Match
Definitions:
Across
Two
Water
Body
Little, Small
Color
Between
Pre/fix, Root words:
Aqu- (or Aqua-)
-Elle
Chrom-
Bi-
-Some (or Soma-)
Trans-
Inter-
Across: trans-
Two: Bi-
Water: Aqu- (or Aqua-)
Body: -Some (or Soma-)
Little, Small: -Elle
Color: Chrom-
Between: Inter-
Matching
Definition:
Inside, Inner
Thread
Cell
Green
Out of
True, good
Without, lack of, not
Pre/fix, Root words:
Chloro-
Ex-
Endo-
-Cyte (or cyto-)
A- (or An-)
Eu-
Mito-
Inside, Inner: Endo-
Thread: Mito-
Cell: -Cyte (or cyto-)
Green: Chloro-
Out of: Ex-
True, good: Eu-
Without, lack of, not: A- (or An-)
Matching
Definition:
Below, less than
Same
Eat
Above, greater than
Formed substance
Small
Leaf
Pre/fix, Root words:
Hyper-
Phyll-
Sym-
Phago-
- Plasm
Hypo-
Micro-
Below, less than: Hypo-
Same: Sym-
Eat: Phago-
Above, greater than: Hyper-
Formed substance: -Plasm
Small: Micro-
Leaf: -Phyll
Beginning within the nucleus, the first step leading to the synthesis of a polypeptide is _____.
A. Translation of an RNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids
B. Transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA
C. Removal of introns from RNA and the stitching together of exons
D. Linking of nucleotides to form a polypeptide
E. Translation of a DNA nucleotide sequence into a sequence of amino acids
B. Transferring of information from DNA to messenger RNA
Pancreatic cells, which secrete a large amount of digestive enzymes, are labeled with radioactive leucine and then chased for several hours with nonradioactive leucine. Photographic emulsions are prepared at different times during the chase. Where would the black spots appear on an emulsion prepared 3 hours after the pulse?
A. Golgi apparatus
B. Secretory vesicles
C. Exterior of the cell
D. Rough ER
C. Exterior of the cell
What path does a protein in the secretory pathway take, starting from its site of synthesis?
A. Rough ER, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles, plasma membrane
B. Plasma membrane, secretory vesicles, Golgi apparatus, rough ER
C. Rough ER, secretory vesicles, Golgi apparatus, plasma membrane
D. Golgi apparatus, rough ER, secretory vesicles, plasma membrane
A. Rough ER, Golgi apparatus, secretory vesicles, plasma membrane
During a pulse-chase experiment, photographic emulsions were prepared at different times during the chase, and radioactive spots were detected at the following times and locations: 5 minutes: rough ER; 10 minutes: Golgi apparatus; 40 minutes: endosomes; 70 minutes: lysosomes; 140 minutes: lysosomes. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from these results?
A. The final destination of the proteins was the lysosome.
B. The proteins were secreted.
C. The proteins traveled from lysosomes to endosomes.
D. The proteins did not travel through the Golgi apparatus.
A. The final destination of the proteins was the lysosome.
What scientific hypotheses can be tested by a pulse-chase experiment?
A. Movement of molecules through a cell over time
B. Molecular zip code of a protein
C. Solubility of a molecule
D. The steady-state amount of protein in a cell
A. Movement of molecules through a cell over time
True or false? Proteins produced during the "chase" phase of a pulse–chase experiment are labeled with radioactive material.
True or False
False
What is the first step in a pulse-chase experiment?
A. Preparing cells for electron microscopy
B. Examining cells for the location of the labeled molecules
C. Incubating cells with an unlabeled molecule
D. Incubating cells with a labeled molecule
D. Incubating cells with a labeled molecule
_____ are surface appendages that allow a bacterium to stick to a surface.
A. Flagella
B. Ribosomes
C. Cell walls
D. Fimbriae
E. Mitochondria
D. Fimbriae
What is the function of a bacterium's capsule?
A. Protein synthesis
B. Adhesion
C. DNA storage
D. Protection
E. Propulsion
D. Protection
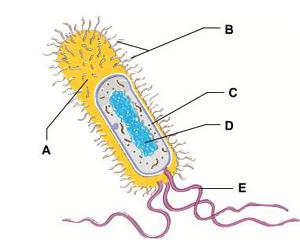
The DNA-containing region of this bacterial cell is indicated by the letter _____.
A. A
B. B
C. C
E. E
D. D
Where is a bacterial cell's DNA found?
A. Ribosomes
B. Nucleus
C. Peroxisome
D. Nucleoid region
E. Capsule
D. Nucleoid region
In a bacterium, where are proteins synthesized?
A. Ribosomes
B. Nucleus
C. Peroxisome
D. Nucleoid region
E. Capsule
A. Ribosomes
What name is given to the rigid structure, found outside the plasma membrane, that surrounds and supports the bacterial cell?
A. Capsule
B. Pili
C. Cell wall
D. Flagella
E. Nucleoid region
C. Cell wall
The _____ is the bacterial structure that acts as a selective barrier, allowing nutrients to enter the cell and wastes to leave the cell.
A. Plasma membrane
B. Nucleoid region
C. Ribosome
D. Pili
E. Cell wall
A. Plasma membrane
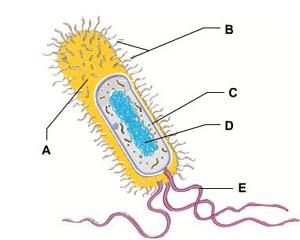
The structure that regulates the passage of material into and out of this bacterial cell is indicated by the letter _____.
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
C. C
Categories:
Plant cell only
Animal cell only
Both
Options:
Central vacuole
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Centriole
Nucleus
Chloroplasts
Plasma membrane
Cytoskeleton
Cellulose cell wall
Mitochondria
Plant cell only:
Central vacuole
Cellulose cell wall
Chloroplasts
Animal cell only:
Centriole
Both:
Endoplasmic reticulum
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
Cytoskeleton
Golgi apparatus
Mitochondria
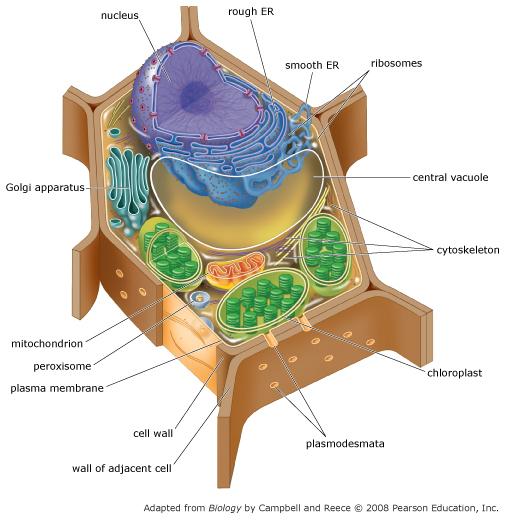
Categories:
Plant cell wall
Central vacuole
Chloroplast
Mitochondrion
Golgi apparatus
Options:
Produces chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell
Makes sugar by converting light energy into chemical energy
Strong, protective structure made from cellulose fibrils
Modifies and packages proteins
Regulates cytoplasm, creates internal pressure, and stores cell compounds
Plant cell wall: Strong, protective structure made from cellulose fibrils
Central vacuole: Regulates cytoplasm, creates internal pressure, and stores cell compounds
Chloroplast: Makes sugar by converting light energy into chemical energy
Mitochondrion: Produces chemical energy (ATP) that can power the cell
Golgi apparatus: Modifies and packages proteins
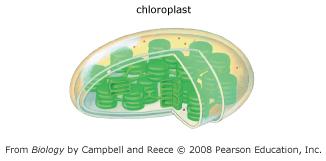
Which statements are true for chloroplasts? Select the three that apply.
Their inner membrane has infoldings called cristae.
They are the sites of reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy.
They have membranous sacs called thylakoids that are surrounded by a fluid called stroma.
Their matrix contains enzymes that function in cellular respiration.
They are the sites of reactions that convert chemical energy to ATP.
They contain the green pigment chlorophyll.
They are the sites of reactions that convert solar energy into chemical energy.
They have membranous sacs called thylakoids that are surrounded by a fluid called stroma.
They contain the green pigment chlorophyll.
Where do scientists obtain adult stem cells?
A. Pancreas
B. Skin
C. Saliva
D. Bone marrow
D. Bone marrow
Ideally, the best scaffold for growing a replacement tissue or organ would be made of what?
A. Cotton
B. Extracellular matrix
C. Plastic
D. Silicon
B. Extracellular matrix
In order to best eliminate the chance for rejection, a tissue or organ should be made from cells obtained from which of the following?
A. A sibling
B. The patient
C. A cadaver
D. A donor pig
B. The patient
If a fabricated windpipe is not receiving proper oxygen and nutrients, which of the following failed to properly regenerate?
A. White blood cells
B. Blood vessels
C. Keratin
D. Mucus producing cells
B. Blood vessels
Which of the following is most likely to receive a fabricated organ made from his own cells?
A. Lung cancer patient
B. Pancreatic cancer patient
C. Bladder cancer patient
D. Thyroid cancer patient
C. Bladder cancer patient
Organelles:
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
Nucleolous
Lysosomes
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Golgi Apparatus
Cytoskeleton
Mitochondria
Roles:
Generates ATP
Modefies and sorts proteins
Assembles ribosomes
Digests proteins
Produces secretory proteins
Synthesizes lipids
Defines cell shape
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum: Synthesizes lipids
Nucleolous: Assembles ribosomes
Lysosomes: Digests proteins
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum: Produces secretory proteins
Golgi Apparatus: Modefies and sorts proteins
Cytoskeleton: Defines cell shape
Mitochondria: Generates ATP
Categories:
Prokaryotic only
Eukaryotic only
Both
Options:
Mitochondria
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
Nucleoid
Lysosome
Nucleolus
Flagella
Prokaryotic only:
Nucleoid
Eukaryotic only:
Mitochondria
Nucleolus
Lysosome
Both:
Flagella
Ribosomes
Plasma membrane
1. In eukaryotic flagella, the fibers that slide past one another due to the activity of dynein proteins are ___.
2. Many cell organelles, most notably the nucleus, are anchored by ___ which are assembled from a diverse class of proteins.
3. Centrosomes are sites where protein dimers assemble into ___.
4. The extension of psuedopodia in amoeba is due to the regulated assembly and destruction of ___.
5. The only cytoskeletal fibers not associated with intracellular movement or whole cell locomotion are the ___.
6. During muscle contractions, myosin motor proteins move across tracks of ___.
Options:
Intermediate filaments
Microtubules
Microfilaments
1. In eukaryotic flagella, the fibers that slide past one another due to the activity of dynein proteins are microtubules.
2. Many cell organelles, most notably the nucleus, are anchored by intermediate filaments which are assembled from a diverse class of proteins.
3. Centrosomes are sites where protein dimers assemble into microtubules.
4. The extension of psuedopodia in amoeba is due to the regulated assembly and destruction of microfilaments.
5. The only cytoskeletal fibers not associated with intracellular movement or whole cell locomotion are the intermediate filaments.
6. During muscle contractions, myosin motor proteins move across tracks of microfilaments.
Which molecules do not normally cross the nuclear membrane?
A. DNA
B. mRNA
C. Proteins
D. Nucleotide triphosphates
A. DNA
Which of the following statements about the nuclear envelope is false?
A. The nuclear envelope is composed of two lipid bilayers.
B. Molecules pass into and out of the nucleus through nuclear pores.
C. The nuclear envelope is continuous with the Golgi apparatus.
D .Nuclear pores are made up of a group of proteins that are collectively called the nuclear pore complex.
C. The nuclear envelope is continuous with the Golgi apparatus.
True or false? Large proteins containing a nuclear localization signal (NLS) bind to the nuclear pore and enter the nucleus without any expenditure of energy.
False
A small protein (molecular weight = 25,000 daltons) is injected into a cell and observed in the nucleus a short time later. What type of transport has taken place?
A. Passive transport
B. Active transport
C. Osmosis
A. Passive transport
In experiments to test whether a protein can enter the nucleus, why would proteins be labeled with fluorescent molecules?
A. To make the proteins easy to see
B. To give the protein molecules energy
C. To make the proteins bigger
D. To target the proteins to the nucleus
A. To make the proteins easy to see
Nucleoplasmin is a nuclear protein. This protein was divided into two segments and linked to the same large cytoplasmic protein, generating two fusion proteins. After injecting these fusion proteins into a cell, one of the proteins was found in the nucleus and the other in the cytoplasm. Which of the following conclusions can be drawn from these results?
A. One of the fusion proteins entered the nucleus by passive transport.
B. The cytoplasmic protein contains a nuclear localization signal.
C. Nucleoplasmin does not have a nuclear localization signal.
D. Only one of the two fusion proteins possesses a nuclear localization signal.
D. Only one of the two fusion proteins possesses a nuclear localization signal.
Which of these cell junctions form a barrier to the passage of materials?
A. Desmosomes (anchoring junctions)
B. Tight junctions
C. Keratin fibers
D. Gap (communicating) junctions
E. Plasmodesmata
B. Tight junctions
The primary role of _____ is to bind animal cells together.
A. The cytoskeleton
B. Plasmodesmata
C. Gap (communicating) junctions
D. Desmosomes
E. Tight junctions
D. Desmosomes
_____ aid in the coordination of the activities of adjacent animal cells.
A. Desmosomes
B. Plasmodesmata
C. Tight junctions
D. Gap (communicating) junctions
E. Keratin fibers
D. Gap (communicating) junctions