How many women will develop breast cancer?
1 in 8
True or False?
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death in middle aged women
True
When should a breast scan be performed?
a mass is located by palpation or mammography
What is the primary reason for breast sonography?
differentiate between
simple cysts
complex cysts
solid masses
Why is breast sonography at a disadvantage on young women?
less fat and more parenchyma.
what type of machines are used on breast exams?
state of art
less than 5 years
What type of transducer should be used on breast exams?
7 MHz - 12 MHz linear
What should you do if you find a mass larger than the footprint of the transducer?
change to a curvilinear
What is said about the sonographer of breast exams?
breast exams are operator dependent and so should be experienced
True or False?
Multiple focuses give better resolution.
true
but temporal resolution takes a hit
Where is the retromammary layer located?
in the pectoralis muscles
Where are the acini cells?
within the lobules
What are acini cells?
milk producing cells
lobules + lobules + lobules =
lobe
where are lymphatic vessels in the breast?
run from the acini cells to the nipple
What are ducts made up of?
basement membrane and a ductal epithelium
True or False?
Ductal epithelium are contractile.
True
Why does dynamic range improve imaging?
by adding more shades of gray and may demonstrate subtle tissue differences
Why are neither color or power Doppler reliable in distinguishing benign from malignant lesions?
both may demonstrate internal flow
Why is Doppler helpful during a breast exam?
distinguishing
solid vs cystic - flow confirms a solid
inflamed vs noninflamed - increased flow
complex cyst vs intraductal papilloma
True or False?
Doppler can positively confirm solid vs cystic lesions
False
flow confirms a solid
flow does NOT confirm cystic
Explain the sonographic appearance of cysts.
anechoic and circular
thin walls
through transmission
What is the superficial fascia?
triangular bag that contains the contents of the breast
contained within the subcutaneous layer anterior to the mammary layer
Breast anterior to posterior
skin
subcutaneous layer
mammary layer
retromammary space
muscle layer
chest wall
How thick is the skin on the breast?
.5 - 2 mm
How many lactiferous ducts openings in the nipple?
15-20
What does the nipple consist of?
nerve endings & lactiferous ducts
What is the areola?
area of dark pigmentation
What are Montgomery's glands
small bumps
What does the subcutaneous layer primarily consist of?
fat
True or False?
Breast fat increases with age
True
Does the Fat extend behind the nipple?
NO
Explain the sonographic appearance of the subcutaneous layer of the breast.
multiple
homegenous
midlevel gray
lobule structures separated by brightly echogenic ligaments
Where are the cooper's ligaments?
runs between superficial to deep layers
extends from the clavicle and the pectoralis muscles to the skin
What is the sonographic appearance of Cooper's ligaments?
thin brightly echogenic membranes separating fat lobules
What is the purpose of Cooper's ligaments?
provide skeletal framework of the breast
Why can Cooper's ligaments be a pitfall?
may cause acoustic shadowing
What is another name for the Mammary layer?
parenchymal
Glandular layer
What is the Tail of Spence?
portion of the glandular tissue that extends into the axilla
What does the mammary layer consist of?
stoma
epithelium
What is breast stroma?
supportive tissue in the mammary layer
What does the stroma consist of?
interlobular fat
loose and dense connective tissue
cooper's ligaments
What is Breast Epithelium?
Functional tissue of the breast
What does breast epithelium consist of?
acini
terminal Duct Lobular units TDLU
Lobules
Lobes
Lactiferous ducts
What are the smallest functional unit in the breast?
acini cells
How many acini cells in each breast?
hundreds
How many acini cells in each TDLU?
30
True or False?
Each acini gives rise to a terminal duct.
true
What is the order of the breast?
Acini (30)
TDLU (lots)
Lobules (10-15)
Lobes (15-20)
Breast
What is a TDLU
terminal Duct Lobular units
What is the usual measurement for the TDLU?
2 mm or less
Where does almost all breast pathology originate?
TDLU
How many acini and terminal ducts form a lobule?
30
How many lobules make up a lobe
10-15
How many lobes in a breast?
15 to 20
What emerges from each from lobe and travels toward the nipple?
lactiferous duct
What carries milk?
lactiferous duct
acini to nipple
What are the lactiferous ducts called arising from the acini?
terminal ducts
What are the lactiferous ducts called in the lobules?
intralobular
What are the lactiferous ducts called in the lobes?
extralobular
What are the lactiferous ducts beneath the areola?
lactiferous sinus
What are the two muscles of the breast?
pectoralis major
pectoralis minor
Where does the pectoralis minor arise?
3rd, 4th and 5th ribs
Where does the pectoralis major arise?
clavicle and costal cartilage of the sternum
Which muscle is anterior?
pectoralis major
What causes breast development?
hormonal stimulation by the ovaries
What does Estrogen stimulate in the breast?
elongation
increase in connective tissue
adipose tissue
vascularity
What does progesterone stimulate in the breast?
growth of TDLU
What are the menstrual Breast changes during days 1-5?
decrease in size
What are the menstrual Breast changes during days 6-9?
Menstrual post
What are the menstrual Breast changes during days 6-13?
proliferated or production of acini cells TDLU
What are the menstrual Breast changes during days 13-28?
Secretory - ducts enlarge edematous
What happens to the breast in the early stage of pregnancy?
lactiferous ducts increase in size
What happens to the breast in the late stage of pregnancy?
stroma is crowded and displaced
What stimulates the production of milk?
prolactin dominates after birth and acini cells secrete milk
When do ducts and lobules return to their normal size after pregnancy?
3 months after termination of breast feeding
What happens to the breast during menopause?
Shrivel and roll forward
loose - dense
dense - stoma
strom - fat
What two main arteries supply the breast?
Lateral Thoracic
Internal Mammary
Where does the Lateral Thoracic Artery arise from?
the axillary artery
Where does the Internal Mammary Artery arise from?
subclavian artery
What are the secondary arterial supplies of the breast?
Thoracoacromial artery
intercostal artery
What artery is used for the CABG procedure?
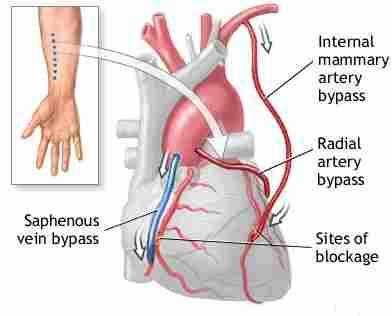
Internal Mammary
What veins drain the breast?
Internal Mammary Vein
Axillary Vein
Subclavian Vein
Intercostal Veins
How does breast cancer most frequently spread?
blood flow routes
What vein is commonly blamed for breast cancer metastasis to ribs?
Intercostal Veins - communicates with vertebral veins
What is the most common metastasis of Breast Cancer?
bone
lung
liver
Why is the axillary lymph node chain important in predicting the spread of breast cancer?
75% of lymphatic drainage is the the axilla
How do you identify the sentinel lymph node
A surgeon injects a radioactive substance, a blue dye, or both near the tumor to locate the position of the sentinel lymph node. The surgeon then uses a device that detects radioactivity to find the sentinel node or looks for lymph nodes that are stained with the blue dye.
Why is the sentinel lymph node important?
if the sentinel lymph node is clear then the rest will be clear.
Explain the Lymphatic drainage of the breast.
Most lymphatics of the breast first drain superficially to the anterior mammary fascia.
Then to the periareolar plexus and the axilla
What is the most common cancer to metastasize to the breast?
Melanoma
True or False?
Metastatic disease of the breast from another primary cancer is uncommon.
True
What is the pancake view?
medio-lateral oblique
What is the omelet view?
cranio-caudal
What is a stand-off pad
allows for greater detail in the superficial layers of the breast
What is the ideal thickness of a stand-off pad?
1 cm
What would you explain to the patient about a breast exam?
The sonographer should explain to the patient that the exam is being performed to visualize the breast and to investigate mammogram findings
How should a patient dress for a breast exam?
The patient should undress from the waist up and wear a hospital gown open in the front.
What transducer should be used on a breast exam?
7 – 12 MHz linear array transducer
What do you do if the mass is larger than the footprint?
change to a curvilinear probe.
What positions should be used for a breast exam?
Supine
Supine oblique may be used for the lateral margin of the breast
What are the scan planes for a breast exam?
radial and anti-radial, sagittal and Transverse
Radial plane – runs parallel to the ducts, the transducer is held at a radial plane with the nipple in the center.
Anti-radial plane – runs perpendicular to the ducts
What is a radial & anti-radial scan plane?
radial - runs parallel to the ducts, the transducer is held at a radial plane with the nipple in the center.
Anti-radial plane – runs perpendicular to the ducts
What techniques can be used during a breast exam?
Fremitus: Have the patient hum with power Doppler, everything lights up except for mass
Ipsilateral arm is raised above the head -- provides a more stable scanning surface
Stand-off pad to visualize superficial structures
Gentle but firm pressure - forces tissues into a parallel plane
Describe the anatomy of the breast.
The breast lies anterior to the 6th rib and pectoralis muscles. Breast tissue is supported by cooper’s ligaments that extend from deep muscle fascia to the skin. The breast is described in layers.
What does the Subcutaneous Layer consist of?
Consists of skin and adipose tissue.
What does the Mammary Layer consist of?
Consists of 15 to 20 lobes containing glandular tissue, ducts, fat lobules and connective tissue.
What does the Retromammary Layer consist of?
Consists of fat lobules, connective tissue and muscle.
What are appropriate reasons for the breast exam?
Mass found by palpitation
Mass found by mammogram
Differentiate
- Simple cyst
- Complex cyst
- Solid mass
What are appropriate History Questions for a breast exam?
When was the last time you had menstrual Period?
Are you in pain?
Where is your pain located?
How long have you been in pain?
How long does the pain last and does it go away?
Are you experiencing any other symptoms?
Do you have a family history of breast cancer?
Have you had any lab work done?
What are the required images in a breast exam?
Document the lesion in at least two planes.
- Lesions
- Lesion w/measurements
What is the sonographic appearance of the Subcutaneous Layer?
Most superficial layer, The skin appears as a hyperechoic border. Inferior to the skin is the subcutaneous fat lobules which appear as low-level echoes with hyperechoic margins
What is the sonographic appearance of the Mammary Layer?
Mix between fat and glandular tissue, Depending on the fat content the parenchyma can appear highly echogenic with little fat or areas of low echogenicity mixed with areas of high echogenicity.
What is the sonographic appearance of the Retromammary Layer?
Generally hypoechoic relative to the mammary layer. Inferior to the breast the pectoralis muscle can be seen as a hypoechoic area.
.
What is the sonographic appearance of breasts in young patients?
Young patients have little fat and dense breasts will appear highly echogenic.
What is the sonographic appearance of breasts in child-bearing age patients?
Women of child-bearing age have an increase in fibrous tissue and dense connective tissue which will cause the breast to be highly echogenic.
What is the sonographic appearance of breasts in post-menopausal patients?
As the patient ages the glandular tissue shrinks. The breast appears hypoechoic
What are normal variants of breasts?
Amastia
Polymastia
Athelia
Amazia
Unilateral early ripening
Nipple inversion
What is Amastia?
complete absence of one or both breasts
What is Polymastia ?
an accessory breast
What is Athelia ?
an accessory nipple
What is Amazia ?
nipple but no breast tissue
What are the measurements for a breast exam?
Simple cyst: record at least greatest dimensions
Solid lesions: record all 3 dimensions
Multiple lesions: record largest and smallest
Ducts: 2-3 mm
What are benign conditions?
noncancerous disorders that can affect the breast
Sonographic Appearance:
Round, oval
Wider than tall
Thin walls
Anechoic, hyperechoic, homogenous
Posterior enhancement
Edge shadowing
Calcifications
Along Fibrous planes
Ducts measure 2-3 mm
Doppler – no flow
Presentation: breast lump, redness, pain, tenderness swelling, multiple cysts, palpable superficial, spherical nodule, discharge, nipple retraction , feeling of fullness, subareolar thickenin
What is the Sonographic Appearance of benign breast lesions?
Round, oval
Wider than tall
Thin walls
Anechoic, hyperechoic, homogenous
Posterior enhancement
Ducts measure 2-3 mm
Doppler – no flow
What are the presentations of women with benign breast conditions?
breast lump
redness
pain
tenderness swelling
multiple cysts
palpable superficial
spherical nodule
discharge
nipple retraction
feeling of fullness
subareolar thickening
What are Malignant conditions?
cancerous disorders that can affect the breast
What is the Sonographic Appearance of malignant breast lesions?
Taller than wide
Angular, ill-defined, microlobulations
Thick borders
Echogenic halo
Almost anechoic, heterogenous
Shadowing
Color Doppler - more peripheral and internal flow
Invade tissue planes
What is a simple cyst?
benign breast condition
Very common in women ages 35 to 50
Results from obstructed duct or hormonal changes
Regress after menopause
Presentation: breast lump, pain & tenderness
What is the Sonographic Appearance of simple cysts?
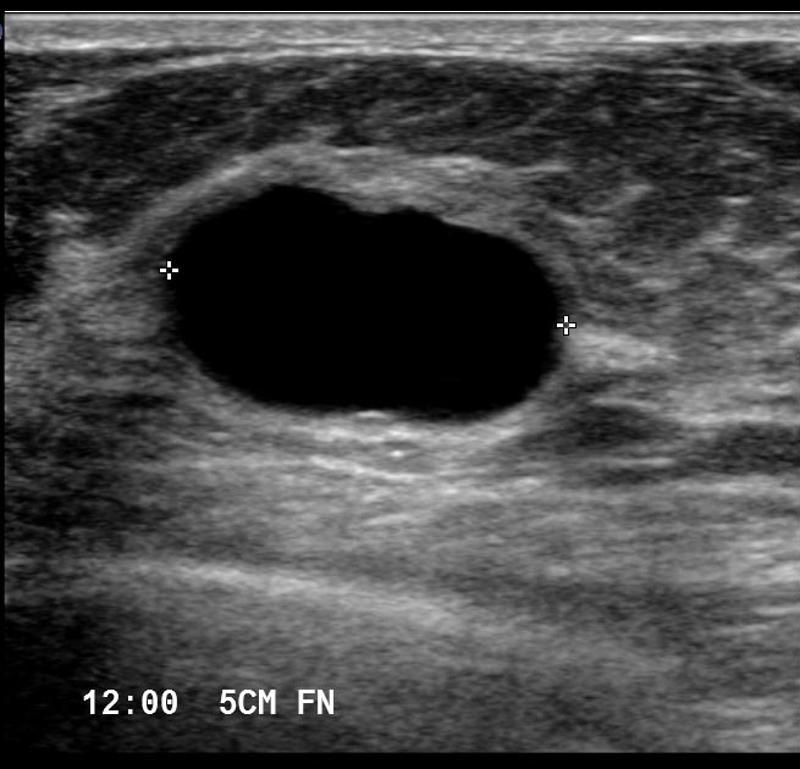
Oval or round
anechoic
smooth walls
well circumscribed shape
posterior enhancement
edge refraction
sharp anterior and posterior borders
reverberation
What is a Complex Cysts?
benign breast condition
contain some low level internal echotexture or intra-cystic debris.
Risk of malignancy among complicated breast cysts is thought to be 0.3-2%
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Complex Cysts?
Low to medium echogenicity
Irregular walls
hetertogenous
fluid filled levels
septations
wall thickening
debris
varying degrees of shadowing
What are the presentations of Complex Cysts?
breast lump
What is Galactocele?
benign breast condition
Milk filled cyst, results from obstructed duct after childbirth
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Galactocele?
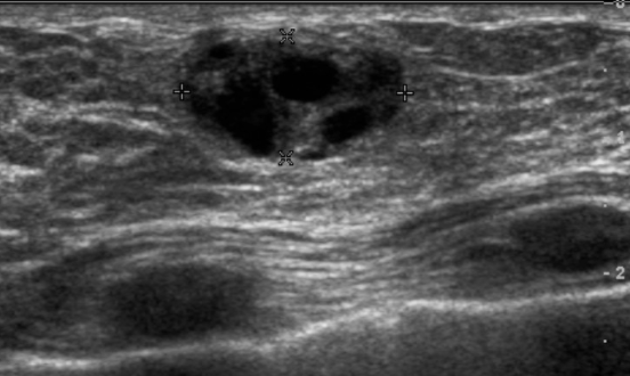
Round
Hyperechoic
Homeogenous
What are the presentations of Galactocele?
breast lump
What is a Sebaceous Cyst?
benign breast condition
Superficial, sebum containing, results from obstructed sebaceous gland
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Sebaceous Cyst?
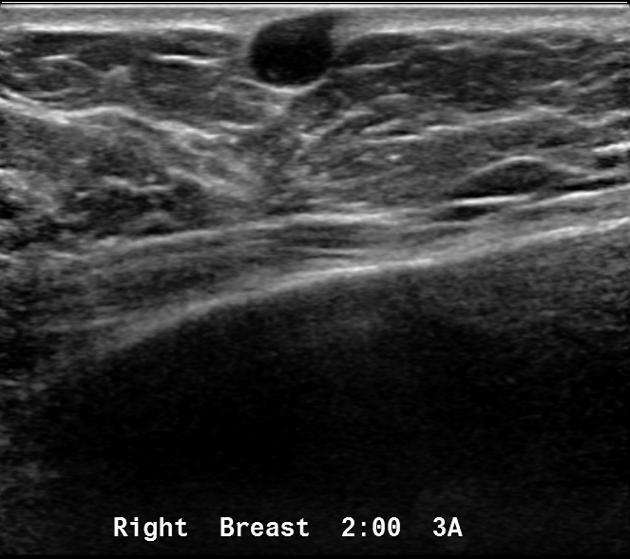
Small
Hypoechoic
Close to the skin surface
Through transmission
No detectable vascular flow
Hypo- and hyperechoic alternating rings
A characteristic track may be seen extending into the skin surface
What are the presentations of Sebaceous Cyst?
breast lump
What is Fibrocystic Condition?
benign breast condition
Produce tissue alterations in both epithelial and connective tissue. Fluctuates with normal hormonal cycles
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Fibrocystic Condition?
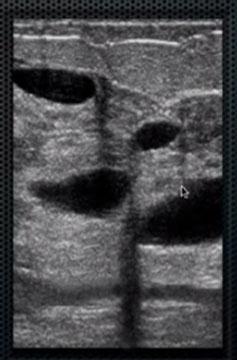
Multiple cysts
Well circumscribed thins walls
Increased fibrous stroma
What are the presentations of Fibrocystic Condition?
multiple cysts, pain & tenderness.
What is Fibroadenoma?
benign breast condition
Estrogen related tumor. Most common benign solid tumor of the breast.
Primarily in young women
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Fibroadenoma?
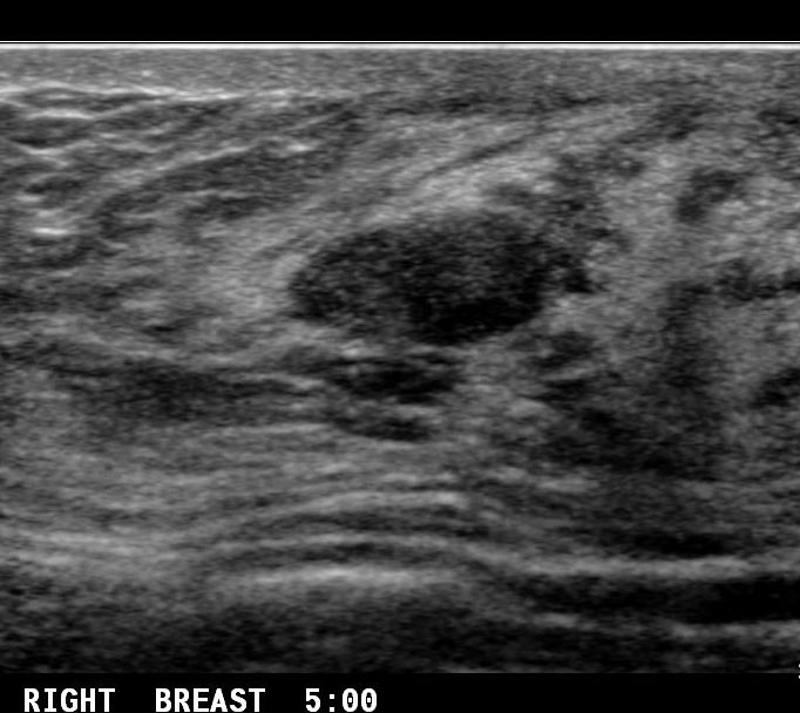
Oval
Gently lobulated
Hyperechoic
Uniform echogenicity
Smooth distinct borders
Wider than tall
Enhancement
Edge shadowing
Arise from TDLU
Pseudo-encapsulated
What are the presentations of Fibroadenoma?
Painless palpable mass, firm rubbery
What is Lipoma?
benign breast condition
Encapsulated tumor of mature adipose tissue.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Lipoma?
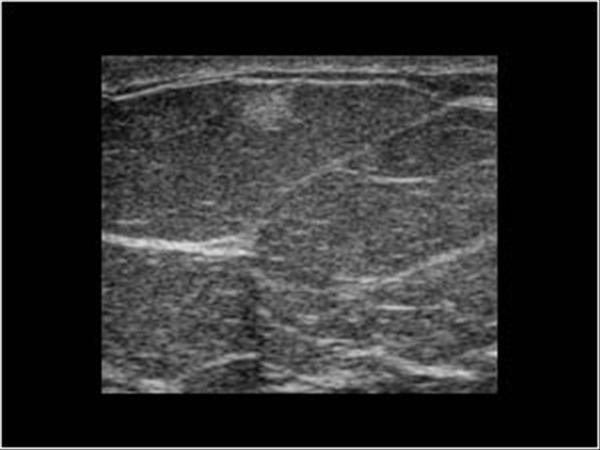
Well-defined
Oval
Thin smooth walls
Homeogenous
hyperechoic
Isoechoic with fat
Enhancement
Edge shadowing
no calcification
What are the presentations of Lipoma?
Asymptomatic, painless palpable breast lump which is soft and mobile
What is Fat Necrosis?
benign breast condition
May be caused by trauma to the breast or other disease present
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Fat Necrosis?
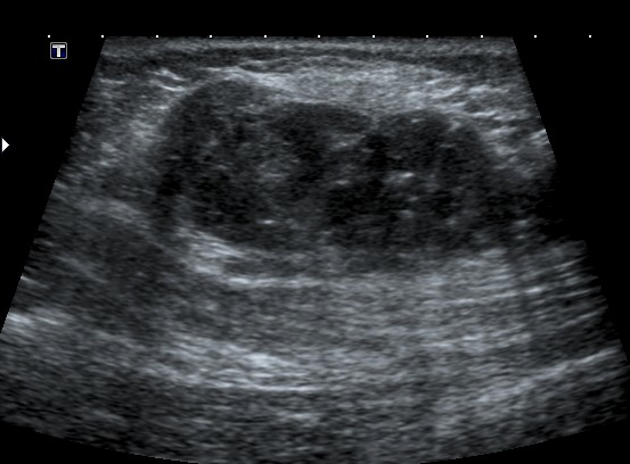
Irregular complex mass
Low-level echoes
Edge shadowing
Separate from breast parenchyma
Mimic malignant tumor
What are the presentations of Fat Necrosis?
palpable superficial, spherical nodule
What is Acute Mastitis?
benign breast condition
Inflammation of the breast, lactational is most common. Antibiotics
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Acute Mastitis?
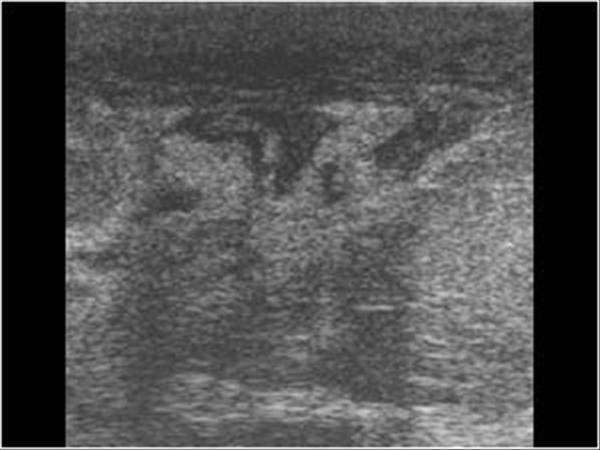
Blurred tissue planes
Skin thickening
Ductal dilation
Increased color flow
What are the presentations of Acute Mastitis?
localized or whole breast, Redness, pain and swelling
What is Chronic Mastitis?
benign breast condition
Inflammation of the glandular tissue, usually found in older women
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Chronic Mastitis?
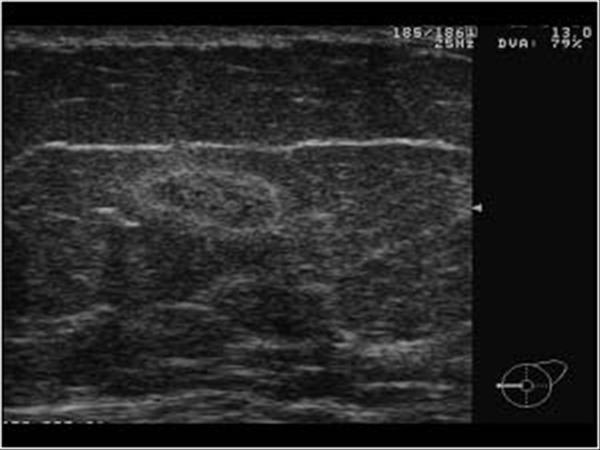
Difficult to differentiate by ultrasound
Diffused echo patterns
Thickening of connective tissue
What are the presentations of Chronic Mastitis?
discharge, nipple retraction, subareolar thickening
What is Abscess?
benign breast condition
complication of mastitis, usually in subareolar region
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Abscess?
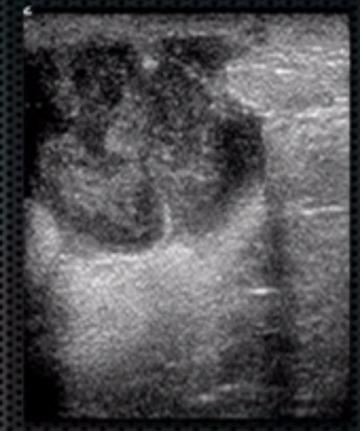
hyperechoic
Complex
Irregular borders
Posterior enhancement
Skin thickening
Increased color flow
What are the presentations of Abscess?
painful lump, swelling, nipple discharge
What is Gynecomastia?
benign breast condition
Enlargement of the male breast
Causes include – hormonal changes, testicular failure, neoplasm, marijuana, klinefelters (XXY)
Lab Values: ↑Estrogen, ↓Testosterone
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Gynecomastia?
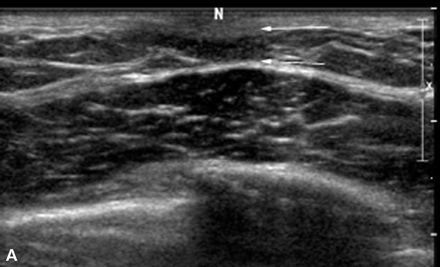
nodular pattern
dendritic pattern
diffuse glandular pattern
What is Cystosarcoma?
benign breast condition
A rare disease mostly benign breast neoplasm
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Cystosarcoma?
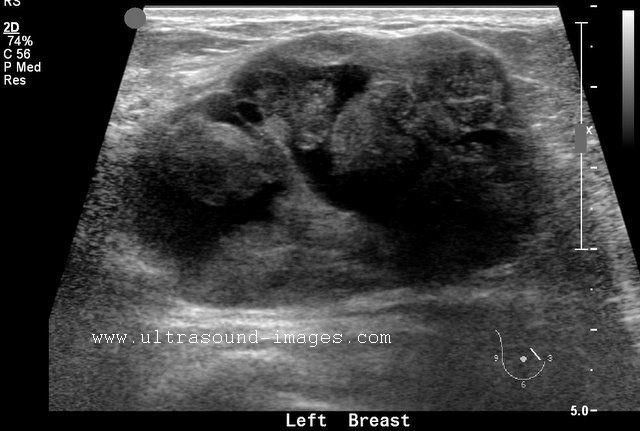
Large
Hypoechoic tumor
Well-defined
Decreased through transmission
Fine or course internal echoes
Variable amounts of shadowing
What are the presentations of Cystosarcoma?
small breast mass that suddenly enlarges
What is Intraductal Papilloma?
benign breast condition
Benign tumor originating from the ductal epithelium and projecting into the lumen of the duct. Commonly in women ages 35 to 55.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Intraductal Papilloma?
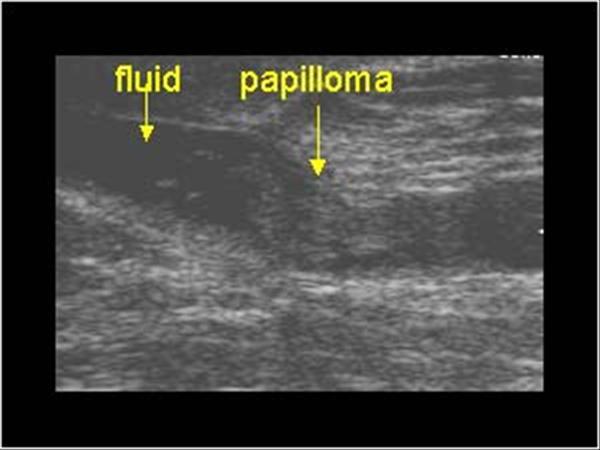
Less than 2 mm
Subareolar region
broad-based
pedunculated
fibrovascular stalk
What are the presentations of Intraductal Papilloma?
bloody discharge, feeling of fullness or pain in the areola
What is Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DSIS)?
malignant breast condition
Most common non-invasive breast cancer. Arises from the TDLU, malignant changes of the ductal epithelium without extension past basement membrane.
Excellent cure rate
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DSIS)?
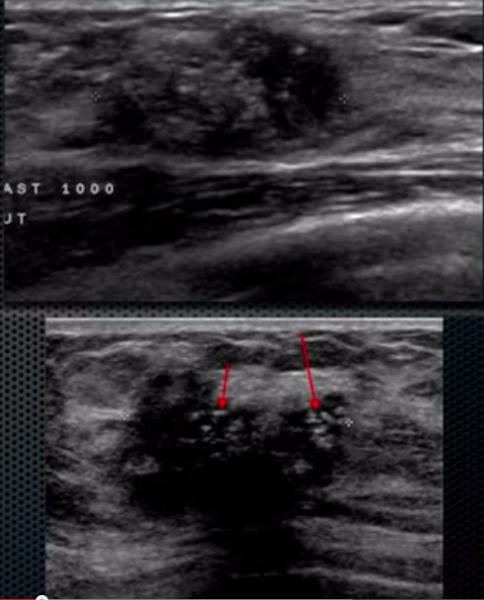
Calcifications
Ductal enlargements
Extensions within the ducts
What is Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)?
malignant breast condition
80% of Breast cancer. Begin in the duct and invade the fatty tissue. Potential for metastases
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC)?
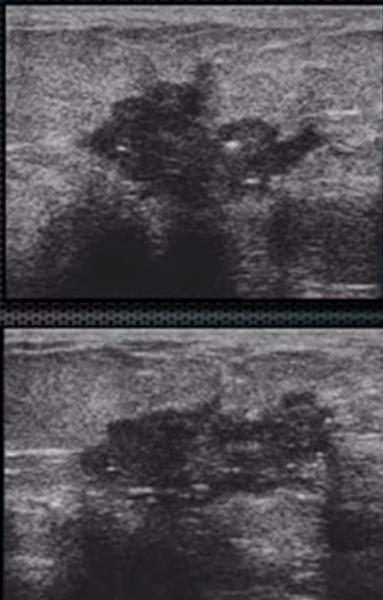
Calcifications
Ductal enlargements
Invasion of the breast parenchyma
What is Lobular Carcinoma in Situ(LCIS)?
malignant breast condition
precancerous, considered lobular neoplasm.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Lobular Carcinoma in Situ(LCIS)?
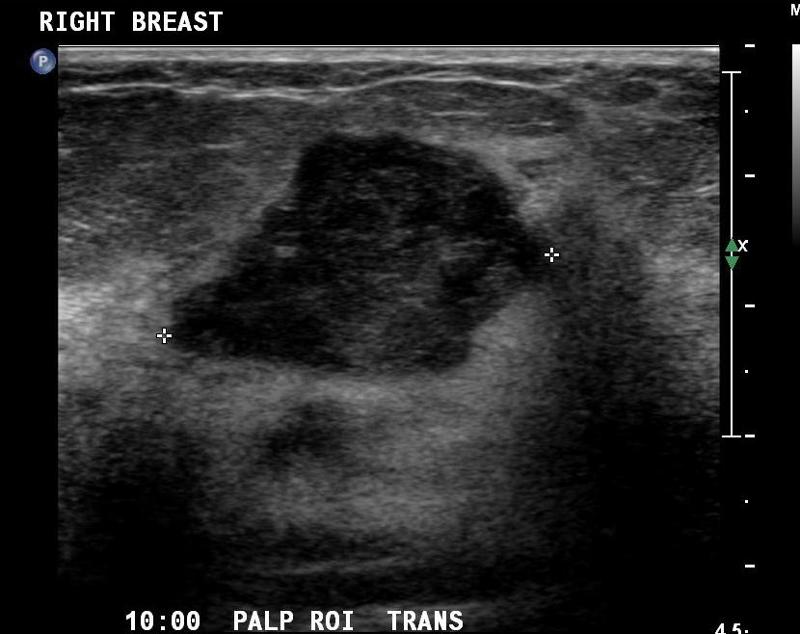
Confined to the gland
Difficult to distinguish with sonograms
What is Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)?
malignant breast condition
10 to 15% of breast cancer, begins in the duct and invades the fatty tissue. Potential for metastases.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC)?
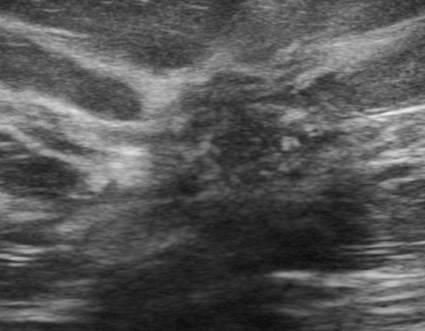
Begins in the lobule
Extends into fatty tissue
Bilateral
Multicentric
multifocal
What is Comedocarcinoma?
malignant breast condition
Intraductal solid carcinoma ducts filled with yellow paste-like that resembles a plug.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Comedocarcinoma?
Microcalcifications
Irregular borders
Diffuse internal echoes
shadowing
What are the presentations of Comedocarcinoma?
pain, sensation of insects crawling, nipple retraction, dominant mass, clear discharge
What is Juvenile Breast Cancer?
malignant breast condition
Similar to DCIS & IDC found in girls 8 to 15.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Juvenile Breast Cancer?
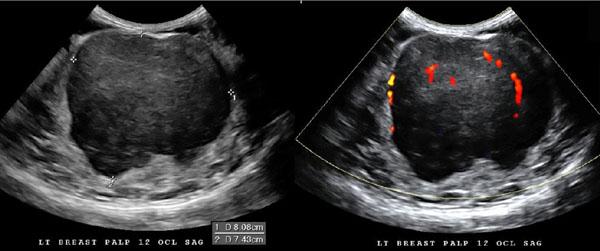
Calcifications
Ductal enlargements
Extensions within the ducts
What is Papillary Carcinoma?
malignant breast condition
Tumor that arises as an intraductal mass. 1% – 2% of Breast Cancer
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Papillary Carcinoma?
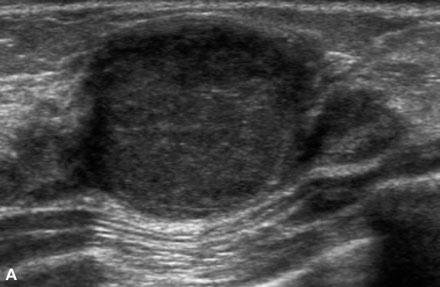
Hypoechoic solid mass
Posterior enhancement
Complex cystic and solid masses may be evident.
Relatively vascular
What are the presentations of Papillary Carcinoma?
bloody discharge, palpable mass
What is Paget’s Disease?
malignant breast condition
Rare tumor, arises in the retroareolar duct and grows toward the nipple.
Women over 50
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Paget’s Disease?
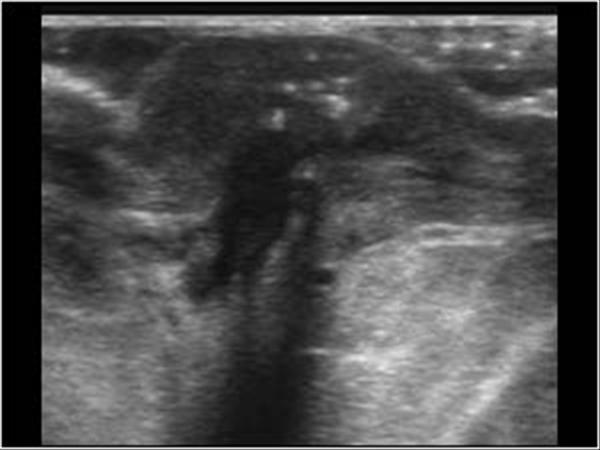
Retroareolar Mass
Irregular borders
Hetergenous internal echoes
Posterior enhancement
What are the presentations of Paget’s Disease?
rash—like appearance
What is Scirrhous Carcinoma?
malignant breast condition
intraductal tumor with extensive fibrous tissue.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Scirrhous Carcinoma?
Focal calcifications
Dense
fibrous
What are the presentations of Scirrhous Carcinoma?
firm nodule, nonmovable mass
What is Medullary Carcinoma?
malignant breast condition
densely cellular tumor.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Medullary Carcinoma?
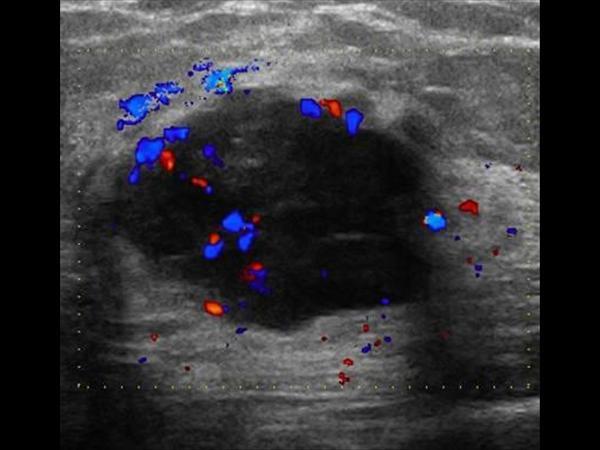
Large
Resemble fibroadenoma
Oval
Gently lobulated
Hyperechoic
Uniform echogenicity
Smooth distinct borders
Wider than tall
Enhancement
Edge shadowing
What are the presentations of Medullary Carcinoma?
Discoloration of the overlying skin, bilateral
What is Colloid Carcinoma?
malignant breast condition
rare ductal carcinoma 3% of breast cancer
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Colloid Carcinoma?

Salt & Pepper echotexture
Resemble fibroadenoma
Oval
Gently lobulated
Hyperechoic
Uniform echogenicity
Smooth distinct borders
Wider than tall
Enhancement
Edge shadowing
What are the presentations of Colloid Carcinoma?
slow-growing, smooth non-firm palpable mass.
What is Tubular Carcinoma?
malignant breast condition
Infectious cystic disease common in sheep herders, a tapeworm that infects.
What is the Sonographic Appearance of Tubular Carcinoma?
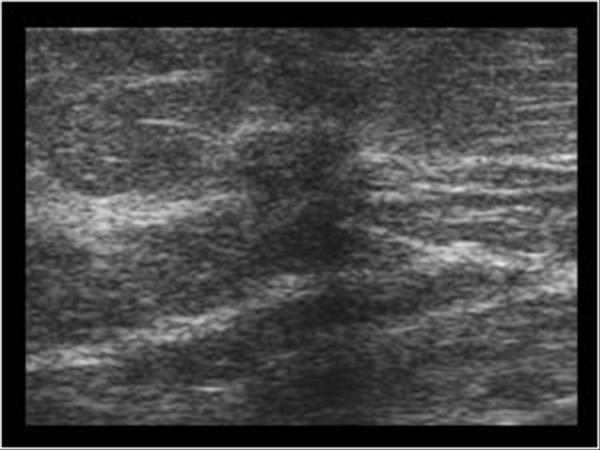
Heterogeneous
Hypoechoic mass
Angular or ill-defined margins
Posterior shadowing
What are the presentations of Tubular Carcinoma?
firm palpable mass