spine
sharp,slender process
tubercle
small rounded projection
crest
narrow ridge of bone
tuberosity
large rounded projection
head
structure supported on neck
ramus
armlike projection
condyle
rounded, convex projection
fissure
narrow opening
Meatus
Canal-like structure
Foramen
Round or oval opening through a bone
Fossa
Shallow depression
Sinus
Air-filled cavity
Trochanter
Large, irregularly shaped projection
Epicondyle
Raised area on or above a condyle
Process
Projection or prominence
facet
smooth, nearly flat articular surface
The four major anatomical classifications of bones are long, short, flat, and irregular. Which category has the least amount of spongy bone relative to its total volume?
long bones
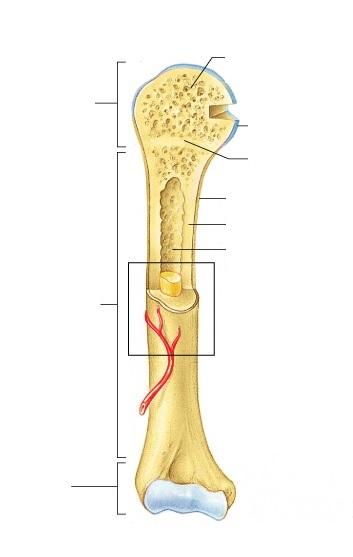
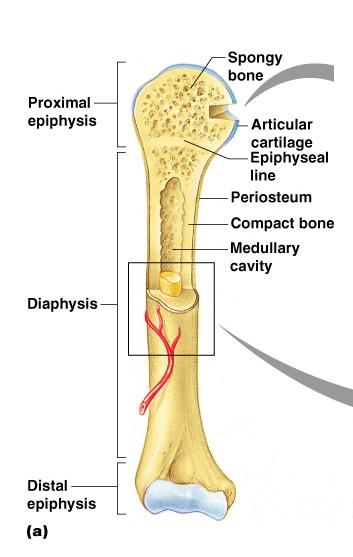
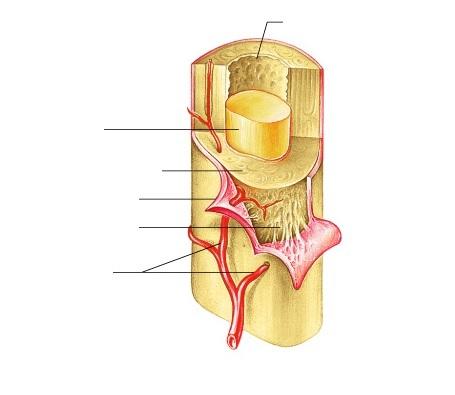
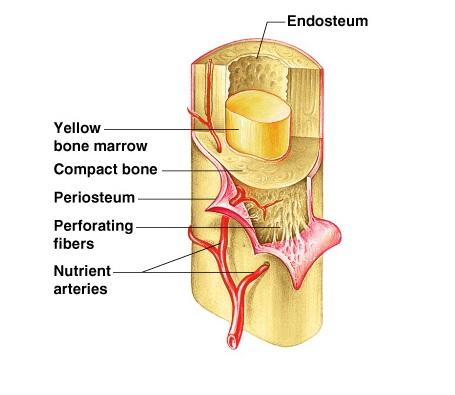
contains spongy bone in adults
F, epiphysis
made of compact bone
C, diaphysis
site of blood cell formation
J, Red Bone Marrow
major submembranous site of osteoclasts
D, endosteum & I, periosteum
scientific term for bone shaft
C, diaphysis
contains fat in adult bones
G, Medullary Cavity
growth plate remnant
E, Epiphyseal line
major submembranous site of osteoblasts
D, endosteum & I, periosteum
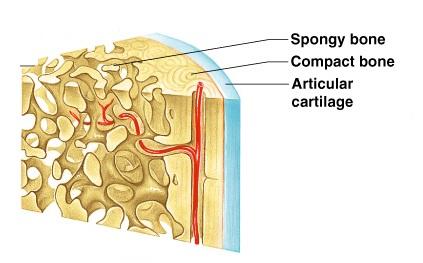
What differences between compact and spongy bone can be seen with the naked eye?
compact bone diaphysis looks solid, practically without holes or gaps-
spongy bone is metaphysis and the epiphysis on the other hand are composed of thousands of spicules or trabeculae of bone, interconnected
What is the function of the periosteum?
The Periosteum serves as an attachment point for muscles and bones through tendons and ligaments.
Trace the route taken by nutrients through the bone, starting with the periosteum and ending with an osteocyte in a lacuna.
The path is: Periosteum, Perforating Canals, Central Canals, Canaliculi, Lancunae, Osteocytes
concentric lamellae
layers of bony matrix around a central canal
lacunae
site of osteocytes
central canal
longitudinal canal carrying blood vessels, lymphatics, nerves
canaliculi
minute canals connecting osteocytes of an osteon
matrix
inorganic salts deposited in organic ground substances
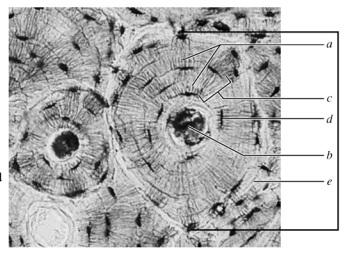
On the photomicrograph of bone on the right (365x), identify all structures maned in the key and bracket an osteon.
A. Canaliculi
B. Concentric Lamellae
C. Lacunae
D. Central canal
E. Matrix
What is the function of the organic matrix in bone?
Gives bone flexibility & strength
Name the important organic bone components
Collagen fibers, osteocytes
Calcium salts form the bulk of the inorganic material in bone. What is the function of the calcium salts?
Gives bone hardness & compressional strength.
Baking removes _______________ from bone. Soaking bone in acid removes _________________.
baking removes what from bone? ORGANIC
soaking in acid removes? MINERALS
Compare and contrast events occurring on the epiphyseal and diaphyseal faces of the epiphyseal plate?
The cartilage cells at the epiphyseal side are continuing to grow and divide mitotically, while the ones on the diaphyseal side are aging, dying and then osteoblasts move in to form bone.
Type of cartilage that supports the external ear
Elastic
Type of cartilage between the vertebrae
Fibrocartilage
Type of cartilage that forms the walls of the voice box (larynx)
Hyaline
Type of cartilage that forms the epiglottis
Elastic
Type of cartilage forming the articular cartilages
Hyaline
Type of cartilage that forms the meniscus
Fibrocartilage
Type of cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum
Hyaline
Type of cartilage thats the most effective at resisting compression
Fibrocartilage
The most springy and flexible type of cartilage
Elastic
The most abundant type of cartilage
Hyaline