A molecule that has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions is:
Amphipathic
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is:
Osmosis
The ___ is dissolved in the ___.
Solute...solvent
All cells are separated from their surroundings by:
A plasma membrane
Which of the following extracellular matrix components is embedded in a cell's phospholipid bilayer?
Integrins
What does cholesterol do in a plasma membrane environment that is in a cold environment?
Increases membrane fluidity
What does cholesterol do in a plasma membrane that is in a warm environment?
Decreases membrane fluidity
Glycoproteins are formed when carbohydrates are attached to proteins using:
Covalent bonds
What protein facilitates the passive transport of water across a membrane?
Aquaporins
Glycoproteins that will wind up on a cell's surface have their carbohydrates attached in the:
Golgi Apparatus
The First Law of Thermodynamics states that:
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
The Second Law of Thermodynamics states that:
The total amount of disorder in the universe is constantly increasing.
The change in the Gibbs Free Energy for a reaction is defined as:
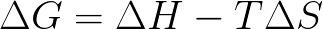
A reaction that has a positive delta G is: Favorable
Spontaneous
Able to proceed without the input of additional energy
All of the above
None of the above
None of the above
A chemical reaction that releases energy is:
Exergonic
How do enzymes work to speed up chemical reactions?
Enzymes lower the activation energy needed for the reaction to start.
The position on an enzyme molecule that catalyzes its chemical reaction is the:
Active site
A molecule that binds to an enzyme (but does NOT bind to the position that #17 asked about) and slows down the enzyme's catalytic activity, is:
An allosteric inhibitor
How do cells make energetically unfavorable reactions proceed?
They couple unfavorable reactions to favorable ones, so the overall change in free energy is negative.
ATP hydrolysis has a free energy change of G = -7.2kCal/mol. Suppose a cell uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to power a multistep anabolic reaction with delta G = +21.6kCal/mol. At Least how many molecules of ATP must be hydrolyzed during the synthesis? (HINT: remember what the 2nd law of thermodynamics says about real-world efficiency!)
4 molecules (it's not 3 due to inefficiency)
Consider the combustion of natural gas in your stove: CH4 + O2 → CO2 + H2O +heat. Which component in this reaction is the reducing agent?
CH4
In the same reaction in #21, what component is the oxidizing agent?
O2
What is the proper order for all the stages of mitochondrial respiration?
Glycolysis => Pyruvate Oxidation => Citric Acid Cycle => Oxidative Phosphorylation
During glycolysis, how many molecules of ATP must the cell invest to begin digesting glucose?
2 molecules
What are the net products of glycolysis?
2 ATP
2 NADH
2 Pyruvate
During the process of respiration, when are the first molecules of CO2 released?
Pyruvate Oxidation
During the process of respiration, what step produces the most molecules of ATP?
Oxidative Phosphorylation
True or false: during the Citric Acid Cycle, the two carbon atoms added to the cycle are released as CO2 during the same round that they were added.
False
Which reaction releases the most energy during the process of respiration?
NADH => NAD+
In respiration, the molecules of ATP that are not produced by oxidative phosphorylation are all produced by:
Substrate-level phosphorylation
Which enzyme produced the most molecules of ATP in respiration?
ATP synthase
During oxidative phosphorylation, Protein Complexes I-IV pump protons from the ___ into the ___.
Mitochondrial matrix...intermembrane space
What is the energy source that directly powers ATP synthesis in oxidative phosphorylation?
A proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial space.
What molecule is the terminal electron acceptor in the mitochondrial electron transport chain?
O2
How does a cell doing alcohol fermentation benefit by converting Pyruvate to CO2 + ethanol?
It regenerates NAD+ needed to continue glycolysis.
Suppose you found a new species of plant whose chloroplasts contained an additional pigment that could absorb green light. What color would the plant most likely be?
Black
___ can produce their own energy while ___ get their energy from consuming material from other organisms.
Autotrophs...heterotrophs
The two main processes of photosynthesis are the Light reactions and:
The Calvin Cycle
What are the reagents used by the light reactions of photosynthesis?
ADP
NADP+
Pi
H2O
What are the products created by the light reactions of photosynthesis?
ATP
NADPH
O2
Which answer is true of photons?
Photons can only have certain fixed wavelengths
They are absorbed and emitted by the protons in the nucleus
The longer the wavelength, the lower the energy
The longer the wavelength, the higher the energy
They are both floor waxes and dessert toppings
The longer the wavelength, the lower the energy
The organelle where photosynthesis takes place in eukaryotes is the:
Chloroplast
The Calvin Cycle takes place inside the:
Stroma
In photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is captured by:
Ribulose Biphosphate Carboxylase(RuBisCo)
At least how many photons must be captured for each molecule of NADPH synthesized during photosynthesis?
2 molecules
What does NOT happen during the Calvin Cycle?
Splitting of water
CAM plants do photosynthesis differently, in order to use what resource more efficiently?
H2O
During the light reactions of photosynthesis, what is the only thing that crosses the membrane to enter the thylakoid space?
Protons
A molecule emitting a photon of a different(longer) wavelength than it absorbed is:
Fluorescence
True or false: glucose is the first carbohydrate released by the Calvin Cycle:
False (it's G3P)