What factors are most important in determining which elements are
most common in living matter?
A) the relative abundances of the
elements in Earth's crust and atmosphere
B) the emergent
properties of the simple compounds made from these elements
C)
the reactivity of the elements with water
D) the chemical
stability of the elements
E) both the relative abundances of
the elements and the emergent properties of the compounds made from
these elements
Answer: E
Why is each element unique and different from other elements in
chemical properties?
A) Each element has a unique atomic mass.
B) Each element has a unique atomic weight.
C) Each
element has a unique number of protons in its nucleus.
D) Each
element has a unique number of neutrons in its nucleus.
E) Each
element has different radioactive properties.
Answer: C
Knowing just the atomic mass of an element allows inferences about
which of the following?
A) the chemical properties of the
element
B) the number of protons in the element
C) the
number of neutrons in the element
D) the number of protons plus
neutrons in the element
E) both the number of protons and the
chemical properties of the element
Answer: D
Electrons exist only at fixed levels of potential energy. However, if
an atom absorbs sufficient energy, a possible result is that
A)
an electron may move to an electron shell farther away from the
nucleus.
B) an electron may move to an electron shell closer to
the nucleus.
C) the atom may become a radioactive isotope.
D) the atom would become a positively charged ion, or cation,
and become a radioactive isotope.
E) the atom would become a
negatively charged ion, or anion.
Answer: A
Which of the following explains most specifically the attraction of
water molecules to one another?
A) nonpolar covalent bond
B) polar covalent bond
C) ionic bond
D) hydrogen
bond
E) hydrophobic interaction
Answer: D
In the term trace element, the modifier trace means that
A)
the element is required in very small amounts.
B) the element
can be used as a label to trace atoms through an organism's
metabolism.
C) the element is very rare on Earth.
D) the
element enhances health but is not essential for the organism's
long-term survival.
E) the element passes rapidly through the organism.
Answer: A
Van der Waals interactions result when
A) hybrid orbitals
overlap.
B) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a
molecule.
C) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water.
D) two polar covalent bonds react.
E) a hydrogen atom
loses an electron.
Answer: B
Which of the following correctly describes chemical equilibrium?
A) Forward and reverse reactions continue with no effect on the
concentrations of the reactants and products.
B) Concentrations
of products are higher than the concentrations of the reactants.
C) Forward and reverse reactions have stopped so that the
concentration of the reactants equals the concentration of the
products.
D) Reactions stop only when all reactants have been
converted to products.
E) There are equal concentrations of
reactants and products, and the reactions have stopped.
Answer: A
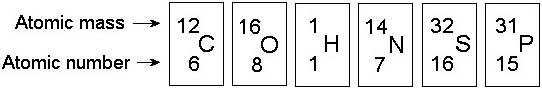
In the figure above, how many electrons does nitrogen have in its valence shell?
A) 2
B) 5
C) 7
D) 8
E) 14
Answer: B
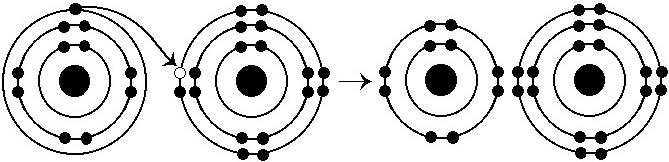
What results from the chemical reaction illustrated above?
A)
a cation with a net charge of +1
B) a cation with a net charge
of -1
C) an anion with a net charge of +1
D) an anion
with a net charge of -1
E) a cation with a net charge of +1 and
an anion with a net charge of -1
Answer: E
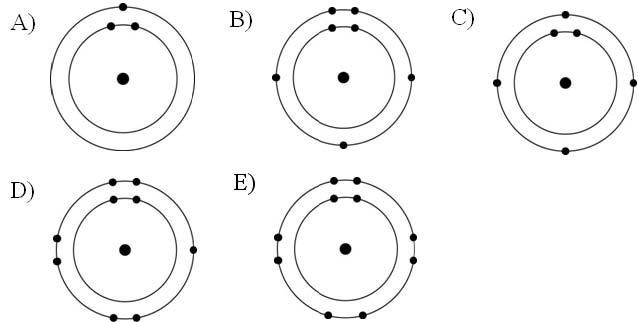
Which one of the atoms shown would be most likely to form an anion with a charge of -1?
Answer: D
Compared with ³¹P, the radioactive isotope ³²P has
A) a
different atomic number.
B) a different charge.
C) one
more proton.
D) one more electron.
E) one more neutron.
Answer: E
About 25 of the 92 natural elements are known to be essential to life. Which four of these 25 elements make up approximately
96% of living matter?
- A) carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, calcium
- B) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
- C) carbon, oxygen, phosphorus, hydrogen
- D) carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen
Answer: D
Liquid water's high specific heat is mainly a consequence of the
A) small size of the water molecules.
B) high specific
heat of oxygen and hydrogen atoms.
C) absorption and release of
heat when hydrogen bonds break and form.
D) fact that water is
a poor heat conductor.
E) higher density of liquid water than
solid water (ice).
Answer: C
Which type of bond must be broken for water to vaporize?
A)
ionic bonds
B) both hydrogen bonds and ionic bonds
C)
polar covalent bonds
D) hydrogen bonds
E) both polar
covalent bonds and hydrogen bonds
Answer: D
Why does ice float in liquid water?
A) The high surface
tension of liquid water keeps the ice on top.
B) The ionic
bonds between the molecules in ice prevent the ice from sinking.
C) Ice always has air bubbles that keep it afloat.
D)
Hydrogen bonds stabilize and keep the molecules of ice farther apart
than the water molecules of liquid water.
E) The crystalline
lattice of ice causes it to be denser than liquid water.
Answer: D
You have a freshly prepared 0.1 M solution of glucose in water. Each
liter of this solution contains how many glucose molecules?
A)
6.02 × 10²³
B) 3.01 × 10²³
C) 6.02 × 10²⁴
D)
12.04 × 10²³
E) 6.02 × 10²²
Answer: E
What is the pH of a solution with a hydroxyl ion [OH⁻] concentration
of 10⁻¹² M?
A) pH 2
B) pH 4
C) pH 10
D) pH
12
E) pH 14
Answer: A
If the pH of a solution is decreased from 9 to 8, it means that the
A) concentration of H⁺ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what
it was at pH 9.
B) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold
(10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
C) concentration of OH⁻
has increased tenfold (10X) compared to what it was at pH 9.
D)
concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what it was at
pH 9.
E) concentration of H⁺ has increased tenfold (10X) and
the concentration of OH⁻ has decreased to one-tenth (1/10) what they
were at pH 9.
Answer: E
How would acidification of seawater affect marine organisms?
A) Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and
promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
B)
Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and
promote faster growth of corals and shell-building animals.
C)
Acidification would increase dissolved carbonate concentrations and
hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
D)
Acidification would decrease dissolved carbonate concentrations and
hinder growth of corals and shell-building animals.
E)
Acidification would increase dissolved bicarbonate concentrations, and
cause increased calcification of corals and shellfish.
Answer: D
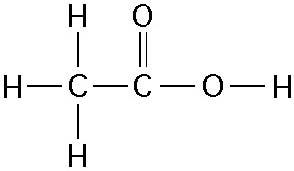
How many grams of the compound in the figure above would be required
to make 1 L of a 0.5 M solution?
(carbon = 12, oxygen = 16,
hydrogen = 1)
A) 29
B) 30
C) 60
D) 150
E) 342
Answer: B
The partial negative charge in a molecule of water occurs because
A) the oxygen atom acquires an additional electron.
B)
the electrons shared between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms spend more
time around the oxygen atom nucleus than around the hydrogen atom
nucleus.
C) the oxygen atom has two pairs of electrons in its
valence shell that are not neutralized by hydrogen atoms.
D)
the oxygen atom forms hybrid orbitals that distribute electrons
unequally around the oxygen nucleus.
E) one of the hydrogen
atoms donates an electron to the oxygen atom.
Answer: B
Which of the following effects is produced by the high surface
tension of water?
A) Lakes don't freeze solid in winter,
despite low temperatures.
B) A water strider can walk across
the surface of a small pond.
C) Organisms resist temperature
changes, although they give off heat due to chemical reactions.
D) Evaporation of sweat from the skin helps to keep people from
overheating.
E) Water flows upward from the roots to the leaves
in plants.
Answer: B
Hydrophobic substances such as vegetable oil are
A) nonpolar
substances that repel water molecules.
B) nonpolar substances
that have an attraction for water molecules.
C) polar
substances that repel water molecules.
D) polar substances that
have an affinity for water.
E) charged molecules that
hydrogen-bond with water molecules
Answer: A
What is the hydrogen ion [H⁺] concentration of a solution of pH 8?
A) 8 M
B) 8 x 10⁻⁶ M
C) 0.01 M
D) 10⁻⁸ M
E) 10⁻⁶ M
Answer: D
If the pH of a solution is increased from pH 5 to pH 7, it means that
the
A) concentration of H⁺ is twice (2X) what it was at pH 5.
B) concentration of H⁺ is one-half (1/2) what it was at pH 5.
C) concentration of OH⁻ is 100 times greater than what it was
at pH 5.
D) concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth (0.01X) what
it was at pH 5.
E) concentration of H⁺ is 100 times greater and
the concentration of OH⁻ is one-hundredth what they were at pH 5.
Answer: C
The element present in all organic molecules is
A) hydrogen.
B) oxygen.
C) carbon.
D) nitrogen.
E) phosphorus.
Answer: C
Hermann Kolbe's synthesis of an organic compound, acetic acid, from
inorganic substances that had been prepared directly from pure
elements was a significant milestone for what reason?
A) It
solved an industrial shortage of acetic acid.
B) It proved that
organic compounds could be synthesized from inorganic compounds.
C) It disproved the concept of vitalism.
D) It showed
that life originated from simple inorganic chemicals.
E) It
proved that organic compounds could be synthesized from inorganic
compounds and disproved the concept of vitalism.
Answer: E
Which of the following statements correctly describes cis-trans
isomers?
A) They have variations in arrangement around a double
bond.
B) They have an asymmetric carbon that makes them mirror
images.
C) They have the same chemical properties.
D)
They have different molecular formulas.
E) Their atoms and
bonds are arranged in different sequences.
Answer: A
Compared to a hydrocarbon chain where all the carbon atoms are linked
by single bonds, a hydrocarbon chain with the same number of carbon
atoms, but with one or more double bonds, will
A) be more
flexible in structure.
B) be more constrained in structure.
C) be more polar.
D) have more hydrogen atoms.
E)
have fewer structurally distinct isomers.
Answer: B
Organic molecules with only hydrogens and five carbon atoms can have
different structures in all of the following ways except
A) by
branching of the carbon skeleton.
B) by varying the number of
double bonds between carbon atoms.
C) by varying the position
of double bonds between carbon atoms.
D) by forming a ring.
E) by forming enantiomers.
Answer: E
Which two functional groups are always found in amino acids?
A) ketone and methyl
B) carbonyl and amino
C)
carboxyl and amino
D) amino and sulfhydryl
E) hydroxyl
and carboxyl
Answer: C
Testosterone and estradiol are
A) soluble in water.
B)
structural isomers of each other.
C) proteins.
D)
lipids.
E) enantiomers of each other.
Answer: B
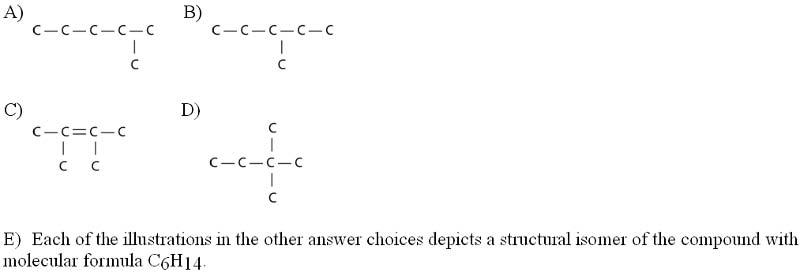
Three or four of the following illustrations depict different structural isomers of the organic compound with molecular formula C₆H₁₄. For clarity, only the carbon skeletons are shown; hydrogen atoms that would be attached to the carbons have been omitted. Which one, if any, is NOT a structural isomer of this compound?
Answer: C
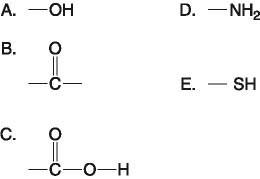
Which functional group(s) shown above is (are) present in all amino
acids?
A) A and B
B) B and D
C) C only
D)
D only
E) C and D
Answer: E
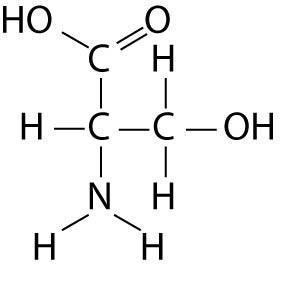
Which functional group is not present in this molecule?
A)
carboxyl
B) sulfhydryl
C) hydroxyl
D) amino
Answer: B
Why are hydrocarbons insoluble in water?
A) The majority of
their bonds are polar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen linkages.
B)
The majority of their bonds are nonpolar covalent carbon-to-hydrogen
linkages.
C) They are hydrophilic.
D) They exhibit
considerable molecular complexity and diversity.
E) They are
lighter than water.
Answer: B
Research indicates that ibuprofen, a drug used to relieve inflammation and pain, is a mixture of two enantiomers; that is, molecules that
A) have identical chemical formulas but differ in the branching
of their carbon skeletons.
B) are mirror images of one
another.
C) exist in either linear chain or ring forms.
D) differ in the location of their double bonds.
E) differ in
the arrangement of atoms around their double bonds.
Answer: B
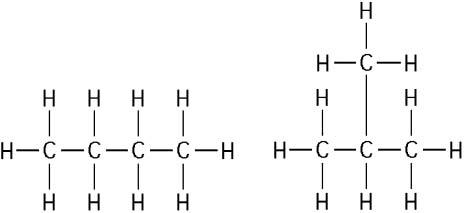
The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) optical isomers.
B) enantiomers.
C) structural
isomers.
D) cis-trans isomers.
E) chain length isomers.
Answer: C
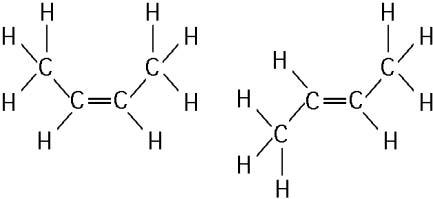
The two molecules shown in the figure above are best described as
A) enantiomers.
B) radioactive isotopes.
C)
structural isomers.
D) nonisotopic isomers.
E)
cis-trans isomers.
Answer: E
Which of these molecules is not formed by dehydration reactions?
A) fatty acids
B) disaccharides
C) DNA
D)
protein
E) amylose
Answer: A
Which of the following is not a polymer?
A) glucose
B)
starch
C) cellulose
D) chitin
E) DNA
Answer: A
On food packages, to what does the term insoluble fiber refer?
A) cellulose
B) polypeptides
C) starch
D)
amylopectin
E) chitin
Answer: A
All of the following contain amino acids except
A) hemoglobin.
B) cholesterol.
C) antibodies.
D) enzymes.
E) insulin.
Answer: B
What aspects of protein structure are stabilized or assisted by
hydrogen bonds?
A) primary structure
B) secondary
structure
C) tertiary structure
D) quaternary structure
E) secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures, but not
primary structure
Answer: E
Which bonds are created during the formation of the primary structure
of a protein?
A) peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds
C) disulfide bonds
D) phosphodiester bonds
E) peptide
bonds, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide bonds
Answer: A
What maintains the secondary structure of a protein?
A)
peptide bonds
B) hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one
peptide bond and the carboxyl group of another peptide bond
C)
disulfide bonds
D) hydrophobic interactions
E) hydrogen
bonds between the R groups
Answer: B
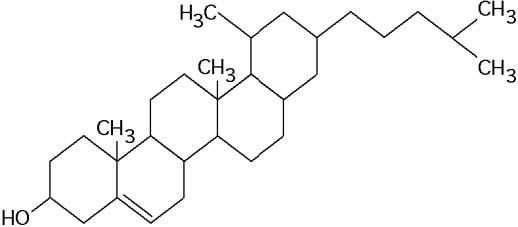
What is the structure shown in the figure?
- A) pentose molecule
- B) fatty acid molecule
- C) steroid molecule
- D) oligosaccharide molecule
- E) phospholipid molecule
Answer: C
Which class of biological polymer has the greatest functional
variety?
A) polysaccharides
B) proteins
C) DNA
D) RNA
Answer: B
The structural level of a protein least affected by a disruption in
hydrogen bonding is the
A) primary level.
B) secondary
level.
C) tertiary level.
D) quaternary level.
E)
All structural levels are equally affected.
Answer: A
Which of the following statements is true for the class of biological
molecules known as lipids?
A) They are insoluble in water.
B) They are made from glycerol, fatty acids, and phosphate.
C) They contain less energy than proteins and carbohydrates.
D) They are made by dehydration reactions.
E) They
contain nitrogen.
Answer: A
There are 20 different amino acids. What makes one amino acid
different from another?
A) different side chains (R groups)
attached to a carboxyl carbon
B) different side chains (R
groups) attached to the amino groups
C) different side chains
(R groups) attached to an α carbon
D) different structural and
optical isomers
E) different asymmetric carbons
Answer: C
Dehydration reactions are used in forming which of the following
compounds?
A) triacylglycerides
B) polysaccharides
C) proteins
D) triacylglycerides and proteins only
E) triacylglycerides, polysaccharides, and proteins
Answer: E
The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often
much larger than the corresponding volume in animal cells. The most
reasonable explanation for this observation is that
A) plant
cells are capable of having a much higher surface-to-volume ratio than
animal cells.
B) plant cells have a much more highly convoluted
(folded) plasma membrane than animal cells.
C) plant cells
contain a large vacuole that reduces the volume of the cytoplasm.
D) animal cells are more spherical, whereas plant cells are
elongated.
E) plant cells can have lower surface-to-volume
ratios than animal cells because plant cells synthesize their own nutrients.
Answer: C
Large numbers of ribosomes are present in cells that specialize in
producing which of the following molecules?
A) lipids
B)
glycogen
C) proteins
D) cellulose
E) nucleic acids
Answer: C
A cell with a predominance of free ribosomes is most likely
A)
producing primarily proteins for secretion.
B) producing
primarily cytoplasmic proteins.
C) constructing an extensive
cell wall or extracellular matrix.
D) digesting large food
particles.
E) enlarging its vacuole.
Answer: B
Hydrolytic enzymes must be segregated and packaged to prevent general
destruction of cellular components. Which of the following organelles
contains these hydrolytic enzymes in animal cells?
A)
chloroplast
B) lysosome
C) central vacuole
D)
peroxisome
E) glyoxysome
Answer: B
One of the key innovations in the evolution of eukaryotes from a
prokaryotic ancestor is the endomembrane system. What eukaryotic
organelles or features might have evolved as a part of, or as an
elaboration of, the endomembrane system?
A) plasma membrane
B) chloroplasts
C) mitochondria
D) nuclear
envelope
E) none of these
Answer: D
If an individual has abnormal microtubules, due to a hereditary
condition, in which organs or tissues would you expect dysfunction?
A) limbs, hearts, areas with a good deal of contraction
B) microvilli, alveoli, and glomeruli: cellular projections that
increase surface area
C) all ducts, such as those from salivary
or sebaceous glands, that transport fluids
D) sperm, larynx,
and trachea: cells and tissues that contain flagella or cilia
E) phagocytic cells and white blood cells that exhibit amoeboid movement
Answer: D
The cell walls of bacteria, fungi, and plant cells and the
extracellular matrix of animal cells are all external to the plasma
membrane. Which of the following is a characteristic common to all of
these extracellular structures?
A) They must block water and
small molecules in order to regulate the exchange of matter and energy
with their environment.
B) They must permit information
transfer between the cell's cytoplasm and the nucleus.
C) They
must provide a rigid structure that maintains an appropriate ratio of
cell surface area to volume.
D) They are constructed of
polymers that are synthesized in the cytoplasm and then transported
out of the cell.
E) They are composed of a mixture of lipids
and carbohydrates.
Answer: D
A mutation that disrupts the ability of an animal cell to add
polysaccharide modifications to proteins would most likely cause
defects in its
A) nuclear lamina and nuclear matrix.
B)
nuclear matrix and extracellular matrix.
C) mitochondria and
Golgi apparatus.
D) Golgi apparatus and extracellular matrix.
E) nuclear pores and secretory vesicles.
Answer: D
In a liver cell detoxifying alcohol and some other poisons, the
enzymes of the peroxisome remove hydrogen from these molecules and
A) combine the hydrogen with water molecules to generate
hydrogen peroxide.
B) use the hydrogen to break down hydrogen
peroxide.
C) transfer the hydrogen to the mitochondria.
D) transfer the hydrogen to oxygen molecules to generate hydrogen peroxide.
Answer: D
The extracellular matrix is thought to participate in the regulation
of animal cell behavior by communicating information from the outside
to the inside of the cell via which of the following?
A) gap
junctions
B) the nucleus
C) DNA and RNA
D)
integrins
E) plasmodesmata
Answer: D
Plasmodesmata in plant cells are most similar in function to which of the following structures in animal cells?
A) peroxisomes
B) desmosomes
C) gap junctions
D) extracellular matrix
E) tight junctions
Answer: C
What types of proteins are not synthesized in the rough ER?
A)
endoplasmic reticulum proteins
B) extracellular matrix proteins
C) secreted proteins
D) mitochondrial proteins
E)
plasma membrane proteins
Answer: D
Which type of organelle is found in plant cells but not in animal
cells?
A) ribosomes
B) mitochondria
C) nuclei
D) plastids
E) none of these
Answer: D
Which of the following is one of the ways that the membranes of
winter wheat are able to remain fluid when it is extremely cold?
A) by increasing the percentage of unsaturated phospholipids in
the membrane
B) by increasing the percentage of cholesterol
molecules in the membrane
C) by decreasing the number of
hydrophobic proteins in the membrane
D) by cotransport of
glucose and hydrogen
E) by using active transport
Answer: A
Water passes quickly through cell membranes because
A) the
bilayer is hydrophilic.
B) it moves through hydrophobic
channels.
C) water movement is tied to ATP hydrolysis.
D) it is a small, polar, charged molecule.
E) it moves through
aquaporins in the membrane.
Answer: E
A bacterium engulfed by a white blood cell through phagocytosis will
be digested by enzymes contained in
A) peroxisomes.
B)
lysosomes.
C) Golgi vesicles.
D) vacuoles.
E)
secretory vesicles.
Answer: B
In the small airways of the lung, a thin layer of liquid is needed
between the epithelial cells and the mucus layer in order for cilia to
beat and move the mucus and trapped particles out of the lung. One
hypothesis is that the volume of this airway surface liquid is
regulated osmotically by transport of sodium and chloride ions across
the epithelial cell membrane. How would the lack of a functional
chloride channel in cystic fibrosis patients affect sodium ion
transport and the volume of the airway surface liquid?
A)
Sodium ion transport will increase; higher osmotic potential will
increase airway surface liquid volume.
B) Sodium ion transport
will increase; higher osmotic potential will decrease airway surface
liquid volume.
C) Sodium ion transport will decrease; lower
osmotic potential will decrease airway surface liquid volume.
D) Sodium ion transport will decrease; lower osmotic potential will
increase the airway surface liquid volume.
E) Sodium ion
transport will be unaffected; lack of chloride transport still reduces
osmotic potential and decreases the airway surface liquid volume.
Answer: C
A protein that spans the phospholipid bilayer one or more times is
A) a transmembrane protein.
B) an integral protein.
C) a peripheral protein.
D) an integrin.
E) a glycoprotein.
Answer: A
What kinds of molecules pass through a cell membrane most easily?
A) large and hydrophobic
B) small and hydrophobic
C) large polar
D) ionic
E) monosaccharides such as glucose
Answer: B
Which of the following would likely move through the lipid bilayer of
a plasma membrane most rapidly?
A) CO₂
B) an amino acid
C) glucose
D) K⁺
E) starch
Answer: A
Which of the following statements is correct about diffusion?
A) It is very rapid over long distances.
B) It requires an
expenditure of energy by the cell.
C) It is a passive process
in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a
region of lower concentration.
D) It is an active process in
which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of
higher concentration.
E) It requires integral proteins in the
cell membrane.
Answer: C
Mammalian blood contains the equivalent of 0.15 M NaCl. Seawater
contains the equivalent of 0.45 M NaCl. What will happen if red blood
cells are transferred to seawater?
A) Water will leave the
cells, causing them to shrivel and collapse.
B) NaCl will be
exported from the red blood cells by facilitated diffusion.
C)
The blood cells will take up water, swell, and eventually burst.
D) NaCl will passively diffuse into the red blood cells.
E) The blood cells will expend ATP for active transport of NaCl into
the cytoplasm.
Answer: A
When a plant cell, such as one from a peony stem, is submerged in a
very hypotonic solution, what is likely to occur?
A) The cell
will burst.
B) The cell membrane will lyse.
C)
Plasmolysis will shrink the interior.
D) The cell will become
flaccid.
E) The cell will become turgid.
Answer: E
Glucose diffuses slowly through artificial phospholipid bilayers. The
cells lining the small intestine, however, rapidly move large
quantities of glucose from the glucose-rich food into their
glucose-poor cytoplasm. Using this information, which transport
mechanism is most probably functioning in the intestinal cells?
A) simple diffusion
B) phagocytosis
C) active transport
pumps
D) exocytosis
E) facilitated diffusion
Answer: E
The sodium-potassium pump is called an electrogenic pump because it
A) pumps equal quantities of Na⁺ and K⁺ across the membrane.
B) pumps hydrogen ions out of the cell.
C) contributes
to the membrane potential.
D) ionizes sodium and potassium
atoms.
E) is used to drive the transport of other molecules
against a concentration gradient.
Answer: C
The movement of potassium into an animal cell requires
A) low
cellular concentrations of sodium.
B) high cellular
concentrations of potassium.
C) an energy source such as ATP.
D) a cotransport protein.
E) a potassium channel protein.
Answer: C
Which term most precisely describes the cellular process of breaking
down large molecules into smaller ones?
A) catalysis
B)
metabolism
C) anabolism
D) dehydration
E) catabolism
Answer: E
Which of the following is (are) true for anabolic pathways?
A)
They do not depend on enzymes.
B) They are usually highly
spontaneous chemical reactions.
C) They consume energy to build
up polymers from monomers.
D) They release energy as they
degrade polymers to monomers.
E) They consume energy to
decrease the entropy of the organism and its environment.
Answer: C
Which of the following is a statement of the first law of
thermodynamics?
A) Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
B) The entropy of the universe is decreasing.
C) The
entropy of the universe is constant.
D) Kinetic energy is
stored energy that results from the specific arrangement of matter.
E) Energy cannot be transferred or transformed.
Answer: A
Living organisms increase in complexity as they grow, resulting in a
decrease in the entropy of an organism. How does this relate to the
second law of thermodynamics?
A) Living organisms do not obey
the second law of thermodynamics, which states that entropy must
increase with time.
B) Life obeys the second law of
thermodynamics because the decrease in entropy as the organism grows
is exactly balanced by an increase in the entropy of the universe.
C) Living organisms do not follow the laws of thermodynamics.
D) As a consequence of growing, organisms cause a greater
increase in entropy in their environment than the decrease in entropy
associated with their growth.
E) Living organisms are able to
transform energy into entropy.
Answer: D
Which of the following types of reactions would decrease the entropy
within a cell?
A) anabolic reactions
B) hydrolysis
C) respiration
D) digestion
E) catabolic reactions
Answer: A
The mathematical expression for the change in free energy of a system
is ΔG =ΔH - TΔS. Which of the following is (are) correct?
A) ΔS
is the change in enthalpy, a measure of randomness.
B) ΔH is
the change in entropy, the energy available to do work.
C) ΔG
is the change in free energy.
D) T is the temperature in
degrees Celsius.
Answer: C
When ATP releases some energy, it also releases inorganic phosphate.
What purpose does this serve (if any) in the cell?
A) The
phosphate is released as an excretory waste.
B) The phosphate
can only be used to regenerate more ATP.
C) The phosphate can
be added to water and excreted as a liquid.
D) The phosphate
may be incorporated into any molecule that contains phosphate.
E) It enters the nucleus to affect gene expression.
Answer: D
Reactants capable of interacting to form products in a chemical
reaction must first overcome a thermodynamic barrier known as the
reaction's
A) entropy.
B) activation energy.
C)
endothermic level.
D) equilibrium point.
E) free-energy content.
Answer: B
How does a noncompetitive inhibitor decrease the rate of an enzyme
reaction?
A) by binding at the active site of the enzyme
B) by changing the shape of the enzyme's active site
C) by
changing the free energy change of the reaction
D) by acting as
a coenzyme for the reaction
E) by decreasing the activation
energy of the reaction
Answer: B
Succinate dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of succinate to
fumarate. The reaction is inhibited by malonic acid, which resembles
succinate but cannot be acted upon by succinate dehydrogenase.
Increasing the ratio of succinate to malonic acid reduces the
inhibitory effect of malonic acid.
What is malonic
acid's role with respect to succinate dehydrogenase?
A) It is a
competitive inhibitor.
B) It blocks the binding of fumarate.
C) It is a noncompetitive inhibitor.
D) It is able to
bind to succinate.
E) It is an allosteric regulator.
Answer: A
If an enzyme in solution is saturated with substrate, the most
effective way to obtain a faster yield of products is to
A) add
more of the enzyme.
B) heat the solution to 90°C.
C) add
more substrate.
D) add an allosteric inhibitor.
E) add a
noncompetitive inhibitor.
Answer: A
Which of the following is the smallest closed system?
A) a
cell
B) an organism
C) an ecosystem
D) Earth
E) the universe
Answer: E
A system at chemical equilibrium
A) consumes energy at a
steady rate.
B) releases energy at a steady rate.
C)
consumes or releases energy, depending on whether it is exergonic or
endergonic.
D) has zero kinetic energy.
E) can do no work.
Answer: E
Which of the following statements describes NAD⁺?
A) NAD⁺ is
reduced to NADH during glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, and the citric
acid cycle.
B) NAD⁺ has more chemical energy than NADH.
C) NAD⁺ is oxidized by the action of hydrogenases.
D) NAD⁺ can
donate electrons for use in oxidative phosphorylation.
E) In
the absence of NAD⁺, glycolysis can still function.
Answer: A
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high energy foods?
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have no nitrogen in
their makeup.
C) They can have very long carbon skeletons.
D) They have a lot of electrons associated with hydrogen.
E) They are easily reduced.
Answer: D
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate
A) two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are
produced.
B) two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules
of ATP are produced.
C) four molecules of ATP are used and two
molecules of ATP are produced.
D) two molecules of ATP are used
and six molecules of ATP are produced.
E) six molecules of ATP
are used and six molecules of ATP are produced.
Answer: B
What is proton-motive force?
A) the force required to remove
an electron from hydrogen
B) the force exerted on a proton by a
transmembrane proton concentration gradient
C) the force that
moves hydrogen into the intermembrane space
D) the force that
moves hydrogen into the mitochondrion
E) the force that moves
hydrogen to NAD⁺
Answer: B
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five
times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must
this serve?
A) It allows for an increased rate of glycolysis.
B) It allows for an increased rate of the citric acid cycle.
C) It increases the surface for oxidative phosphorylation.
D) It increases the surface for substrate-level
phosphorylation.
E) It allows the liver cell to have fewer mitochondria.
Answer: C
Which statement best supports the hypothesis that glycolysis is an
ancient metabolic pathway that originated before the last universal
common ancestor of life on Earth?
A) Glycolysis is widespread
and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
B)
Glycolysis neither uses nor needs O₂.
C) Glycolysis is found in
all eukaryotic cells.
D) The enzymes of glycolysis are found in
the cytosol rather than in a membrane-enclosed organelle.
E)
Ancient prokaryotic cells, the most primitive of cells, made extensive
use of glycolysis long before oxygen was present in Earth's atmosphere.
Answer: A
What is the purpose of beta oxidation in respiration?
A)
oxidation of glucose
B) oxidation of pyruvate
C)
feedback regulation
D) control of ATP accumulation
E)
breakdown of fatty acids
Answer: E
The immediate energy source that drives ATP synthesis by ATP synthase
during oxidative phosphorylation is the
A) oxidation of glucose
and other organic compounds.
B) flow of electrons down the
electron transport chain.
C) affinity of oxygen for electrons.
D) H⁺ concentration across the membrane holding ATP synthase.
E) transfer of phosphate to ADP.
Answer: D
Which metabolic pathway is common to both fermentation and cellular
respiration of a glucose molecule?
A) the citric acid cycle
B) the electron transport chain
C) glycolysis
D)
synthesis of acetyl CoA from pyruvate
E) reduction of pyruvate
to lactate
Answer: C
The final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain that
functions in aerobic oxidative phosphorylation is
A) oxygen.
B) water.
C) NAD⁺.
D) pyruvate.
E) ADP.
Answer: A
When electrons flow along the electron transport chains of
mitochondria, which of the following changes occurs?
A) The pH
of the matrix increases.
B) ATP synthase pumps protons by
active transport.
C) The electrons gain free energy.
D)
The cytochromes phosphorylate ADP to form ATP.
E) NAD⁺ is oxidized.
Answer: A
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether
oxygen (O₂) is present or absent?
A) electron transport
B) glycolysis
C) the citric acid cycle
D) oxidative
phosphorylation
E) chemiosmosis
Answer: B
A molecule that is phosphorylated
A) has been reduced as a
result of a redox reaction involving the loss of an inorganic
phosphate.
B) has a decreased chemical reactivity; it is less
likely to provide energy for cellular work.
C) has been
oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an
inorganic phosphate.
D) has an increased chemical potential
energy; it is primed to do cellular work.
E) has less energy
than before its phosphorylation and therefore less energy for cellular work.
Answer: D
In any ecosystem, terrestrial or aquatic, what group(s) is (are)
always necessary?
A) autotrophs and heterotrophs
B)
producers and primary consumers
C) photosynthesizers
D)
autotrophs
E) green plants
Answer: D
In autotrophic bacteria, where are the enzymes located that can carry
on carbon fixation (reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrate)?
A) in chloroplast membranes
B) in chloroplast stroma
C) in the cytosol
D) in the nucleoid
E) in the
infolded plasma membrane
Answer: C
A plant has a unique photosynthetic pigment. The leaves of this plant
appear to be reddish yellow. What wavelengths of visible light are
being absorbed by this pigment?
A) red and yellow
B)
blue and violet
C) green and yellow
D) blue, green, and
red
E) green, blue, and yellow
Answer: B
Assume a thylakoid is somehow punctured so that the interior of the
thylakoid is no longer separated from the stroma. This damage will
have the most direct effect on which of the following processes?
A) the splitting of water
B) the absorption of light
energy by chlorophyll
C) the flow of electrons from photosystem
II to photosystem I
D) the synthesis of ATP
E) the
reduction of NADP⁺
Answer: D
In photosynthetic cells, synthesis of ATP by the chemiosmotic
mechanism occurs during
A) photosynthesis only.
B)
respiration only.
C) both photosynthesis and respiration.
D) neither photosynthesis nor respiration.
E)
photorespiration only.
Answer: C
In a plant leaf, the reactions that produce NADH occur in
A)
the light reactions alone.
B) the Calvin cycle alone.
C)
both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
D) neither the
light reactions nor the Calvin cycle.
E) the chloroplast, but
is not part of photosynthesis.
Answer: D
Which of the following statements best represents the relationships
between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle?
A) The light
reactions provide ATP and NADPH to the Calvin cycle, and the cycle
returns ADP, Pi, and NADP⁺ to the light reactions.
B) The light
reactions provide ATP and NADPH to the carbon fixation step of the
Calvin cycle, and the cycle provides water and electrons to the light
reactions.
C) The light reactions supply the Calvin cycle with
CO₂ to produce sugars, and the Calvin cycle supplies the light
reactions with sugars to produce ATP.
D) The light reactions
provide the Calvin cycle with oxygen for electron flow, and the Calvin
cycle provides the light reactions with water to split.
E)
There is no relationship between the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
Answer: A
A spaceship is designed to support animal life for a multiyear voyage
to the outer planets of the solar system. Plants will be grown to
provide oxygen and to recycle carbon dioxide.
Since the
spaceship will be too far from the sun for photosynthesis, an
artificial light source will be needed. What wavelengths of light
should be used to maximize plant growth with a minimum of energy
expenditure?
A) full-spectrum white light
B) green light
C) a mixture of blue and red light
D) yellow light
E) UV light
Answer: C
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
A) stroma of the
chloroplast
B) thylakoid membrane
C) cytoplasm
surrounding the chloroplast
D) interior of the thylakoid
(thylakoid space)
E) outer membrane of the chloroplast
Answer: A
What are the products of linear photophosphorylation?
A) heat
and fluorescence
B) ATP and P700
C) ATP and NADPH
D) ADP and NADP
E) P700 and P680
Answer: C
For anaphase to begin, which of the following must occur?
A) Chromatids must lose their kinetochores.
B) Cohesin
must attach the sister chromatids to each other.
C) Cohesin
must be cleaved enzymatically.
D) Kinetochores must attach to
the metaphase plate.
E) Spindle microtubules must begin to depolymerize.
Answer: C
At the M phase checkpoint, the complex allows for what to occur?
A) Separase enzyme cleaves cohesins and allows chromatids to
separate.
B) Cohesins alter separase to allow chromatids to
separate.
C) Kinetochores are able to bind to spindle
microtubules.
D) All microtubules are made to bind to
kinetochores.
E) Daughter cells are allowed to pass into G₁.
Answer: A
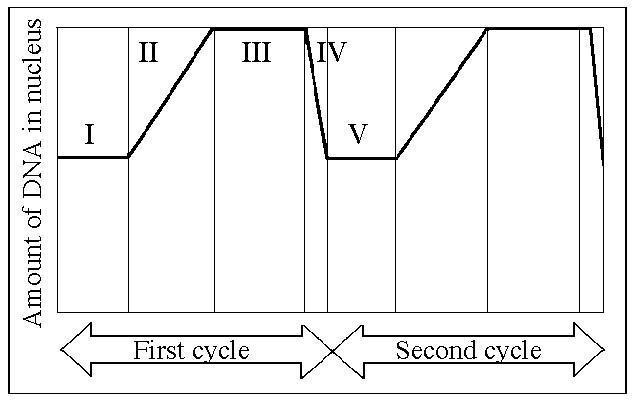
Which number represents DNA synthesis?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Answer: B
Reduction of oxygen to form water occurs during
A)
photosynthesis only.
B) respiration only.
C) both
photosynthesis and respiration.
D) neither photosynthesis nor
respiration.
E) photorespiration only.
Answer: B
The reactions that produce molecular oxygen (O₂) take place in
A) the light reactions alone.
B) the Calvin cycle alone.
C) both the light reactions and the Calvin cycle.
D) neither
the light reactions nor the Calvin cycle.
E) the chloroplast,
but are not part of photosynthesis.
Answer: A
What is the primary function of the Calvin cycle?
A) use ATP
to release carbon dioxide
B) use NADPH to release carbon
dioxide
C) split water and release oxygen
D) transport
RuBP out of the chloroplast
E) synthesize simple sugars from
carbon dioxide
Answer: E
The centromere is a region in which
A) chromatids
remain attached to one another until anaphase.
B) metaphase
chromosomes become aligned at the metaphase plate.
C)
chromosomes are grouped during telophase.
D) the nucleus is
located prior to mitosis.
E) new spindle microtubules form at
either end.
Answer: A
Which of the following describe(s) cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk)?
A) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off," in the
presence of cyclin.
B) Cdk is present throughout the cell
cycle.
C) Cdk is an enzyme that attaches phosphate groups to
other proteins.
D) Cdk is inactive, or "turned off,"
in the presence of cyclin and it is present throughout the cell cycle.
E) Cdk is present throughout the cell cycle and is an enzyme
that attaches phosphate groups to other proteins.
Answer: E
Which of the following most accurately describes a cyclin?
A) It is present in similar concentrations throughout the cell
cycle.
B) It is activated to phosphorylate by complexing with a
Cdk.
C) It decreases in concentration when MPF activity
increases.
D) It activates a Cdk molecule when it is in
sufficient concentration.
E) It activates a Cdk when its
concentration is decreased.
Answer: D
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into
newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their
incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student—faculty research
team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture
of dividing human cells at specific times.
Which of the
following questions might be answered by such a method?
A) How many cells are produced by the culture per hour?
B) What
is the length of the S phase of the cell cycle?
C) When is the
S chromosome synthesized?
D) How many picograms of DNA are made
per cell cycle?
E) When do spindle fibers attach to chromosomes?
Answer: B
Nucleotides can be radiolabeled before they are incorporated into newly forming DNA and can therefore be assayed to track their incorporation. In a set of experiments, a student—faculty research team used labeled T nucleotides and introduced these into the culture of dividing human cells at specific times.
The research team used the setup to study the incorporation of
labeled nucleotides into a culture of lymphocytes and found that the
lymphocytes incorporated the labeled nucleotide at a significantly
higher level after a pathogen was introduced into the culture. They
concluded that
A) the presence of the pathogen made the
experiment too contaminated to trust the results.
B) their
tissue culture methods needed to be relearned.
C) infection
causes lymphocytes to divide more rapidly.
D) infection causes
cell cultures in general to reproduce more rapidly.
E)
infection causes lymphocyte cultures to skip some parts of the cell cycle.
Answer: C
One difference between cancer cells and normal cells is that cancer
cells
A) are unable to synthesize DNA.
B) are
arrested at the S phase of the cell cycle.
C) continue to
divide even when they are tightly packed together.
D) cannot
function properly because they are affected by density-dependent
inhibition.
E) are always in the M phase of the cell cycle.
Answer: C
Which of the following does not occur during mitosis?
A)
condensation of the chromosomes
B) replication of the DNA
C) separation of sister chromatids
D) spindle formation
E) separation of the spindle poles
Answer: B
A particular cell has half as much DNA as some other cells in a
mitotically active tissue. The cell in question is most likely in
A) G₁.
B) G₂.
C) prophase.
D) metaphase.
E) anaphase.
Answer: A
At which phase are centrioles beginning to move apart in animal
cells?
A) telophase
B) anaphase
C)
prometaphase
D) metaphase
E) prophase
Answer: E
Where do the microtubules of the spindle originate during mitosis in
both plant and animal cells?
A) centromere
B)
centrosome
C) centriole
D) chromatid
E) kinetochore
Answer: B
In the human species, all somatic cells have 46 chromosomes. Which of
the following can also be true?
A) A plant species (privet
shrubs) has 46 chromosomes per cell.
B) Some adult humans have
69 chromosomes per cell.
C) Some adult humans have 23
chromosomes per cell.
D) A certain fungal species has only one
chromosome per cell.
E) A certain bacterial species has 23 chromosomes.
Answer: A
The human X and Y chromosomes
A) are both present in every
somatic cell of males and females alike.
B) are of
approximately equal size and number of genes.
C) are almost
entirely homologous, despite their different names.
D) include
genes that determine an individual's sex.
E) include only genes
that govern sex determination.
Answer: D
Which of the following is true of a species that has a chromosome
number of 2n = 16?
A) The species is diploid with 32
chromosomes per cell.
B) The species has 16 sets of chromosomes
per cell.
C) Each cell has eight homologous pairs.
D)
During the S phase of the cell cycle there will be 32 separate
chromosomes.
E) A gamete from this species has four chromosomes.
Answer: C
Referring to a plant's sexual life cycle, which of the following
terms describes the process that leads directly to the formation of
gametes?
A) sporophyte meiosis
B) gametophyte mitosis
C) gametophyte meiosis
D) sporophyte mitosis
E)
alternation of generations
Answer: B
Which of the following best describes a karyotype?
A) a
pictorial representation of all the genes for a species
B) a
display of each of the chromosomes of a single cell
C) the
combination of all the maternal and paternal chromosomes of a species
D) the collection of all the chromosomes in an individual
organism
E) a photograph of all the cells with missing or extra chromosomes
Answer: B
In a human karyotype, chromosomes are arranged in 23 pairs. If we
choose one of these pairs, such as pair 14, which of the following do
the two chromosomes of the pair have in common?
A) Length and
position of the centromere only.
B) Length, centromere
position, and staining pattern only.
C) Length, centromere
position, staining pattern, and traits coded for by their genes.
D) Length, centromere position, staining pattern, and DNA
sequences.
E) They have nothing in common except they are X-shaped.
Answer: C
A cell divides to produce two daughter cells that are genetically
different.
A) The statement is true for mitosis only.
B)
The statement is true for meiosis I only.
C) The statement is
true for meiosis II only.
D) The statement is true for mitosis
and meiosis I.
E) The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
Answer: B
Independent assortment of chromosomes occurs.
A) The statement
is true for mitosis only.
B) The statement is true for meiosis
I only.
C) The statement is true for meiosis II only.
D)
The statement is true for mitosis and meiosis I.
E) The
statement is true for mitosis and meiosis II.
Answer: B
A tetrad includes which of the following sets of DNA strands?
A) two single-stranded chromosomes that have synapsed
B) two
sets of sister chromatids that have synapsed
C) four sets of
sister chromatids
D) four sets of unique chromosomes
E)
eight sets of sister chromatids
Answer: B
To visualize and identify meiotic cells at metaphase with a
microscope, what would you look for?
A) sister chromatids
grouped at the poles
B) individual chromosomes all at the
cell's center
C) an uninterrupted spindle array
D) the
synaptonemal complex
E) tetrads all aligned at the cell's center
Answer: E
For the following question, match the key event of meiosis with the stages listed below.
Tetrads of chromosomes are aligned at the equator of the spindle;
alignment determines independent assortment.
I. Prophase
I V. Prophase II
II. Metaphase I VI. Metaphase II
III.
Anaphase I VII. Anaphase II
IV. Telophase I VIII. Telophase II
A) I
B) II
C) IV
D) VI
E) VIII
Answer: B
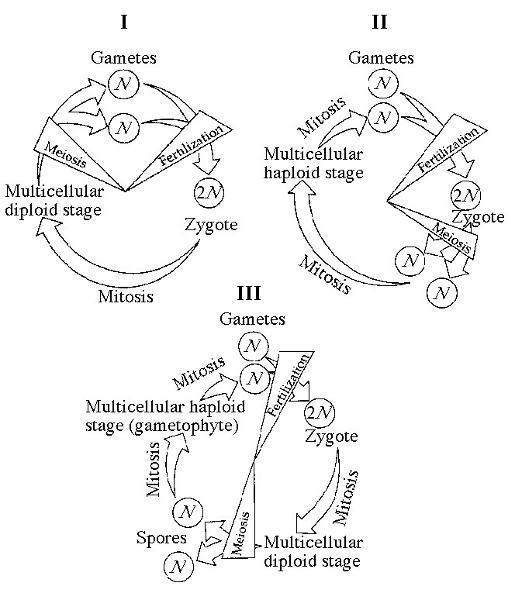
Which of the life cycles is typical for most fungi and some protists?
A) I only
B) II only
C) III only
D) I and
II
E) I and III
Answer: B
After telophase I of meiosis, the chromosomal makeup of each daughter
cell is
A) diploid, and the chromosomes are each composed of a
single chromatid.
B) diploid, and the chromosomes are each
composed of two chromatids.
C) haploid, and the chromosomes are
each composed of a single chromatid.
D) haploid, and the
chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
E) tetraploid,
and the chromosomes are each composed of two chromatids.
Answer: D
Why did Mendel continue some of his experiments to the F₂ or F₃
generation?
A) to obtain a larger number of offspring on
which to base statistics
B) to observe whether or not a
recessive trait would reappear
C) to observe whether or not the
dominant trait would reappear
D) to distinguish which alleles
were segregating
E) to be able to describe the frequency of recombination
Answer: B
Cystic fibrosis affects the lungs, the pancreas, the digestive
system, and other organs, resulting in symptoms ranging from breathing
difficulties to recurrent infections. Which of the following terms
best describes this?
A) incomplete dominance
B) multiple
alleles
C) pleiotropy
D) epistasis
E) codominance
Answer: C
Hydrangea plants of the same genotype are planted in a large flower
garden. Some of the plants produce blue flowers and others pink
flowers. This can be best explained by which of the following?
A) the knowledge that multiple alleles are involved
B) the
allele for blue hydrangea being completely dominant
C) the
alleles being codominant
D) the fact that a mutation has
occurred
E) environmental factors such as soil pH
Answer: E
Which of the following provides an example of epistasis?
A) Recessive genotypes for each of two genes (aabb) results in
an albino corn snake.
B) The allele b17 produces a dominant
phenotype, although b1 through b16 do not.
C) In rabbits and
many other mammals, one genotype (cc) prevents any fur color from
developing.
D) In Drosophila (fruit flies), white eyes can be
due to an X-linked gene or to a combination of other genes.
E)
In cacti, there are several genes for the type of spines.
Answer: C
How could you best predict the maximum number of alleles for a single
gene whose polypeptide product is known?
A) Search the
population for all phenotypic variants of this polypeptide.
B)
Count the number of amino acids in the polypeptide.
C) Mate all
known genotypes and collect all possible offspring different from the
parents.
D) Measure the rate of new mutations in the species
and estimate the number since it first evolved.
E) Count the
number of DNA nucleotides that are in the code for the polypeptides.
Answer: E
One of two major forms of a human condition called neurofibromatosis
(NF 1) is inherited as a dominant gene, although it may range from
mildly to very severely expressed. If a young child is the first in
her family to be diagnosed, which of the following is the best
explanation?
A) The mother carries the gene but does not
express it at all.
B) One of the parents has very mild
expression of the gene.
C) The condition skipped a generation
in the family.
D) The child has a different allele of the gene
than the parents.
Answer: B
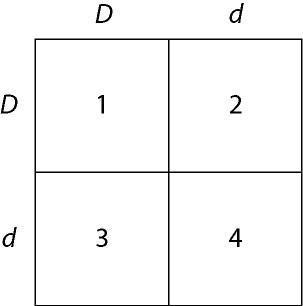
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D.
Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants
with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A
true-breeding dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one,
and the F₁ offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted
outcome of the F₂ is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in Figure
14.1, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to
each box within the square.
37) Which of the boxes
marked 1-4 correspond to plants with dark leaves?
A) 1 only
B) 1 and 2
C) 2 and 3
D) 4 only
E) 1, 2,
and 3
Answer: E
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has
red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F₁
individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and
location assort independently.
If 1,000 F₂ offspring
resulted from the cross, approximately how many of them would you
expect to have red, terminal flowers?
A) 65
B) 190
C) 250
D) 565
E) 750
Answer: B
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F₁ individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and location assort independently.
Among the F₂ offspring, what is the probability of plants with
white axial flowers?
A) 9/16
B) 1/16
C) 3/16
D) 1/8
E) 1/4
Answer: C
Marfan syndrome in humans is caused by an abnormality of the
connective tissue protein fibrillin. Patients are usually very tall
and thin, with long spindly fingers, curvature of the spine, sometimes
weakened arterial walls, and sometimes ocular problems, such as lens
dislocation. Which of the following would you conclude about Marfan
syndrome from this information?
A) It is recessive.
B)
It is dominant.
C) It has a late age of onset (> 60).
D) It is pleiotropic.
E) It is epistatic.
Answer: D
When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single
trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an
offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
A) 0%
B) 25%
C) 50%
D) 75%
E) 100%
Answer: C
Which of the following describes the ability of a single gene to have
multiple phenotypic effects?
A) incomplete dominance
B)
multiple alleles
C) pleiotropy
D) epistasis
Answer: C
Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
A) pink flowers in snapdragons
B) the ABO blood group in humans
C) Huntington's disease in humans
D) white and purple
flower color in peas
E) skin pigmentation in humans
Answer: E
Which of the following is the meaning of the chromosome theory of
inheritance as expressed in the early 20th century?
A)
Individuals inherit particular chromosomes attached to genes.
B) Mendelian genes are at specific loci on the chromosome and in turn
segregate during meiosis.
C) Homologous chromosomes give rise
to some genes and crossover chromosomes to other genes.
D) No
more than a single pair of chromosomes can be found in a healthy
normal cell.
E) Natural selection acts on certain chromosome
arrays rather than on genes.
Answer: B
Thomas Hunt Morgan's choice of Drosophila melanogaster has been
proven to be useful even today. Which of the following has/have
continued to make it a most useful species?
I. its four
pairs of chromosomes
II. a very large number of visible as well
as biochemically mutant phenotypes
III. easy and inexpensive
maintenance
IV. short generation time and large number of
offspring
A) I and IV only
B) II and III only
C) I, II, and III only
D) II, III, and IV only
E)
I, II, III, IV, and V
Answer: E
Calico cats are female because
A) the males die during
embryonic development.
B) a male inherits only one of the two
X-linked genes controlling hair color.
C) the Y chromosome has
a gene blocking orange coloration.
D) only females can have
Barr bodies.
E) multiple crossovers on the Y chromosome prevent
orange pigment production.
Answer: B
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by a gene on the human X
chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because
they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They
rarely live past their 20s. How likely is it for a woman to have this
condition?
A) Women can never have this condition.
B) One-half of the daughters of an affected man could have this
condition.
C) One-fourth of the children of an affected father
and a carrier mother could have this condition.
D) Very rarely
would a woman have this condition; the condition would be due to a
chromosome error.
E) Only if a woman is XXX could she have this condition.
Answer: D
Which of the following statements is true of linkage?
A) The
closer two genes are on a chromosome, the lower the probability that a
crossover will occur between them.
B) The observed frequency of
recombination of two genes that are far apart from each other has a
maximum value of 100%.
C) All of the traits that Mendel
studied–seed color, pod shape, flower color, and others–are due to
genes linked on the same chromosome.
D) Linked genes are found
on different chromosomes.
E) Crossing over occurs during
prophase II of meiosis.
Answer: A
Why does recombination between linked genes continue to occur?
A) Recombination is a requirement for independent assortment.
B) Recombination must occur or genes will not assort independently.
C) New allele combinations are acted upon by natural selection.
D) The forces on the cell during meiosis II always result in
recombination.
E) Without recombination there would be an
insufficient number of gametes.
Answer: C
Map units on a linkage map cannot be relied upon to calculate
physical distances on a chromosome for which of the following reasons?
A) The frequency of crossing over varies along the length of
the chromosome.
B) The relationship between recombination
frequency and map units is different in every individual.
C)
Physical distances between genes change during the course of the cell
cycle.
D) The gene order on the chromosomes is slightly
different in every individual.
E) Linkage map distances are
identical between males and females.
Answer: A
A phenotypically normal prospective couple seeks genetic counseling
because the man knows that he has a translocation of a portion of his
chromosome 4 that has been exchanged with a portion of his chromosome
12. Although he is normal because his translocation is balanced, he
and his wife want to know the probability that his sperm will be
abnormal. What is your prognosis regarding his sperm?
A)
1/4 will be normal, 1/4 will have the translocation, and 1/2 will have
duplications and deletions.
B) All will carry the same
translocation as the father.
C) None will carry the
translocation since abnormal sperm will die.
D) His sperm will
be sterile and the couple might consider adoption.
E) 1/2 will
be normal and the rest will have the father's translocation.
Answer: A
Which of the following is true of aneuploidies in general?
A) A monosomy is more frequent than a trisomy.
B) 45 X is
the only known human live-born monosomy.
C) Some human
aneuploidies have selective advantage in some environments.
D)
Of all human aneuploidies, only Down syndrome is associated with
mental retardation.
E) An aneuploidy resulting in the deletion
of a chromosome segment is less serious than a duplication.
Answer: B
Mitochondrial DNA is primarily involved in coding for proteins needed
for electron transport. Therefore, in which body systems would you
expect most mitochondrial gene mutations to be exhibited?
A)
the immune system and the blood
B) the excretory and
respiratory systems
C) the skin and senses
D) the
nervous and muscular systems
E) the circulation system
Answer: D
Sex determination in mammals is due to the SRY region of the Y
chromosome. An abnormality of this region could allow which of the
following to have a male phenotype?
A) Turner syndrome, 45, X
B) translocation of SRY to an autosome of a 46, XX individual
C) a person with an extra X chromosome
D) a person with
one normal and one shortened (deleted) X
E) Down syndrome, 46, XX
Answer: B
An inversion in a human chromosome often results in no demonstrable
phenotypic effect in the individual. What else may occur?
A)
There may be deletions later in life.
B) Some abnormal gametes
may be formed.
C) There is an increased frequency of mutation.
D) All inverted chromosomes are deleted.
E) The
individual is more likely to get cancer.
Answer: B
What is the source of the extra chromosome 21 in an individual with
Down syndrome?
A) nondisjunction in the mother only
B)
nondisjunction in the father only
C) duplication of the
chromosome
D) nondisjunction or translocation in either parent
E) It is impossible to detect with current technology.
Answer: D
Cytosine makes up 42% of the nucleotides in a sample of DNA from an
organism. Approximately what percentage of the nucleotides in this
sample will be thymine?
A) 8%
B) 16%
C) 31%
D) 42%
E) It cannot be determined from the information provided.
Answer: A
Which of the following can be determined directly from X-ray
diffraction photographs of crystallized DNA?
A) the diameter of
the helix
B) the rate of replication
C) the sequence of
nucleotides
D) the bond angles of the subunits
E) the
frequency of A vs. T nucleotides
Answer: A
In an analysis of the nucleotide composition of DNA, which of the
following will be found?
A) A = C
B) A = G and C = T
C) A + C = G + T
D) G + C = T + A
Answer: C
Replication in prokaryotes differs from replication in eukaryotes for
which of the following reasons?
A) Prokaryotic chromosomes have
histones, whereas eukaryotic chromosomes do not.
B) Prokaryotic
chromosomes have a single origin of replication, whereas eukaryotic
chromosomes have many.
C) The rate of elongation during DNA
replication is slower in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes.
D)
Prokaryotes produce Okazaki fragments during DNA replication, but
eukaryotes do not.
E) Prokaryotes have telomeres, and
eukaryotes do not.
Answer: B
Which enzyme catalyzes the elongation of a DNA strand in the 5' → 3'
direction?
A) primase
B) DNA ligase
C) DNA
polymerase III
D) topoisomerase
E) helicase
Answer: C
Polytene chromosomes of Drosophila salivary glands each consist of
multiple identical DNA strands that are aligned in parallel arrays.
How could these arise?
A) replication followed by mitosis
B) replication without separation
C) meiosis followed by
mitosis
D) fertilization by multiple sperm
E) special
association with histone proteins
Answer: B
To repair a thymine dimer by nucleotide excision repair, in which
order do the necessary enzymes act?
A) exonuclease, DNA
polymerase III, RNA primase
B) helicase, DNA polymerase I, DNA
ligase
C) DNA ligase, nuclease, helicase
D) DNA
polymerase I, DNA polymerase III, DNA ligase
E) endonuclease,
DNA polymerase I, DNA ligase
Answer: E
Which of the following would you expect of a eukaryote lacking
telomerase?
A) a high probability of somatic cells becoming
cancerous
B) production of Okazaki fragments
C)
inability to repair thymine dimers
D) a reduction in chromosome
length in gametes
E) high sensitivity to sunlight
Answer: D
Use the following list of choices for the following question
I. helicase
II. DNA polymerase III
III. ligase
IV. DNA polymerase I
V. primase
Which of the
enzymes synthesizes short segments of RNA?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Answer: E
Which of the following statements describes chromatin?
A)
Heterochromatin is composed of DNA, whereas euchromatin is made of DNA
and RNA.
B) Both heterochromatin and euchromatin are found in
the cytoplasm.
C) Heterochromatin is highly condensed, whereas
euchromatin is less compact.
D) Euchromatin is not transcribed,
whereas heterochromatin is transcribed.
E) Only euchromatin is
visible under the light microscope.
Answer: C
What is the function of topoisomerase?
A) relieving strain in
the DNA ahead of the replication fork
B) elongating new DNA at
a replication fork by adding nucleotides to the existing chain
C) adding methyl groups to bases of DNA
D) unwinding of the
double helix
E) stabilizing single-stranded DNA at the
replication fork
Answer: A
What is the role of DNA ligase in the elongation of the lagging
strand during DNA replication?
A) It synthesizes RNA
nucleotides to make a primer.
B) It catalyzes the lengthening
of telomeres.
C) It joins Okazaki fragments together.
D)
It unwinds the parental double helix.
E) It stabilizes the
unwound parental DNA.
Answer: C
Use the following list of choices for the following question
I. helicase
II. DNA polymerase III
III. ligase
IV. DNA polymerase I
V. primase
Which of the
enzymes removes the RNA nucleotides from the primer and adds
equivalent DNA nucleotides to the 3' end of Okazaki fragments?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Answer: D
Use the following list of choices for the following question
I. helicase
II. DNA polymerase III
III. ligase
IV. DNA polymerase I
V. primase
Which of the
enzymes separates the DNA strands during replication?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Answer: A
Use the following list of choices for the following question
I. helicase
II. DNA polymerase III
III. ligase
IV. DNA polymerase I
V. primase
Which of the
enzymes covalently connects segments of DNA?
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V
Answer: C
Which of the following sets of materials are required by both
eukaryotes and prokaryotes for replication?
A) double-stranded
DNA, four kinds of dNTPs, primers, origins
B) topoisomerases,
telomerases, polymerases
C) G-C rich regions, polymerases,
chromosome nicks
D) nucleosome loosening, four dNTPs, four
rNTPs
E) ligase, primers, nucleases
Answer: A