What does hemoglobin do in the body?
- Hemoglobin consists of four polypeptide chains each containing a heme group with an iron atom that binds to oxygen in the lungs.
- From the lungs hemoglobin transports oxygen to the tissues of the body where it is used to provide energy.
- Once the oxygen is released, hemoglobin binds to carbon dioxide for transport to the lungs where it is released
What does hemoglobin do in the body? (simple answer)
- Hemoglobin transports oxygen to the tissues of the body and transports carbon dioxide to the lungs
Why does aspirin relieve headaches?
- When a part of the body is injured, substances called prostaglandins are produced, which cause inflammation and pain
- Aspirins acts to block the production of prostaglandins, thereby reducing inflammation, pain, and fever.
Chemistry
- the study of the composition, structure, properties, and reactions of matter
- happens all around you every day
Matter
- all the substances that make up the world
-
EXAMPLES:
- antacid
- water
- glass
- air
Examples of a Chemical Reaction
- tarnishing of silver
- antacid fizzing when dropped into water
- digesting food breaking it down into substances you need for energy and health
Chemicals
- substances that always have the same composition and properties wherever it is found
-
EXAMPLES:
- shampoo contains chemicals that remove the oil from hair
- chemicals in toothpaste clean your teeth
- chemicals in lotion help to moisturize skin
Antioxidants
- chemicals added to food to prevent it from spoiling
Calcium carbonate
- used as an abrasive to remove plaque
Sorbitol
- prevents loss of water and hardening of toothpaste
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
- used to loosen plaque
Titanium Dioxide
- makes toothpaste white and opaque
Triclosan
- inhibits bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease
Sodium Fluorophosphate
- prevents formation of cavities by strengthening tooth enamel with fluoride
Methyl Salicylate
- gives toothpaste a pleasant wintergreen flavor
Which of the following contains chemicals?
A. sunlight
B. fruit
C. milk
D. breakfast cereal
B,C,D
- sunlight is an energy given off by the sun therefore does not contains chemicals
Scientific Method
- a set of general principles that helps to describe how a
scientist thinks
- Observations
- Hypothesis
- Experiments
- Conclusion
Observations
- first step in scientific method
- information determined by noting and recording a natural phenomenon
- make observations about nature and ask questions about you observe
Hypothesis
- second step in scientific method
- propose a hypothesis
- which states a possible explanation of the observations
- should be stated in a way that it can be tested by experiments
Experiments
- a procedure that tests the validity of a hypothesis
- several experiments may be done to test the hypothesis
Conclusion
- an explanation of an observation that has been validated by repeated experiments that support a hypothesis
- done when the experiments are analyzed
- conclusion is made as to whether the hypothesis is true or false
Ones Place (place value)

- first place to the left of the decimal point
Tens Place (place value)

- second place to the left of the decimal point
Tenths Place (place value)
- first place to the right of the decimal point
Hundredths Place (place value)
- second place to the right of the decimal point
Graph
- represents the relationship between two variables
- contains to perpendicular axes
- has a horizontal axis/ x axis
- has a vertical axis/ y axis
Positive Number
- any number that is greater than zero and has a positive (+) sign
Negative Number
- any number that is less than zero and is written with e negative (-) sign
Multiplication and Division of Positive and Negative Numbers

- when two positive or two negative number are multiplied or divided, the answer is positive
- when a positive and a negative number are multiplied or divided, the answer is negative
Addition of Positive and Negative Numbers

- when two positive numbers are added ,the answer is positive
- when two negative numbers are added, the answer is negative
- when a positive and a negative are added, the smaller number is subtracted from the larger number and the result has the same sign as the larger number
Subtraction of Positive and Negative Numbers
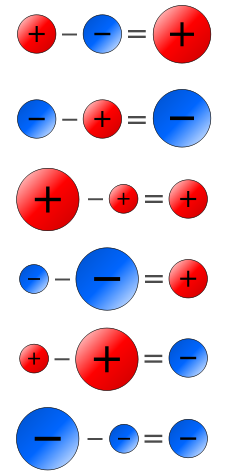
- when two numbers are subtracted change the sign of the number to be subtracted
Calculating a Percentage
- divide the parts by the total (whole) and multiply by 100
Solving Equations
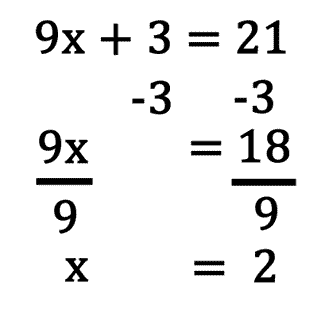
- place all like items on one side
- isolate the variable we need to solve for
- check your answer by substituting your value for x back into the original equations
Writing Numbers in Scientific Notation

- number has two parts
- coefficient
- has to be at least 1 but less than 10
- power of 10
- coefficient
-
EXAMPLE:
- 2400 in scientific notation
- 2.4 x 10^3
Scientific Notation on Calculator

Scientific Notation
- a form of writing large and small numbers using a coefficient that is at least 1 but less then 10 followed by a power of 10