fermentation
b. citric acid
cycle
c. oxidative phosphorilation
d. oxidation of pyruvate
to acetyl CoA
e. fermentation and chemiosmosis
Answer: a