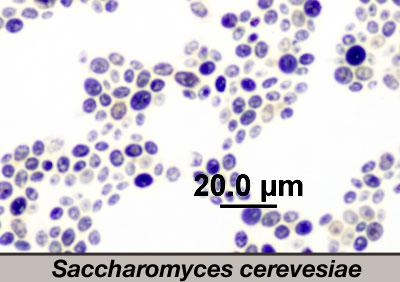
Saccharomyces is the common yeast often used in making wine, beeer and bread.
The term "yeast" simply refer to fungi that grow as single, round cells and don't form hyphae.
Yeast is not a taxonomic group, it's a Description of a body type.
these eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus (stained dark in this image) and a central vacuole.
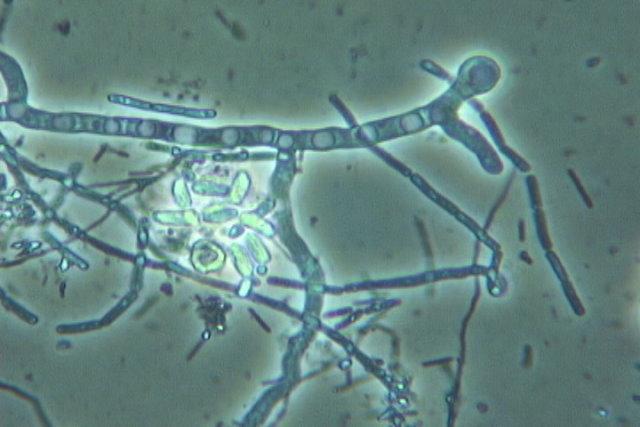
Hyphae- individual fungal filaments which collectively form a Mycelium.
They are dark in dematiaceous fungi and lack pigment in hyaline (moniliaceous)fungi.
Hyaline- All hyaline hyphae lack pigment- see photo
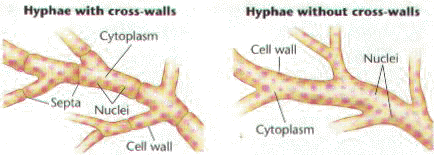
Septate -non septate
Hyphae with septa are called septate hyphae.
Septa are cross walls with pores to allow the movement of cytoplasm in hyphae.
Hyphae may be septate, and walls separate adjacent cells, or non septate if walls are absent.

Macrofungi-
Filamentous fungi that produce fleshy reproductive structures-mushrooms, puffballs, and shelf fungi- although the majority of the fungus is filamentous and hidden underground or within decaying matter...
we call them Macrofungi
Define
conidia
Various asexual spores may be produced during the life cycle of many fungi. If they form at the ends of hyphae this is what they are.
Define
blastospores
Other asexual spores which are produced by budding.
Define
arthrospores
produced when a hypha breaks
Most distinctive features of The Kingdom fungi
Non Motile
Absorptive heterotrophs (they don't ingest)
Chitin = cell wall
Spores = reproductive means
Sexual & asexual
Define
absorptive heterotroph
Secretes exoenzymes into the environment, then absorbs the digested nutrients.
Most are saphrophytes that decompose dead organic matter but some are parasites of plants, animals or humans.
Define
saphrophyte (saprobe)
consumes dead organic matter.
Define
dimorphoc fungi
These have both mold and yeast life-cycle stages.
Define
mycelium
These are tangled mats of hyphae, or many hyphae tangled together.
Define
chlamydospores (chlamydoconidia)
These are formed at the end of some hyphae and are a resting stage
How are Fungi taxonomic categories created or what are they based on?
Formal taxonomic categories are based on the pattern of sexual spore production and the presence of crosswalls inthe hyphae.
Define the Class zygomycetes
terrestrial, have nonseptate hyphae, and produce nonmotile sporangiospores and zygospores
Define the Class Ascomycetes
Produce a sac (an ascus) in which the zygote undergoes meiosis to produce haploid ascospores. hyphae are septate
Define the Class Basidiomycetes
Septate hyphae, and during sexual reproduction produce a basidium that undergoes meiosis to produce four basidiospores attached to its surface.
Define the Class deuteromycetes
An unnatural assemblage of fungi in which sexual stages are either unknown or not used in classification. Most of these resemble ascomycetes.
Zygomycetes (specifics for lab)
*Called sporangium fungi
* ex: Rhizopus Stolonifer
* non septate
* asexual structure called sporangium- produces sporangiospores
* Sexual spore produced by conjugagtion when (+) hyphae and (-) fused is called zygospore.
* Zygospores can endure harsh environments until conditions improve and new sporangium.
Ascomycetes (specifics for lab)
* Called sac fungi
* ex: saccharomyces cerevisiae
* Can reproduce both sexually and asexually
* yeast reproduce asexually by budding
* Asexual spores called conidia
* Ascus (sacs)
basidiomycetes (specifics for lab)
* Called club fungi
* ex: mushrooms, puffballs, shelf fungi
* Some used as food, others cause crop damage
* seldom asexual
* Vegetative structures found below ground (hyphae and mycelium)for anchor and absorbing nutrients
Candida albicans Vegetative cells
Note the oval shape and the nuclei
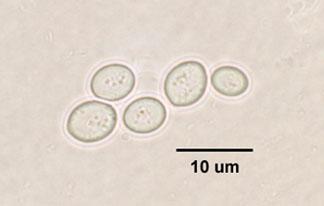
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Unstained
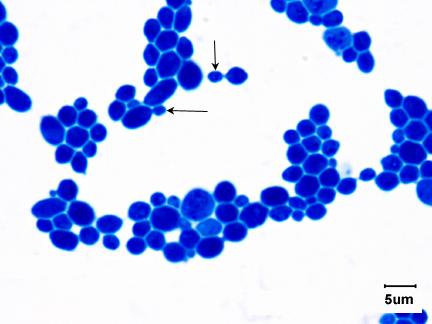
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
note the budding cells (arrows)
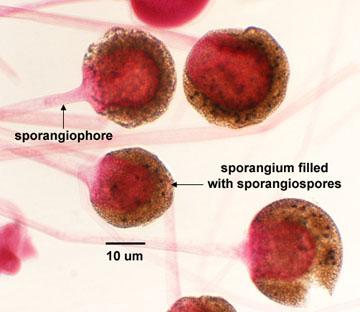
Rhizopus sporangiosphores
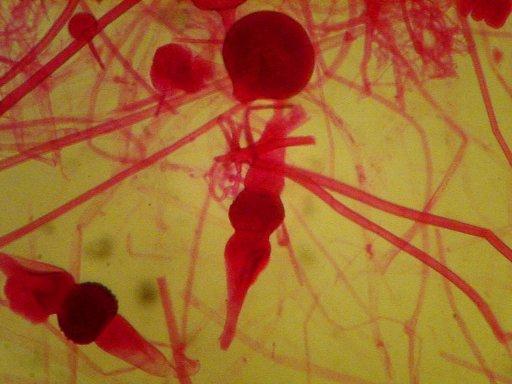
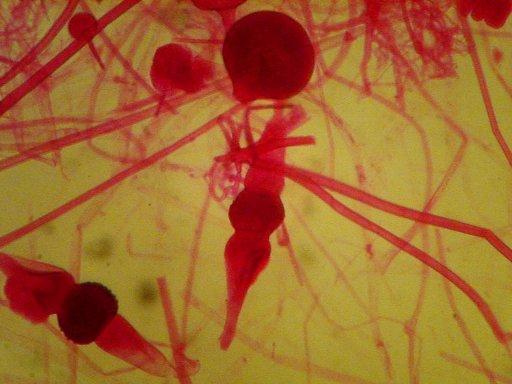
Rhizopus (nigricans) Zygospore
Perfect example of Rhizopus Zygospores in the middle and at bottom left.
look close there is a sporangium at center top too.
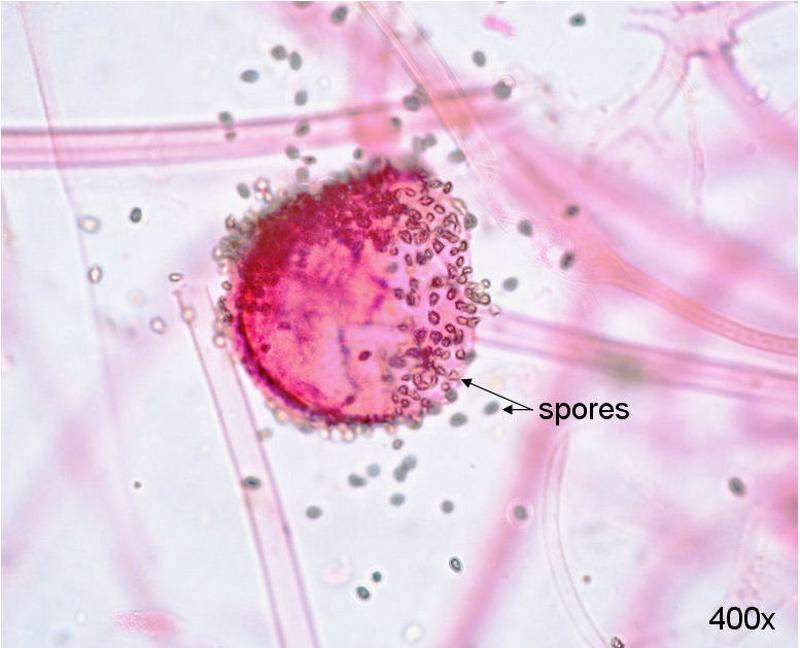
Rhizopus Sporangium
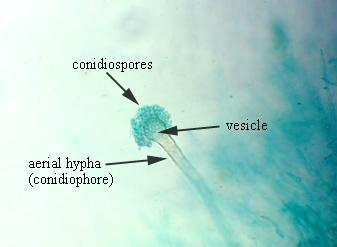
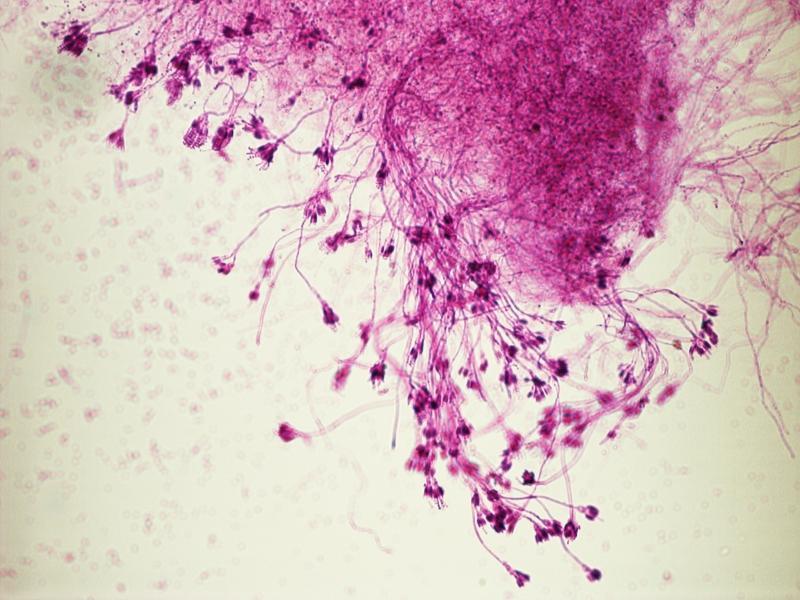
Aspergillus Conidiiospores
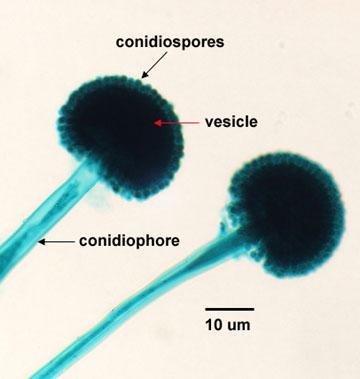
Aspergillus Conidiiospores
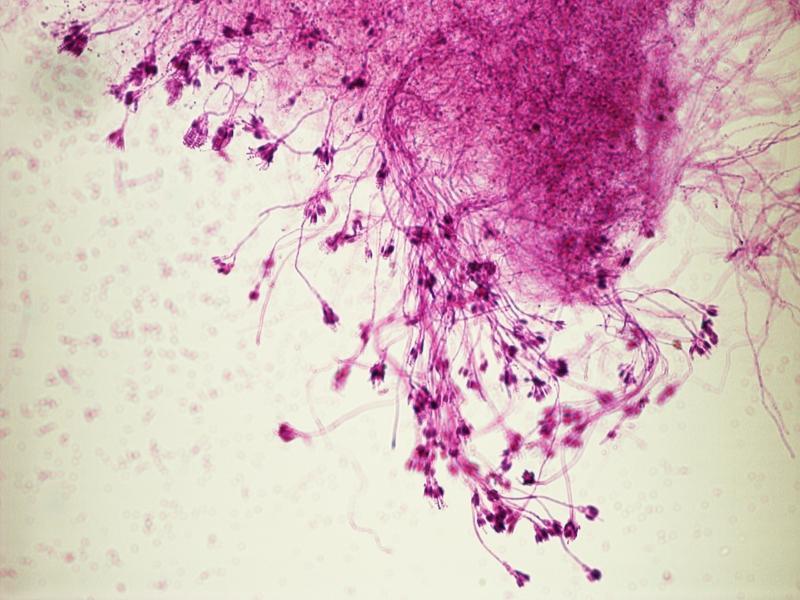
Penicillium
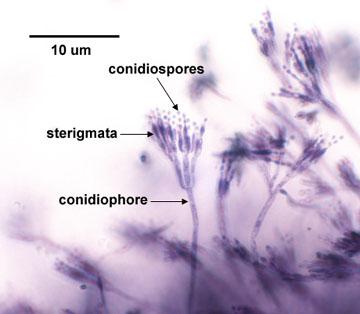
Penicillium Conidiospores
name the Group (yeast or mold)
Class / Phylum
Distinctive Features &
Diseases caused or uses
Rhizopus
* Mold
* Zygomycetes
* Features are sexual and asexual stages
* is a bread mold. certain species cause Zygomycosis
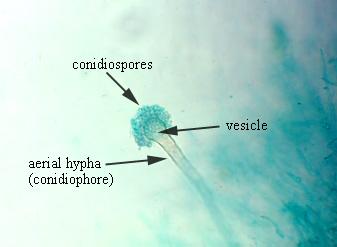
name the Group (yeast or mold)
Class / Phylum
Distinctive Features &
Diseases caused or uses
Aspergillus
* Mold
* Ascomycetes
* Features: the fruiting body with chains of conidia arising from one or two rows of philalides attached to a swollen vesicle at the end of an unbranched conidiopore.
* Used in soy sauce, citric acid (causes aspergillosis)
name the Group (yeast or mold)
Class / Phylum
Distinctive Features &
Diseases caused or uses
Penicillum
* Mold
* Ascomycetes
* Features: sexual reproduction results in the formation of ascospores, hence we classify in Ascomycetes
* Used to make penicillin. Only one species is pathogenic (P. marneffei) in Asia
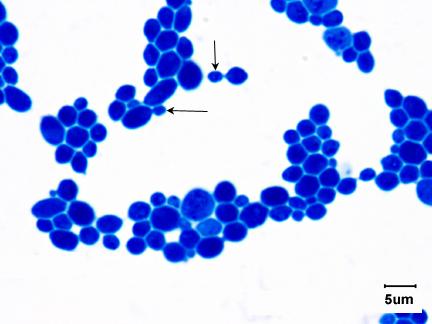
name the Group (yeast or mold)
Class / Phylum
Distinctive Features &
Diseases caused or uses
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
* Yeast
* Ascomycetes
* One of the budding yeasts, used to make bread, beer, wine, no mycelium, produces a colony like bacteria (
* Not a pathogen)
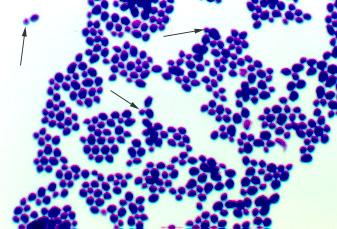
name the Group (yeast or mold)
Class / Phylum
Distinctive Features &
Diseases caused or uses
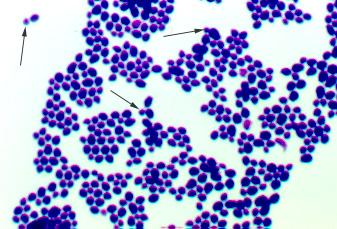
Candida albicans
* yeast
* Ascomycetes
* Budding yeast, normal part of human flora
* Causes thrush, vulvovaginitis, candidiasis