11) An autoimmune problem involving the thyroid gland.
A) Pituitary dwarfism
B) Diabetes mellitus
C) Addisonʹs disease
D) Gravesʹ disease
E) Acromegaly
D) Gravesʹ disease
12) Hyposecretion of growth hormone.
A) Pituitary dwarfism
B) Diabetes mellitus
C) Addisonʹs disease
D) Gravesʹ disease
E) Acromegaly
A) Pituitary dwarfism
14) Hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex.
A) Pituitary dwarfism
B) Diabetes mellitus
C) Addisonʹs disease
D) Gravesʹ disease
E) Acromegaly
C) Addisonʹs disease
15) Hypersecretion of growth hormone.
A) Pituitary dwarfism
B) Diabetes mellitus
C) Addisonʹs disease
D) Gravesʹ disease
E) Acromegaly
E) Acromegaly
13) Hyposecretion of insulin.
A) Pituitary dwarfism
B) Diabetes mellitus
C) Addisonʹs disease
D) Gravesʹ disease
E) Acromegaly
B) Diabetes mellitus
16) Hyposecretion of the thyroid in adults.
A) Cretinism
B) Myxedema
C) Cushingʹs disease
D) Gigantism
B) Myxedema
17) Hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex.
A) Cretinism
B) Myxedema
C) Cushingʹs disease
D) Gigantism
C) Cushingʹs disease
18) Hypersecretion of growth hormone.
A) Cretinism
B) Myxedema
C) Cushingʹs disease
D) Gigantism
D) Gigantism
19) Hyposecretion of the thyroid in infants.
A) Cretinism
B) Myxedema
C) Cushingʹs disease
D) Gigantism
A) Cretinism
1) Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver due to the action of ________.
A) aldosterone
B) insulin
C) secretin
D) glucagon
D) glucagon
Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular ________.
A) ions
B) deactivators
C) nucleotides
D) second messengers
D) second messengers
Oxytocin ________.
A) release is an example of a positive feedback control mechanism
B) is an adenohypophyseal secretion
C) exerts its most important effects during menstruation
D) controls milk production
B) is an adenohypophyseal secretion
ADH ________.
A) increases urine production
B) promotes dehydration
C) is produced in the adenohypophysis
D) is inhibited by alcohol
D) is inhibited by alcohol
The ability of a specific tissue or organ to respond to the presence of a hormone is dependent on ________.
A) the location of the tissue or organ with respect to the circulatory path
B) the membrane potential of the cells of the target organ
C) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
D) nothingall hormones of the human body are able to stimulate any and all cell types
because hormones are powerful and nonspecific
C) the presence of the appropriate receptors on the cells of the target tissue or organ
Several hormones are synthesized in the hypothalamus and transported to the anterior pituitary gland. The mechanism of transportation from hypothalamus to anterior pituitary gland is through the ________.
A) hepatic portal system
B) general circulatory system
C) hypophyseal portal system
D) feedback loop
C) hypophyseal portal system
The neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of the pituitary gland is not a true endocrine gland because ________.
A) it is strictly a part of the neural system and has little or nothing to do with hormonal
release
B) embryonically it was an endocrine tissue, but in the adult human it is no longer
functional
C) it is unable to function as an endocrine tissue because it is actually part of the neural
system due to its location
D) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for
release
D) it is only a hormone storage area that receives hormones from the hypothalamus for
release
Steroid hormones exert their action by ________.
A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene
B) finding an appropriate cell receptor and initiating cAMP activity
C) stimulating the synthesis of a glycogen
D) increasing blood pressure
A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene
Thyroid hormone (a small iodinated amine) enters target cells in a manner similar to ________.
A) insulin, because insulin is a small peptide
B) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells
C) growth hormone, because the thyroid works synergistically with thyroid hormone
D) glucagon, because the structure of glucagon is similar to that of thyroid hormone
B) steroid hormones, because both diffuse easily into target cells
When it becomes necessary to enlist the fight-or-flight response, a hormone that is released during the alarm phase of the general adaptation syndrome is ________.
A) estrogen
B) epinephrine
C) angiotensinogen
D) renin
B) epinephrine
The major targets of growth hormone are ________.
A) the blood vessels
B) the adrenal glands
C) the liver
D) bones and skeletal muscles
D) bones and skeletal muscles
Mineralocorticoid is to aldosterone as glucocorticoid is to ________.
A) testosterone
B) estrogen
C) cortisol
D) epinephrine
C) cortisol
The most important regulator of electrolyte concentrations in extracellular fluids is ________.
A) insulin
B) aldosterone
C) glucagon
D) cortisol
B) aldosterone
Which of the following is not a steroid-based hormone?
A) estrogen
B) aldosterone
C) epinephrine
D) cortisone
C) epinephrine
Cellular responses to hormones that initiate second-messenger systems include ________.
A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
B) cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase formation of an active second messenger
C) formation of a specific protein kinase that acts on a series of extracellular intermediates
D) hormone binding to intracellular receptors
A) possible activation of several different second-messenger systems
ACTH ________.
A) is secreted by the posterior pituitary
B) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic secretion
C) causes the release of hormones from the adrenal medulla
D) is not a tropic hormone
B) secretion is regulated by a hypothalamic secretion
Aldosterone ________.
A) is secreted by the neurohypophysis
B) functions to increase sodium reabsorption
C) presence increases potassium concentration in the blood
D) production is greatly influenced by ACTH
B) functions to increase sodium reabsorption
Which organ does not have hormone production?
A) heart
B) kidney
C) spleen
D) skin
C) spleen
In circumstances where the body requires prolonged or increased levels of a hormone, the DNA of target cells will specify the synthesis of more receptors on the surface of the cells of the target organ. This is known as ________.
A) the cellʹs sensitivity reaction
B) cellular affinity
C) up-regulation
D) a reaction to a stressor
C) up-regulation
Thyroxine is a peptide hormone, but its mechanism is different from other peptide hormones. Which of the following statements is true concerning this difference?
A) It causes positive feedback.
B) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response.
C) It is very specific in the cell type it targets.
D) It is a stimulant of cellular metabolism and targets all cells.
B) It does not require a second messenger to effect a response.
The second-messenger mechanism of hormone action operates by ________.
A) synthesizing more of the hormone than is actually needed
B) increasing the basal metabolic rate in the target organ
C) not responding to a feedback mechanism
D) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP
D) binding to specific receptors and employing the services of G proteins and cAMP
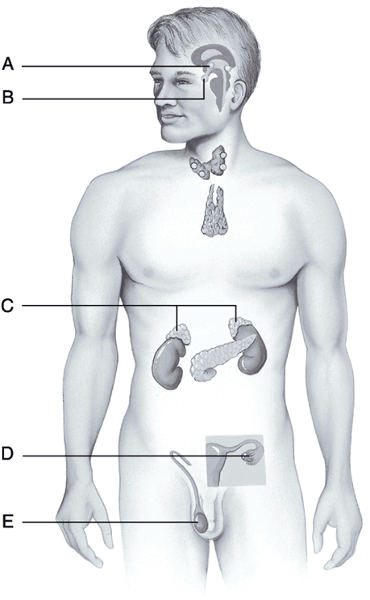
Produces the hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
D

Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain.
B

Produces the hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics.
E

Produce steroid hormones and glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids.
C

Produces hormones and is considered a neuroendocrine organ.
A
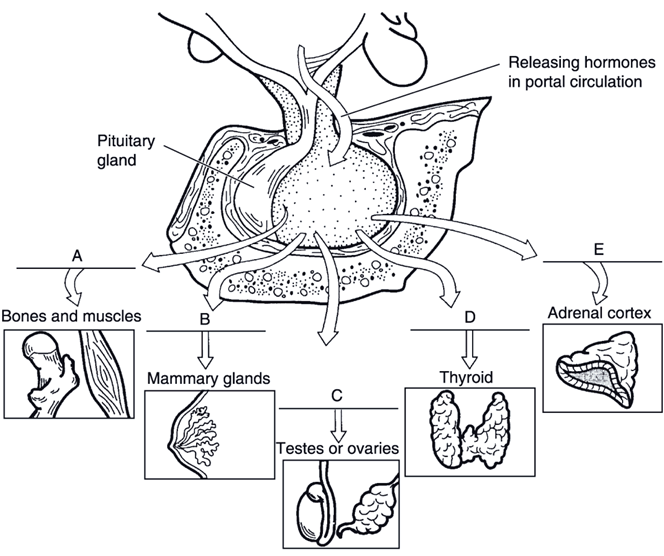
Match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target:
Growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH).
A

Match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target:
Follicle hormone (GnRH).
C

Match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target:
Prolactin-releasing hormone (PRH).
B

Match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target:
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH).
E

Match the following hypothalamic hormone with the pituitary hormone target:
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH).
D

Which part of the adrenal gland produces glucocorticoids?
B

Which part of the adrenal gland produces epinephrine?
D

Which part of the adrenal gland produces aldosterone?
A

Excess hormone levels result in Cushing's syndrome.
B

Hormones mimic sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters.
D

Which layer produces androgens.
C
In a patient who has Type II Diabetes Mellitus we commonly see_________
A) an increase in insulin production and secretion
B)a decrease in insulin production and secretion
C)an increase in the production and presentation of insulin receptors
D)a decrease in the production and presentation of insulin receptors
D) a decrease in the production and presentation of insulin receptors
Which of the following hormones is released by the kidney?
A)angiotensinogen
B)Renin
C)ACE
D)ANP
B) Renin
Which of the following hormones is released by the liver?
A)angiotensinogen
B)Renin
C)ACE
D)ANP
A) angiotensinogen
Which of the following hormones is released by the lungs?
A)angiotensinogen
B)Renin
C)ACE
D)ANP
C) ACE
Which of the following hormones is released by the heart?
A)angiotensinogen
B)Renin
C)ACE
D)ANP
D) ANP
Protein hormones exert their action by _____________.
A) entering the nucleus of a cell and initiating or altering the expression of a gene
B) binding cell receptors and initiating activity via secondary intracellular signal
C) entering the cell and activating mitochondrial DNA
D) activating the hypothalamic release of regulating hormones
B) binding cell receptors and initiating activity via secondary intracellular signal
Which of the following is not a parathyroid gland mechanism to maintain adequate levels of blood calcium?
A) activation of osteoclasts
B) increase calcium ion reabsorption by the kidneys
C) increase in intestinal reabsorption of calcium ions
D) inhibition of calcitonin synthesis
D) inhibition of calcitonin synthesis
Which of the following structures produces a precursor to hormonal vitamin D, important for Ca+ regulation?
A) stomach
B) heart
C) kidney
D) skin
D) skin
The secretion of __________ helps regulate our sleep cycle.
A) estrogen
B) testosterone
C) thyroid hormones
D) melatonin
D) melatonin