The Nurse has charted: "Client has an open wound located on the lateral aspect of the leg". This wound would be located on which portion of the leg?
outer surface or lateral side
The serous membrane that covers the intestines is what?
Visceral Peritoneum
A vertical section through the body, dividing it into anterior and posterior portions is what?
Coronal or frontal
The anatomical position is used as what?
A standard reference point for directional terms regardless of the actual position of the body
The frontal plane is also called the _______ plane?
Coronal
The dorsal body cavity is the site of what?
Brain and spinal cord
The spleen is located in which quadrant of the body?
Left upper quadrant
Place the following in correct sequence from simplest to most complex
molecule, atom, tissue, cell, organ
Atom, molecule, cell, tissue, organ
Homeostasis is the condition in which the b.
body maintains what?
A relatively stable internal environment, within limits
The parietal pleura would represent a serous membrane that does what?
lines the thoracic cavity
The anatomical position is characterized by all of the following except_______
body erect
palms turned posteriorly
arms at side
thumbs pointed laterally
palms turned posteriorly
A negative feedback mechanism works how?
To prevent sudden severe changes within the body
The main, general purpose of negative feedback is?
to maintain homeostasis
True or false
The epigastric region is located superior to the umbilical region.
True
True or False
The major function of serous membranes is to decrease friction.
True
True or False
The serous membrane that lines the peritoneal cavity is termed the visceral peritoneum.
False
True or False
The elbow is proximal to the shoulder.
False
Directly causes mechanical motion
Muscular
Responds to environmental changes by transmitting electrical impulses
Nervous
Provides support and levers for muscle to work on
Skeletal
Protects underlying organs from mechanical damage and synthesizes vitamin D
Integumentary
The other two terms for the horizontal plane are what?
Transverse and cross section
The elbow is _________ to the wrist?
Proximal
The knee is _________ to the hip?
Distal
The knee is ______ to the ankle?
Proximal
True or False
In the anatomic position the posterior surface of the body is the dorsal surface.
True
True or False
In the anatomic position the little finger (5th finger) is the medial side
True
In anatomic position the great (1st toe) is which of the following?
Medial or Lateral
medial
A chain of 25 amino acids would be called a what?
Polypeptide
The coiling of the protein chain backbone into an alpha helix is referred to as the what?
Secondary structure
Carbohydrates and proteins are built up from their basic building blocks by the _____?
Removal of a water molecule between each two units
Which statement about enzymes is NOT true?
Enzymes are composed mostly of protein
Enzymes raise the activation energy needed to start a reaction
Enzymes are organic catalysts
Enzymes may be damaged by high temperature
Enzymes raise the activation energy needed to start a reaction
What four elements make up about 96% of body matter?
Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Nitrogen
The structure composed of glycerol and 3 fatty acids is what?
Tryglycerides
The major function of carbohydrates in humans is what?
Generation of ATP
Which of the following is NOT a type of lipid?
Cholesterol
Prostaglandin
Glycogen
Oils
Glycogen
The major functions of proteins in the body are what?
Structures and enzymes
Having a polar and nonpolar portion is called?
Amphiphatic
The plasma membrane on the extracellular side and the cytosolic side are what?
Not identical in structure
The hydrophobic portion of the plasma membrane is made up of what?
Fatty acid tails
The most abundant substance in the plasma membrane is what?
Phospholipids
The cholesterol molecules separate phospholipids, provides an anchoring function in the outer portions of the membrane and what?
Contributes to fluidity in the inner portion of the membrane
Glycolipids and glycoproteins are located at which sites in the plasma membrane?
Extracellular side
Lipid rafts display what characteristic?
Less fluid than the rest of the membrane
The plasma membrane will be disrupted with the removal of what types of proteins?
Integral proteins
Most of the integral proteins are positioned such that they what?
Face both the cytosolic and extracellular side
Peripheral proteins are associated with which portion of the plasma membrane?
Hydrophilic portion
Plasma membrane proteins can move how?
Laterally in the membrane
Integral proteins do not function how?
Exclusively as transport channels
Glycocalyx is associated with what functions?
Cell recognition, Maintaining the hydration status of the cell, Making the cell slippery
The major function of a microvilli is what?
Increase the surface area of the cell
What are the characteristics asoociated with passive movement across a plasma membrane?
Nonpolar and small molecular size
Give examples of classified passive processes?
Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion, Diffusion through channels
What is one example that is not a classified passive process?
Vesicular transport
What are examples of passive process simple diffusion?
Oxygen, alcohol
What are examples of passive process Facilitated diffusion?
Glucose, Galactose
What are examples of passive process Osmosis?
Water
Osmosis is the movement of water from?
An area of low to high solute concentration
The generation of the resting membrane potential is most associated with what channel?
Leakage channel
There are not more leakage channels for sodium in the plasma membrane than for what?
Potassium
Gated channels can be opened by what mechanism?
Ligands, Voltage change, Mechanical stimulation of the plasma membrane
A cell that is surrounded by a hypertonic extracellular fluid will do what?
shrink
A substance that binds to a plasma membrane receptor to trigger a cellular response is what?
Ligand
What are some examples of ligands?
Neurostansmitter, hormones and drugs
What does the sodium-potassium ATPase pump do?
3 sodium ions are pumped from the intracellular to the extracellular space
Active transport does what?
Release of acetylcholine from a secretory vesicel via exocytosis
Phagocytosis is best described by what?
An active process in which lysosomes fuse with the enveloped vesicle
Membrane-enclosed vesicles formed in the golgi complex that contains strong hydrolytic and digestive enzymes
Lysosomes
Network of protein filaments that extend throughout the cytoplasm, providing cellular shape, organization and movement
Cytoskeleton
Sites of protein synthesis
Ribosomes and Rough ER
Contains enzymes that break apart unneeded, damaged or faulty proteins into smaller peptides
proteosomes
Site where secretory proteins and membrane molecules are synthesized
Rough ER
Membrane-enclosed vesicle that contains enzymes that oxidize various organic substances
Peroxisomes
Short microtubular structures extending from the plasma membrane and involved in movement of materials along the cell's surface
Cilia
Modifies, sorts, packages, and transports molecules synthesized in the rough ER
Golgi complex
An organizing center for growth of the mitotic spindle
Centrosome
Functions in ATP generation
Mitochondria
Functions in synthesizing fatty acids and steroids, helping liver cells release glucose into the bloodstream, and detoxification
Smooth ER
Membrane-bound sacs that transport, transfer or secrete proteins
Vesicles
Long microtubular structures extending from the plasma membrane and involved in the movement of a cell
Flagellum
Cristae
Mitochondria
Cis and trans face
Golgi apparatus
Cisternal system that is located immediately adjacent to the nucleus and is involved in protein synthesis
Rough ER
movement of sperm
Flagellum
Vesicles that contain oxidases and catalases
Peroxisome
Smallest of the cytoskeletal elements; example is actin
Microfilaments
Site of attachment of tRNA
Ribosome
Exhibits a beating motion for movement of particles in the respiratory and female reproductive tract
Cilia
Site of assembly of ribosomes
Nucleolus
Associated with the proteins kinesins and dyneins for movement
Microtubules
Degradation of damaged or old proteins; peptide chains broken down into amino acids
Proteosome
Electron transport chain
Mitochondria
Cisternal system that has vesicles budding from its surface
Golgi apparatus
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Smooth ER
Mitotic spindle
centriole
Vesicle containing hydrolytic enzymes
Lysosome
Conversion of hydrogen peroxide to a non-harmful substance
Perioxisome
Transport of substances that have entered the cell via endocytosis to various organelles
Endosomes
Opening in double layered membrane by which mRNA exits in route to the cytosol
Nuclear pore
Synthesis of fatty acids and steroids and detoxification of some substances (ex: alcohol)
Smooth ER
Cytoskeletal element associated with red blood cell structural integrity
Intermediate filament
What processes occur in the cell's nucleus?
Replication and trancription
How many nucleus' do all cell's contain?
1 or more
Double layered and selectively permeable
Nuclear membrane
A nucleosome contains how many histone proteins wrapped in the DNA strand?
8
When the cell is carrying out normal daily activity the DNA is in what form?
Extended form(chromatin)
Deoxyribose and the phosphate group is part of what?
DNA nucleotide
The shortest portion of interphase is what?
G2
During interphase the cell is doing what?
Performing its usual metabolic activities
What is the correct sequence of bases for the complementary strand of DNA formed during replication for the DNA template bases of CGTA?
GCAT
Shortest sequences of RNA are needed to initiate the process of replication. These RNA nucleotides are later what?
Replaced by DNA nucleotides
The complementary strand of DNA made during replication that is synthesized in segments that are spliced together is what?
Lagging strand
What cells do not have the ability to divide in the human adult?
Cardiac muscle cells and neurons
What is a trigger for cells to stop dividing?
Contact inhibition
What rise and fall in a cyclic pattern during interphase and mitosis?
Cyclin and MFP
The longest phase of mitosis is what?
Prophase
What is the correct sequence of events in mitosis?
Prophase, Metaphaose, Anaphase, and Telophase
During prophase the nuclear membrane disintegrates. It reforms during what stage?
Telophase
The phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes separate and move to opposite poles of the cell is what?
Anaphase
The microtubular elements of the mitotic spindle that are attached to the centromere of the chromosomes is what?
Kinetochores
The phase of mitosis in which the chromosomes are lined up at the equator of the cell is what?
Metaphase
Kinetochores pulls the chromosomes to the middle of the cell. Polar microtubules push the poles of the cell which way?
apart
Nucleoli remain visible or nonvisible thoughout mitosis?
nonvisible
The shortest phase of mitosis is what?
Anaphase
The term chromosomes refers to 2 chromatids connected by a centromere. Once anaphase has occurred and the individual chromatids have separated, each chromatid is now what?
termed a chromosome
Telophase is in most ways ________ in reverse?
Prophase
The cleavage furrow is most associated with which stage of mitosis?
Telophase
The base pair of RNA is what?
AUCG
The 3 base pair groupings of mRNA is what?
Codon
The RNA that is cloverleaf-shaped and has an end for bases and an end for a specific amino acid is what?
tRNA
The process of transcription is best described as what?
A strand of mRNA and is made from a DNA template
What type of RNA is used in the process of translation?
tRNA, mRNA and rRNA
Transcription factor performs what function?
Loosens the histones and binds to the promotor region of DNA
What would be the complementary codon for a DNA template with the bases TAACGA?
AUUGCU
What would be the complementary anticodon for a codon with the base ACG?
UGC
What would be the anticodon for the DNA bases of ATGC?
AUGC
The portion of pre-RNA that is removed is termed what?
introns
The mRNA binds to what following translation?
A site
The sequence for tRNA to the large ribosomal subunit during translation is what?
A site....P site....E site
The basic physical unit of heredity, consisting of a sequence of DNA that occupies a specific location on a chromosome and determines a particular characteristic in an organism is what?
Gene
Complex of proteins and enzymes required for replication
Replisome
Removes the introns from the pre-mRNA
Spliceosome
Microtubules attached to the centrioles
Asters
Aids in the attachment of chromatids to each other
Cohesin
Protective caps on the ends of chromosomes
Telomeres
Histones wrapped together by DNA helix
Nucleosomes
Y-shaped area site of replication
Replication fork
Enzyme used in transcription
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that unwinds the DNA strands during replications
Helicase
Enzyme involved in replication by placing the correct nucleotide and creating bonds
DNA ploymerase III
Enzyme that splices together the segments of DNA made during replication on the lagging strand
DNA ligase
Enzyme that cleaves the cohesin holding the chromatids together
Separase
The area surrounding the centrioles
Centrosomes
Mitotic spindle
Centrioles
Connects to chromatids
Centromeres
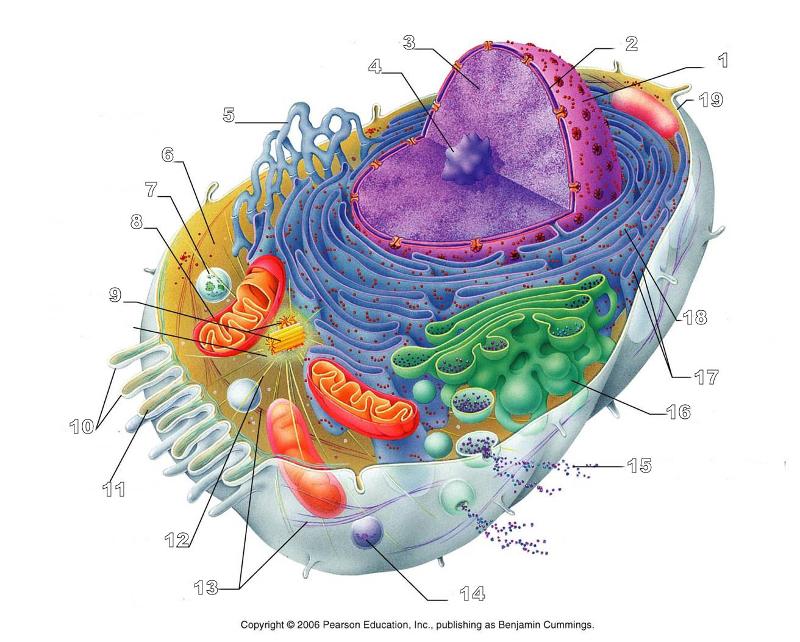
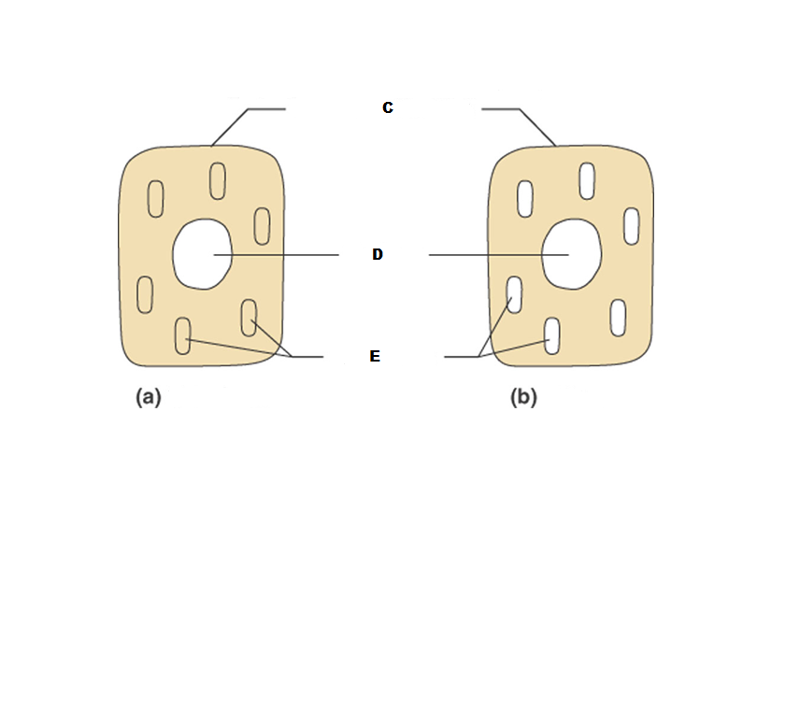
What is #1 in this picture?
Nucleus
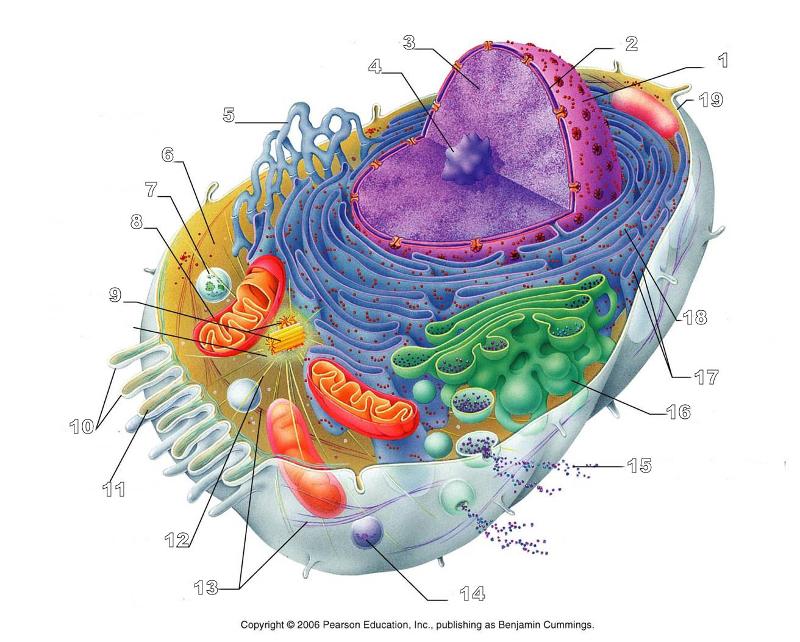
What is #2 in this picture?
Nuclear envelope
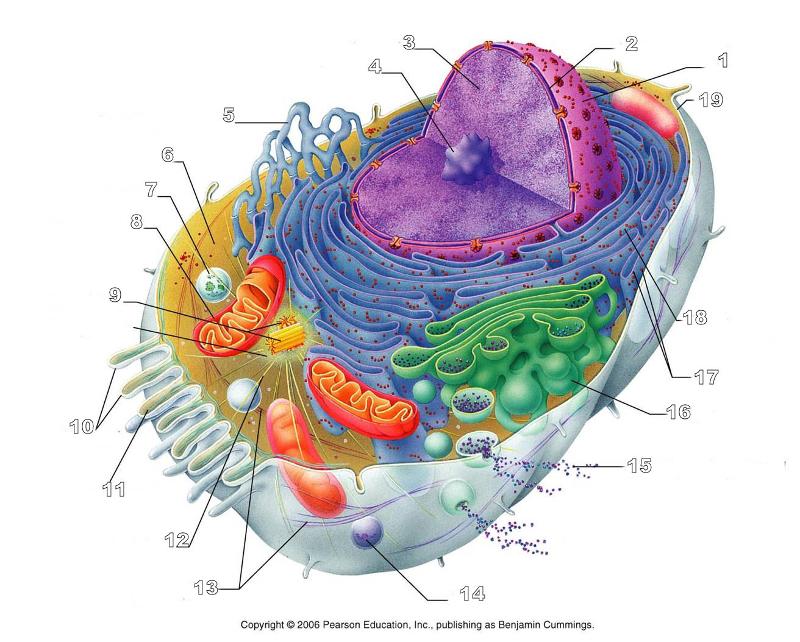
What is #3 in this picture?
Chromatin
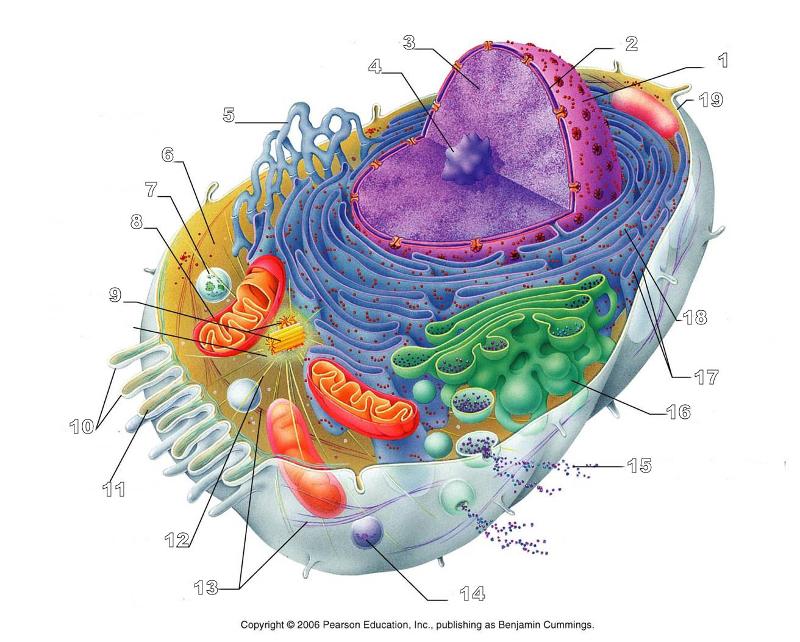
What is number #4 in this picture?
Nucleolus
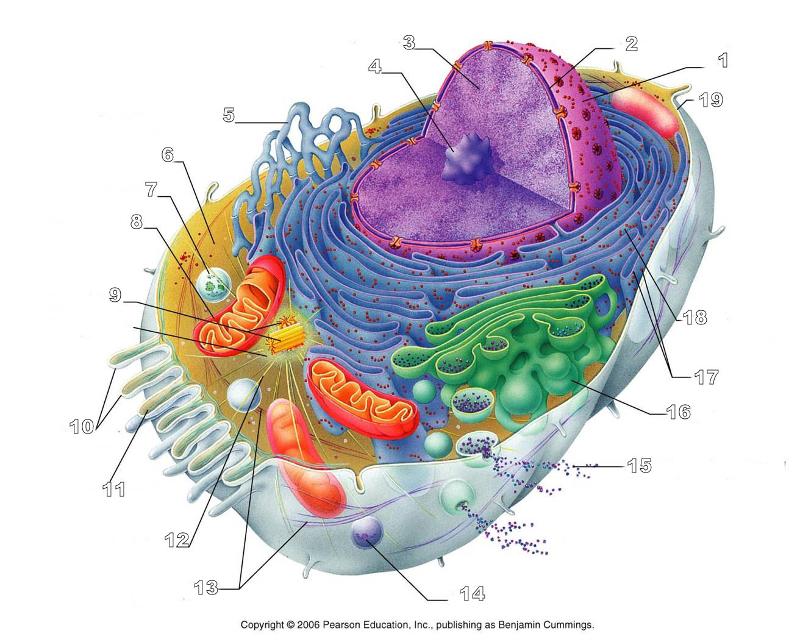
What is #5 in this picture?
Smooth ER
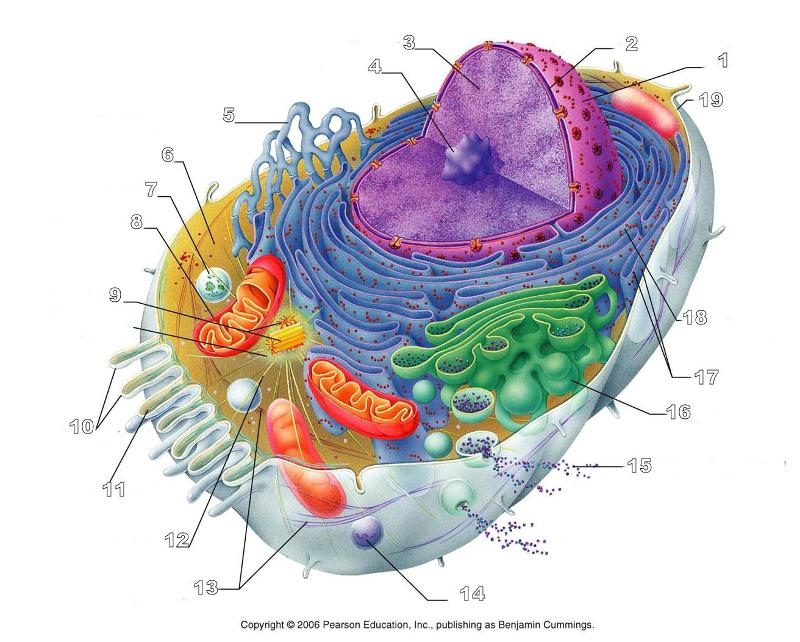
What is #6 in this picture?
Cytosol
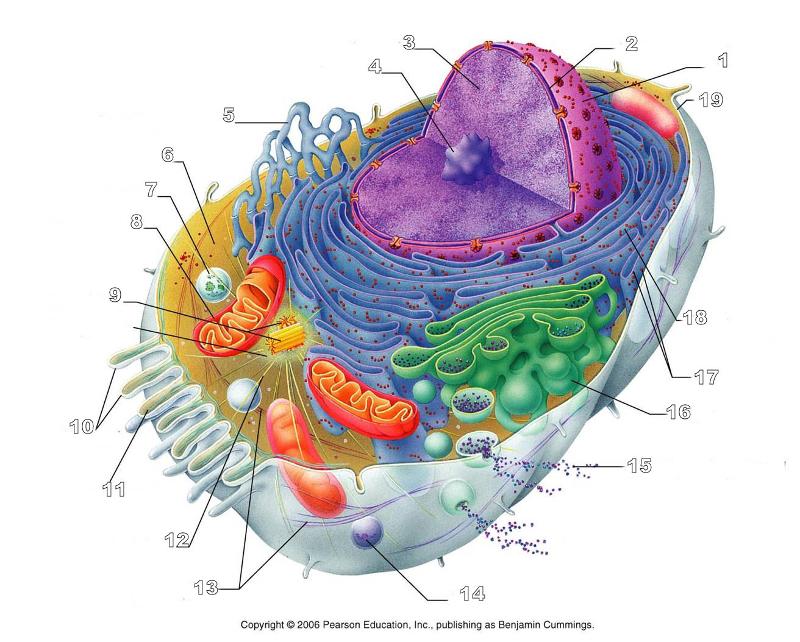
What is # 7 in this picture?
Lysosome
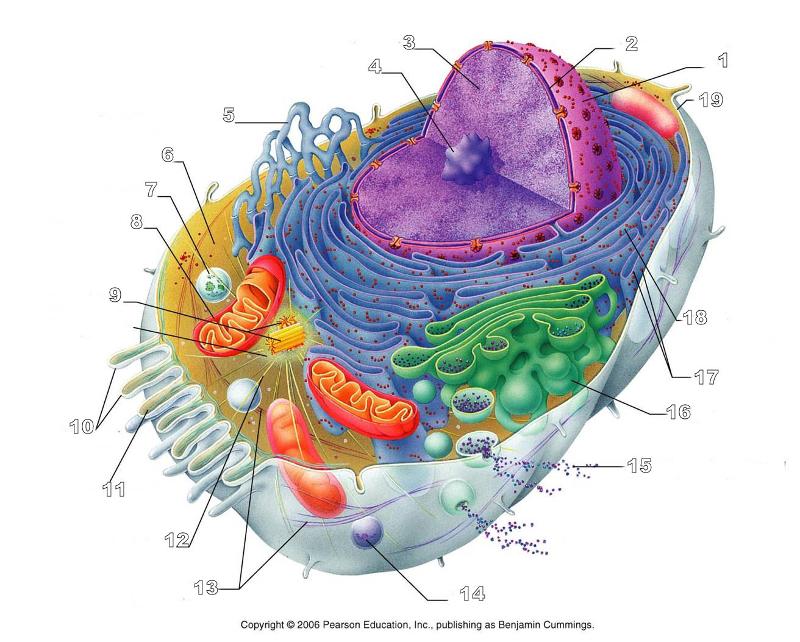
What is #8 in this picture?
Mitochondrion
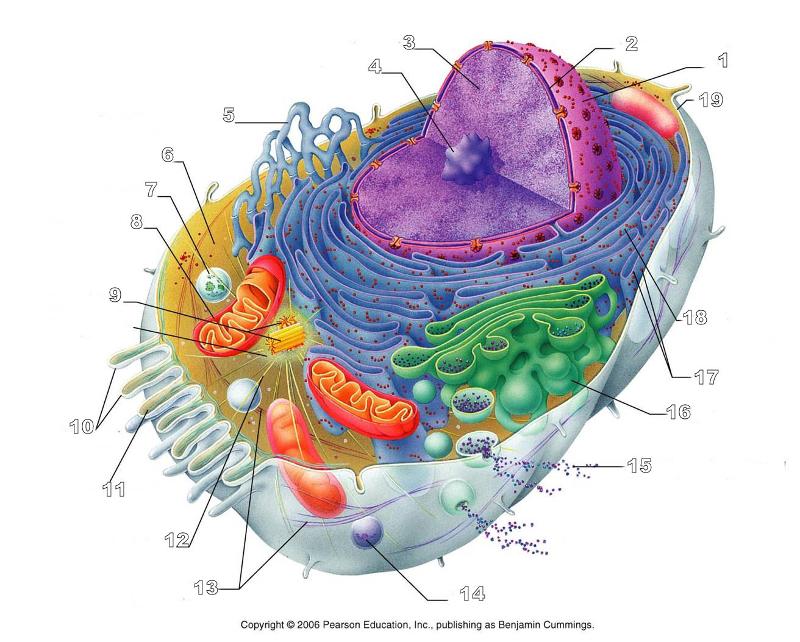
What is #9 in this picture?
Centrioles
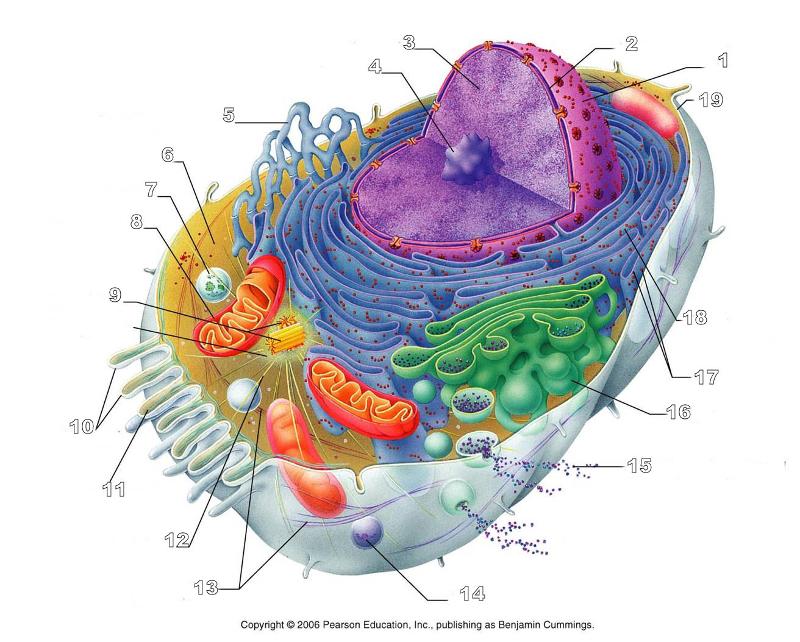
What is #10 in this picture?
Microvilli
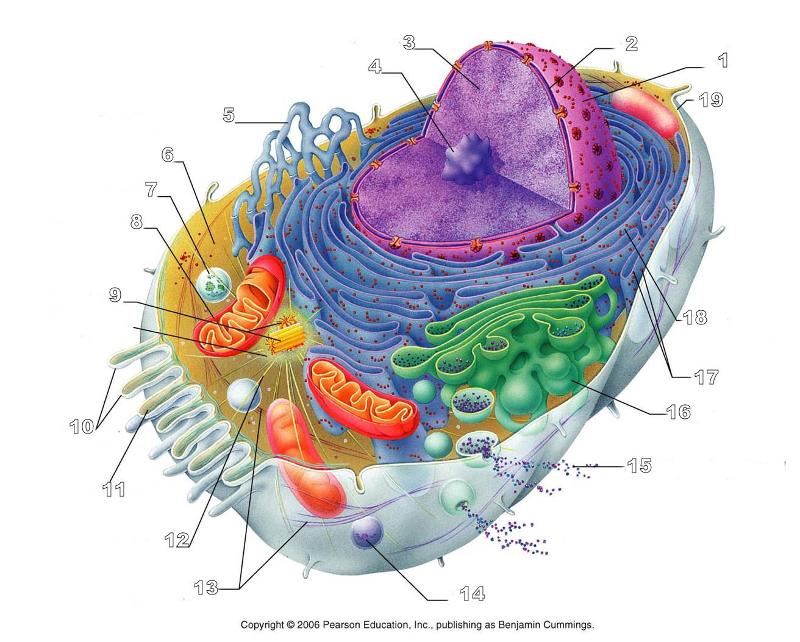
What is #11 in this picture?
Microfilament
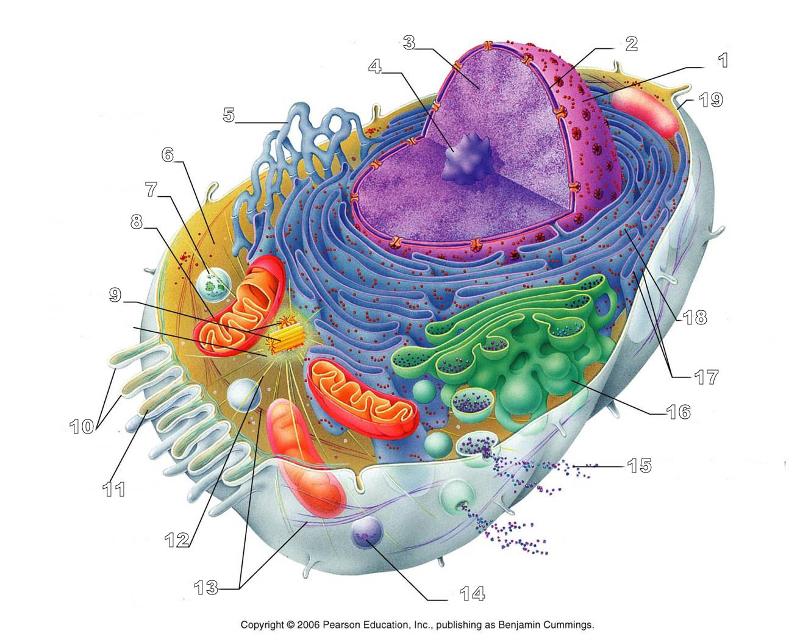
What is #13 in this picture?
Intermediate Filament
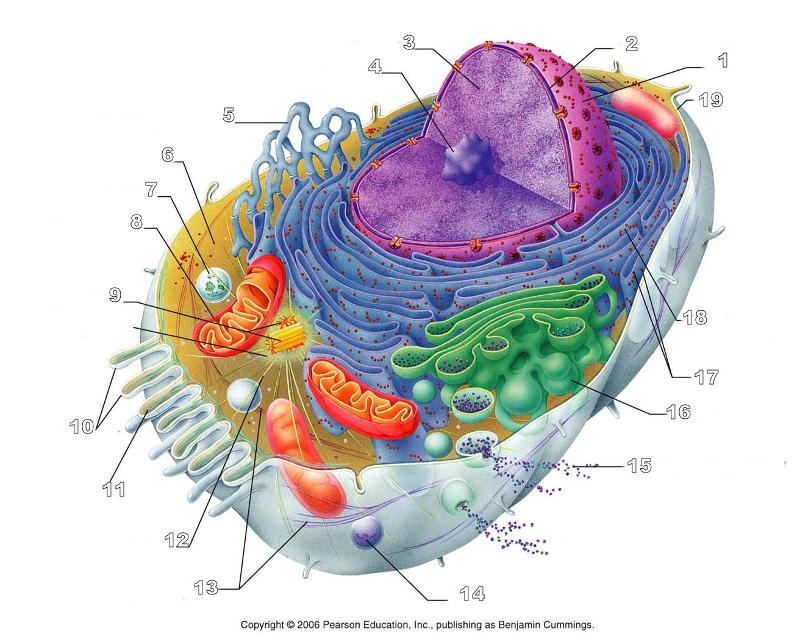
What is #14 in this picture?
Peroxisome
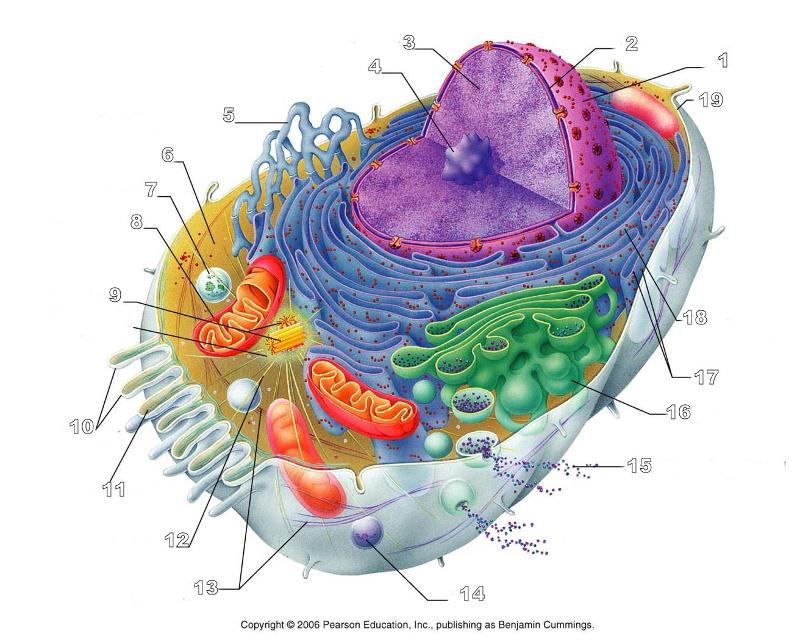
What is #15 in this picture?
Exocytosis
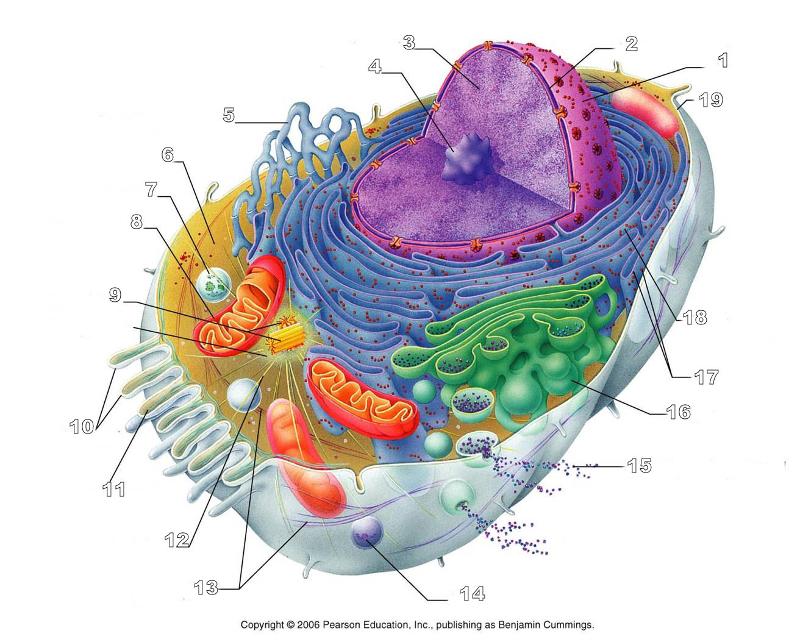
What is #16 in this picture?
Golgi Apparatus
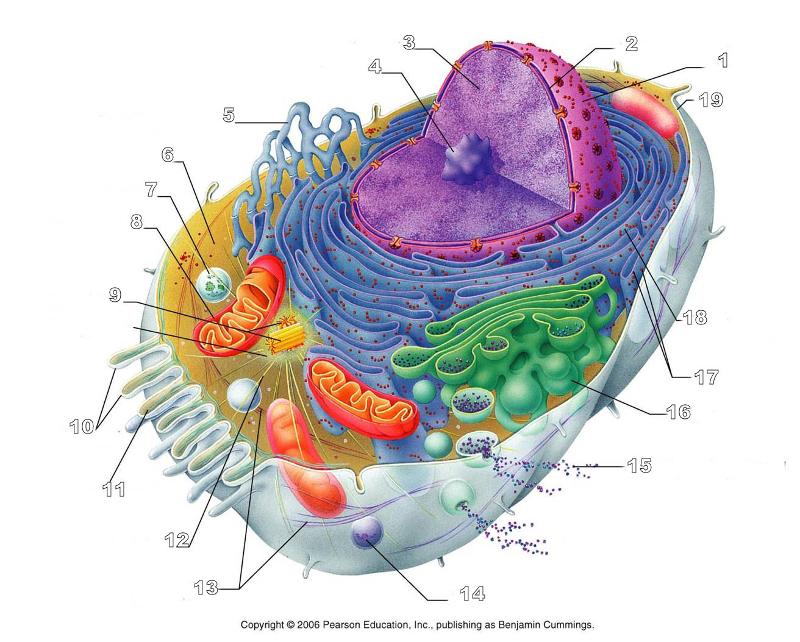
What is #17 in this picture?
Ribosomes
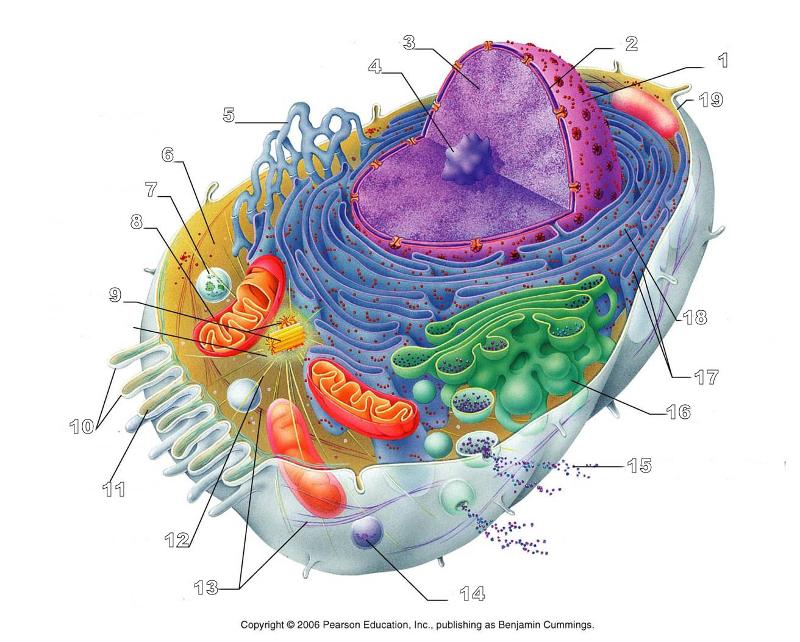
What is #18 in this picture?
Rough ER
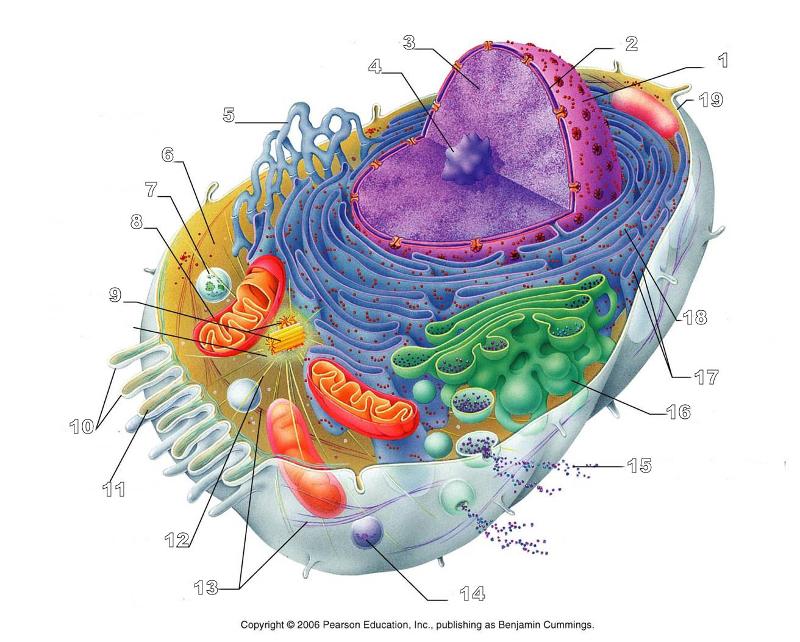
What is #19 in this picture?
Plasma Membrane
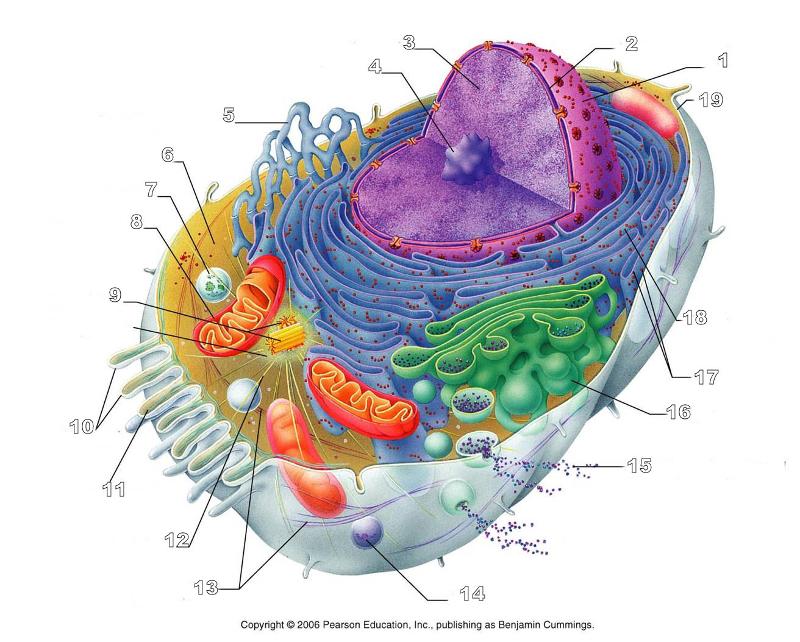
What is #12 in this picture?
Microtubules
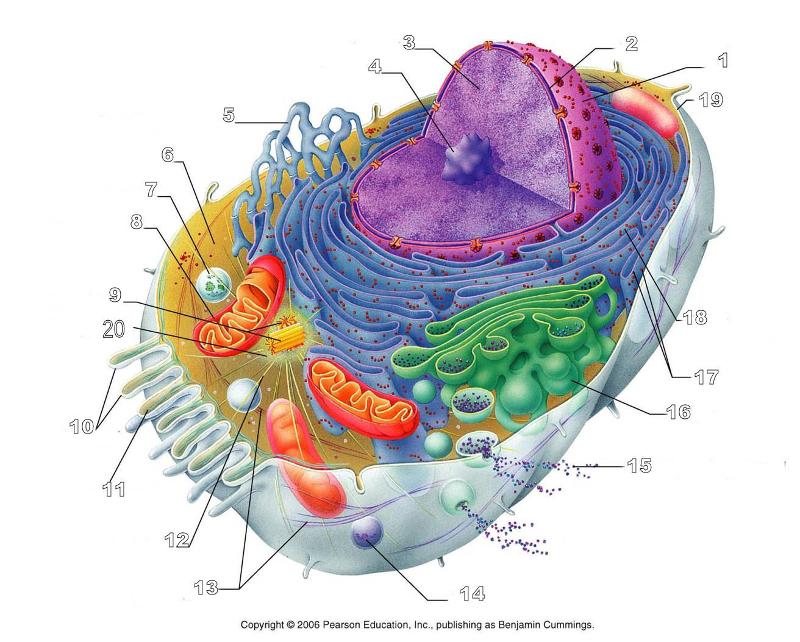
What is #20 in this picture?
Centrosome Matric
What does pollex mean?
Thumb
What does hallux mean?
big toe
What does sural mean?
calf
What does Crural mean?
(front) lower leg
What does popliteal mean?
back side of knee
What does palmar mean?
palm of hand
What is a phospholipid?
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acid chains, and a phosphate group
What % of plasma lipids do cholesterol have?
20%
Cholesterol molecules are aligned with the phospholipid molecules where?
On both sides of the bilayer
Glycolipids are found where?
Only in the portion of the plasma membrane that faces the extracellular fluid space
Which one gets cut out during transcriptions Introns or exons?
Introns
What has a cloverleaf structure?
tRNA
What % of body mass makes up fluids in the female?
55%
What % of body mass makes up fluids in males?
60%
How much of the bodily fluid is in the intracellular cells?
2/3
How much of the bodily fluid is in the extracellular fluid?
1/3
In our extracellular fluid what % is in the Interstitial fluid?
80%
The cytoplasm is what?
The cellular material inside the plasma membrane and outside the nucleus
What % of the total cell volume is made up of the cytoplasm?
55%
Major functional area of a cell where most cellular activities are accomplished
Cytoplasm
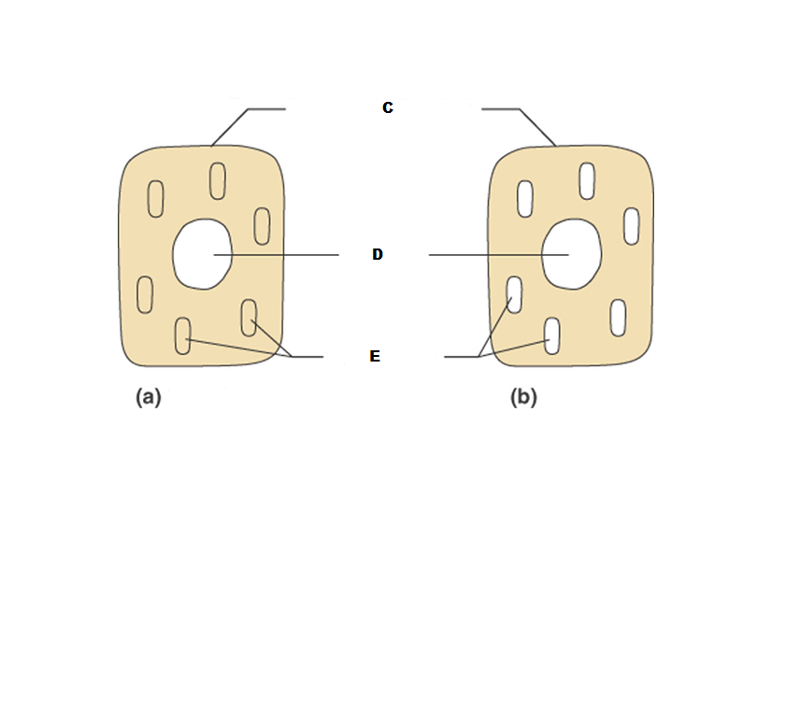
What is A in this picture?
Cytoplasm
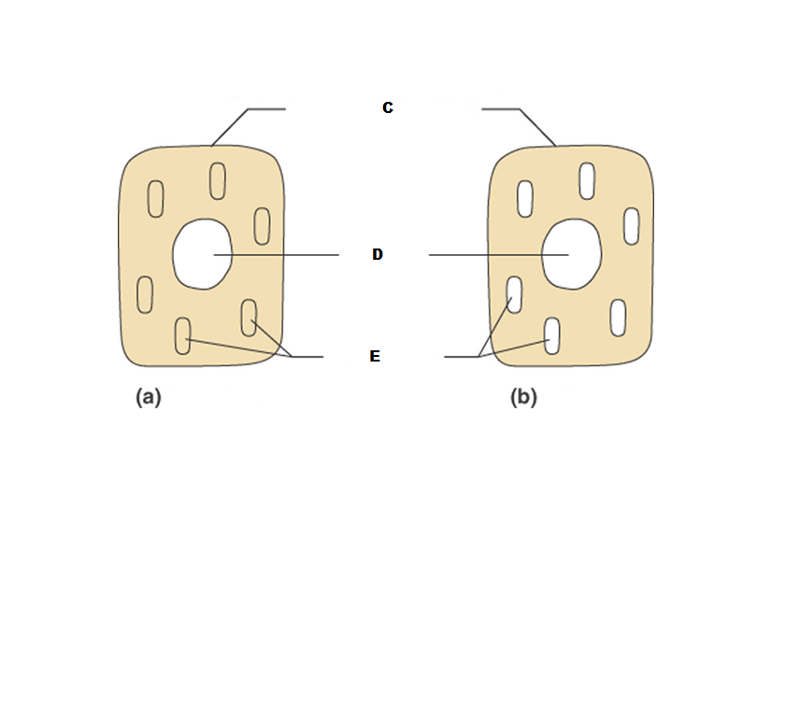
What is B in this picture?
Cytosol
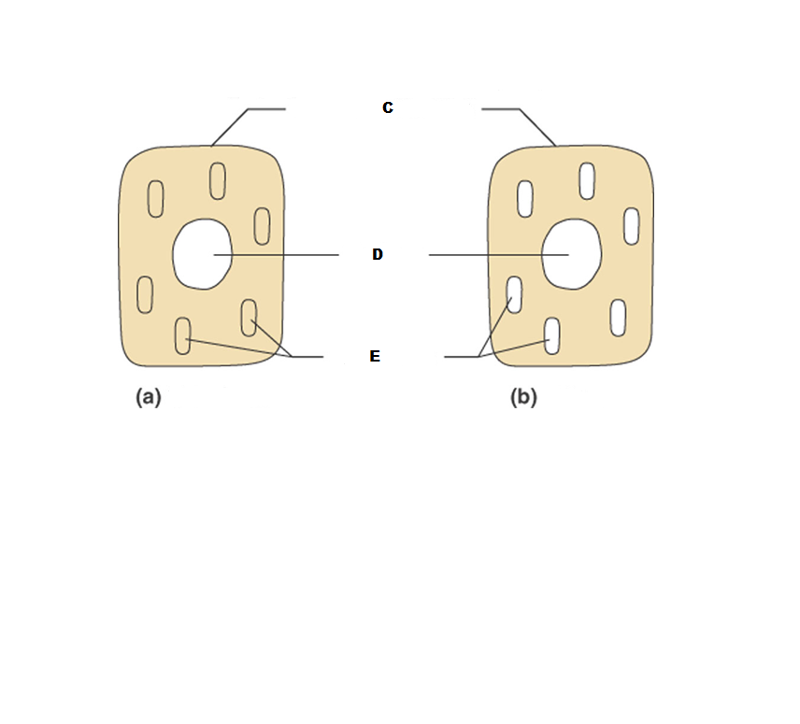
What is C in this picture?
Plasma membrane
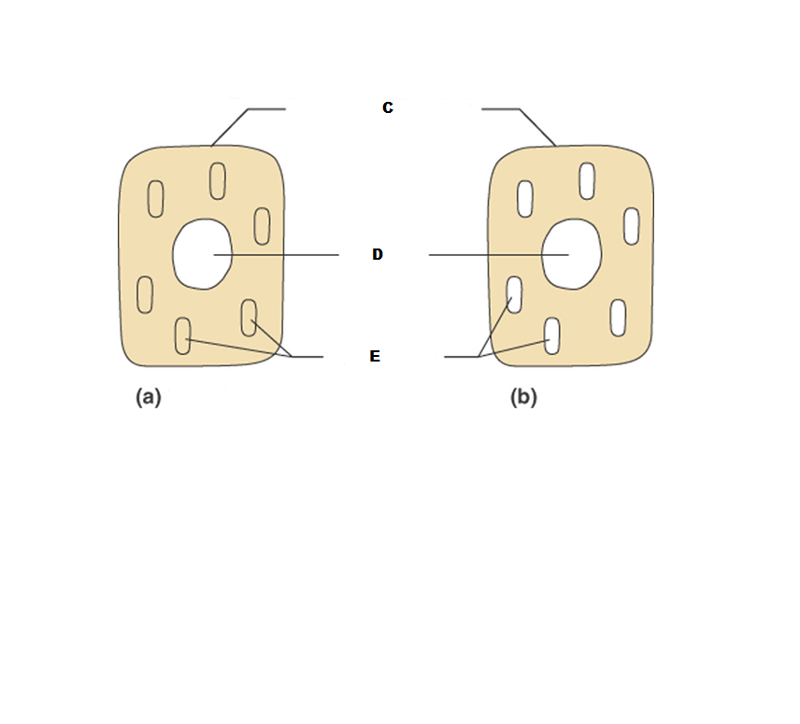
What is D in this picture?
Nucleus
What is E in this picture?
Organelles
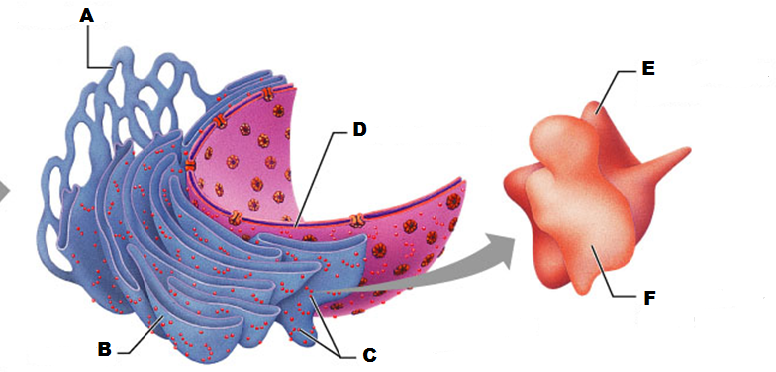
What is A in this picture
Smooth ER
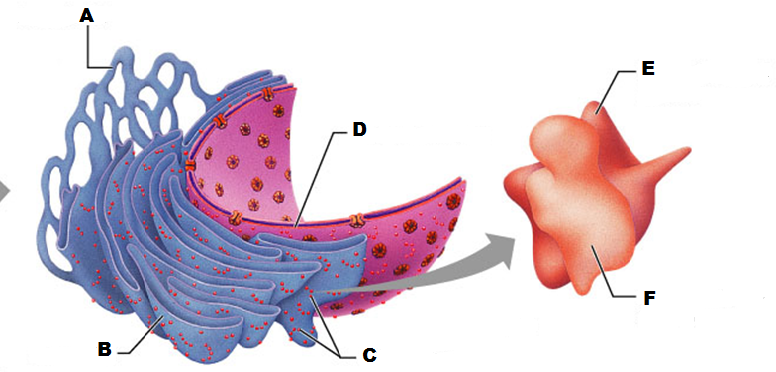
What is B in this picture?
Rough ER
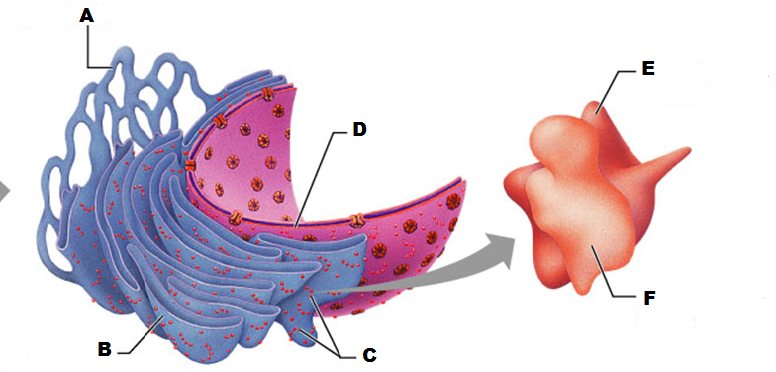
What is C in this picture?
Ribosomes
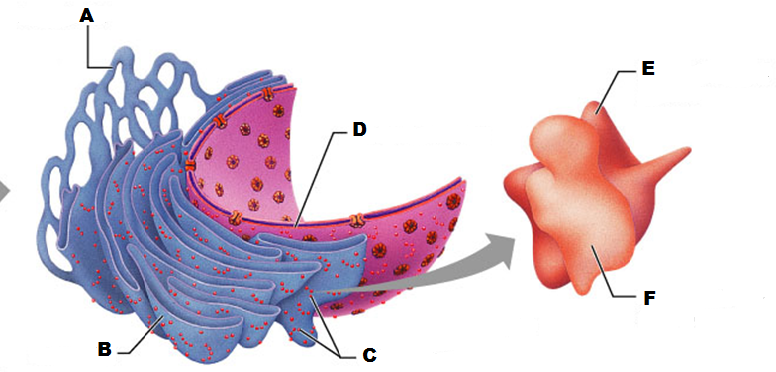
What is D in this picture?
Nuclear Envelope
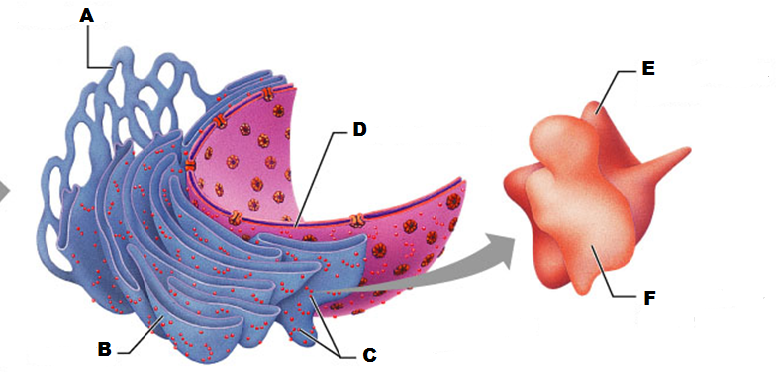
What is E in this picture?
Large ribosomal subunit
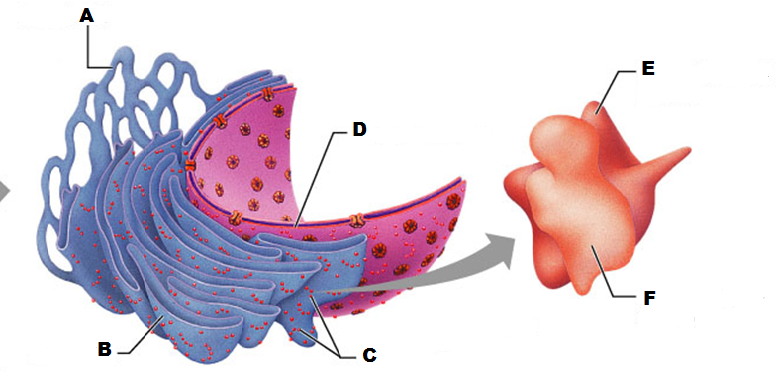
What is F in this picture?
Small ribosomal subunit
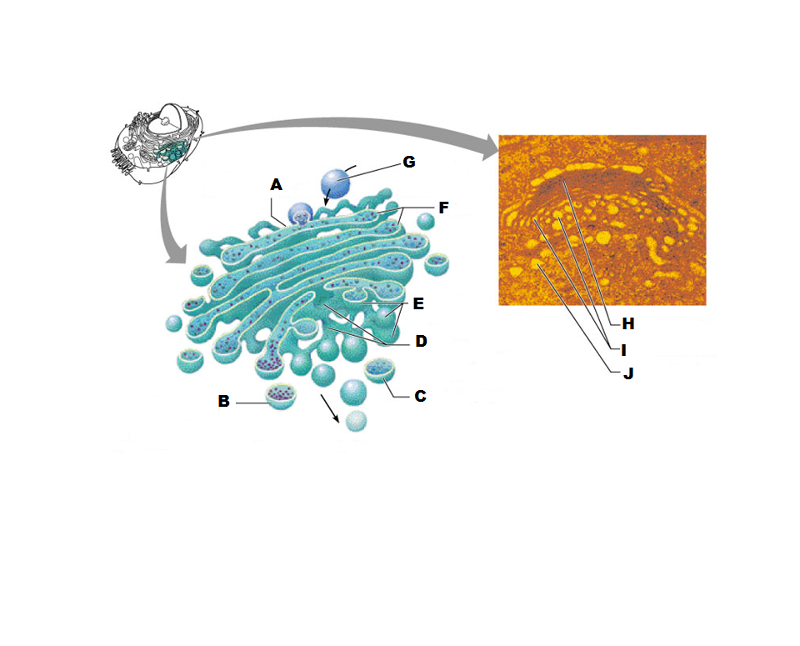
What is A in this picture?
Cis face "receiving" side of golgi apparatus
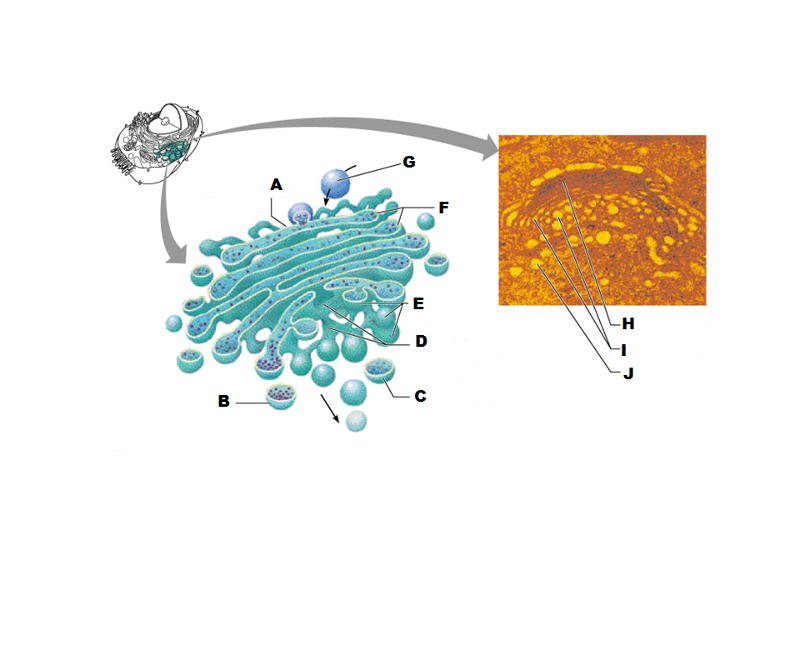
What is B in this picture?
Transport vesicle from the golgi
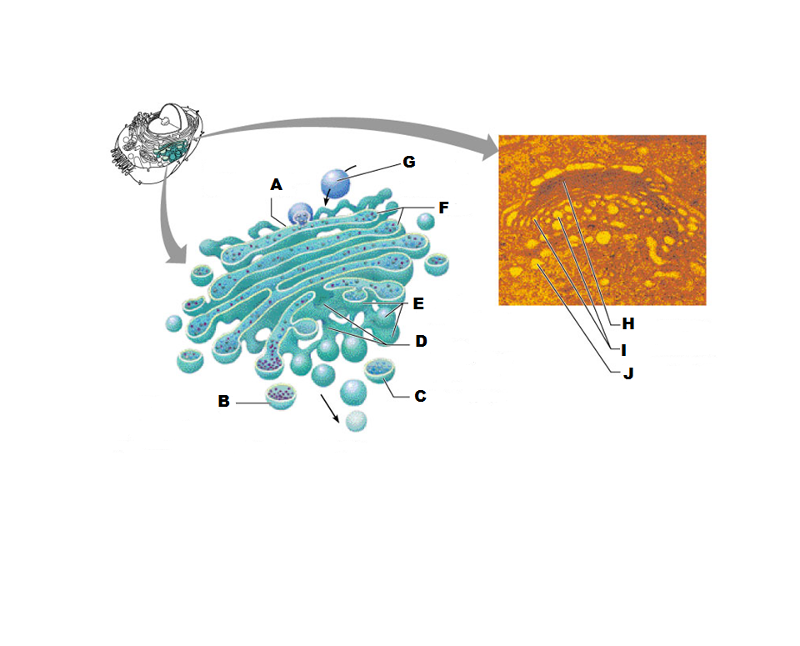
What is C in this picture?
Secretory vesicle from trans face
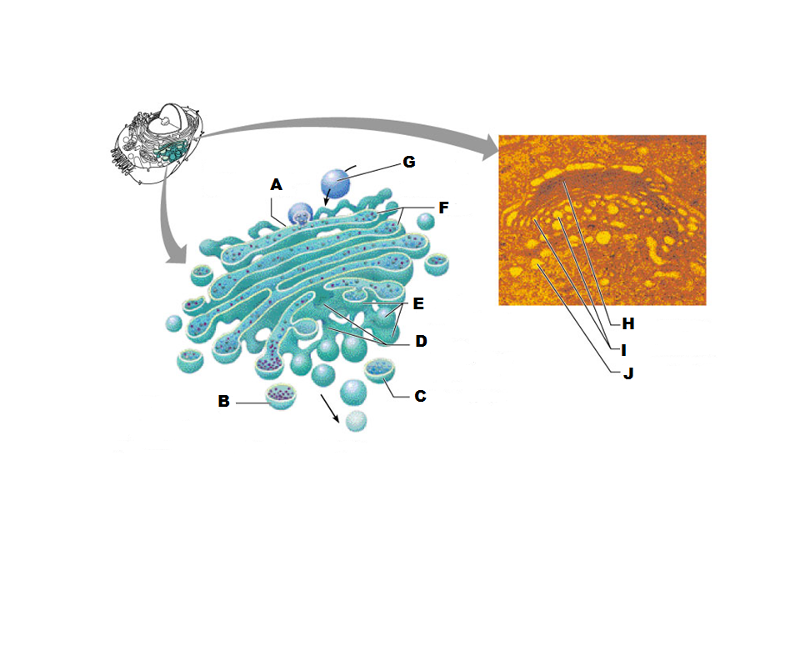
What is D in this picture?
Trans face "shipping" side of golgi apparatus
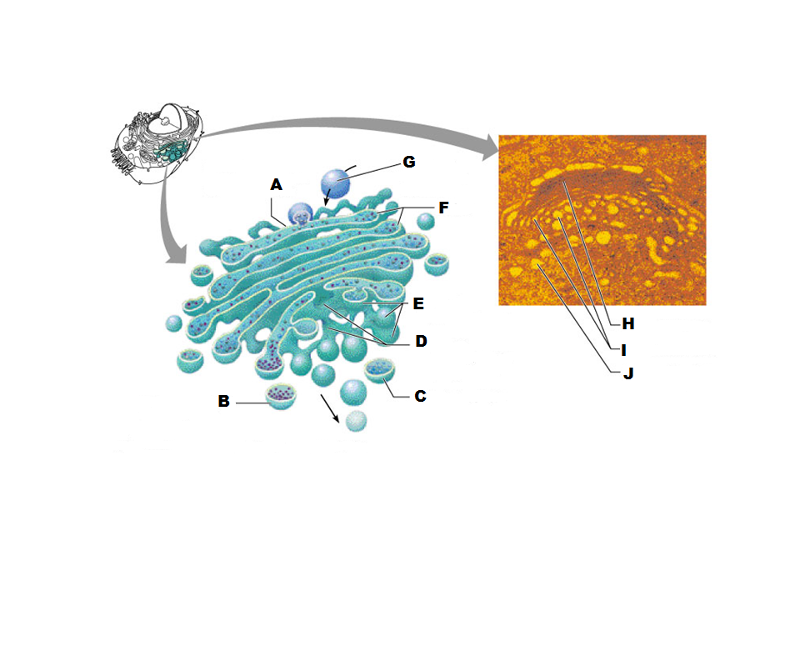
What is E in this picture?
New vesicles forming
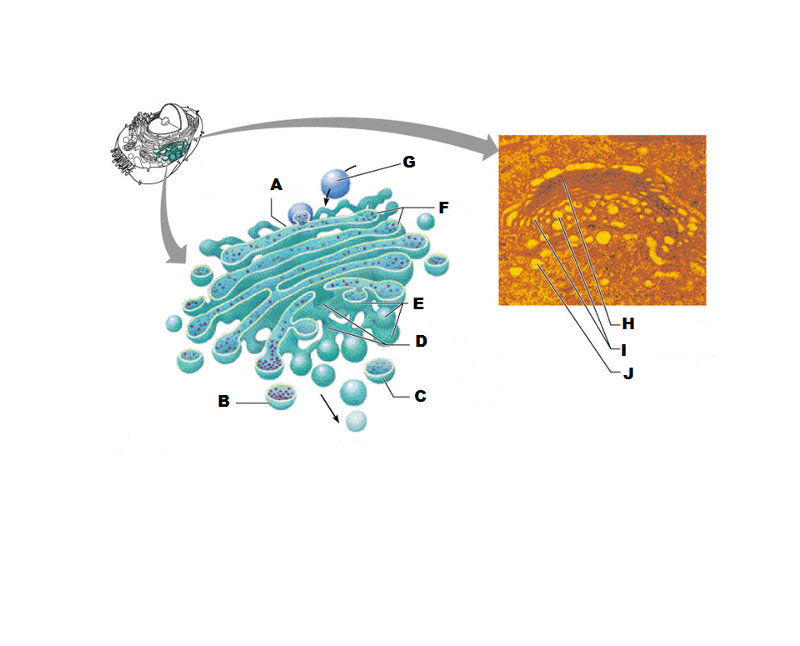
What is F in this picture?
Cisternae
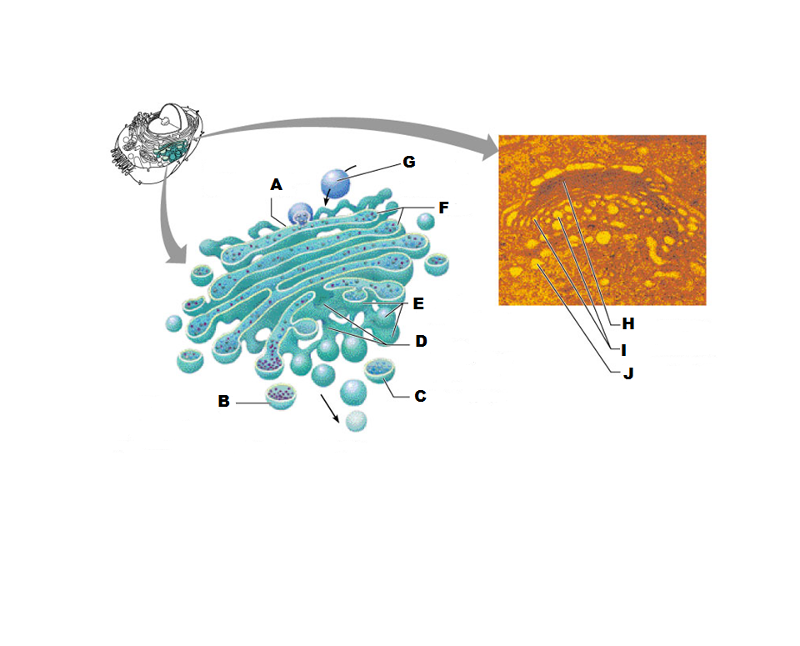
What is G in this picture?
Transport vesicle from rough ER
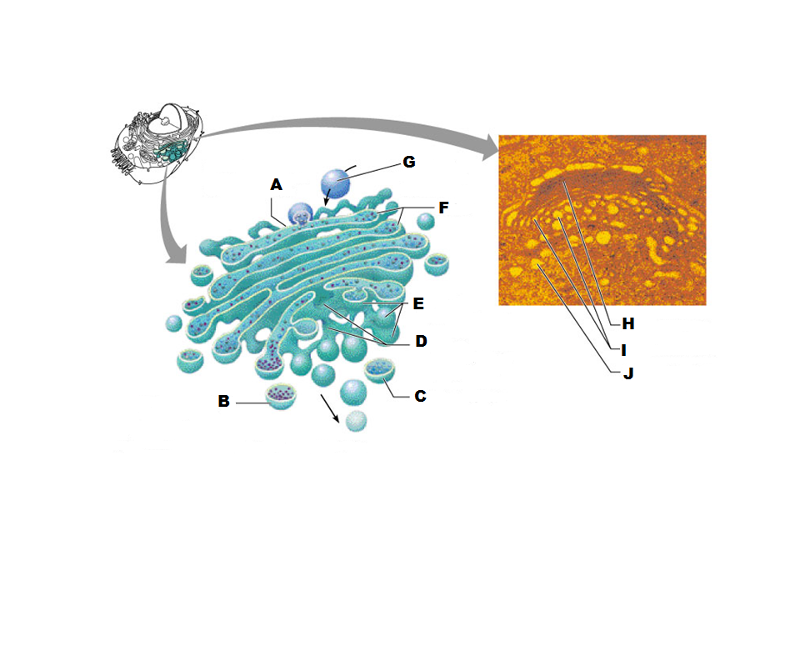
What is H in this picture?
Golgi apparatus
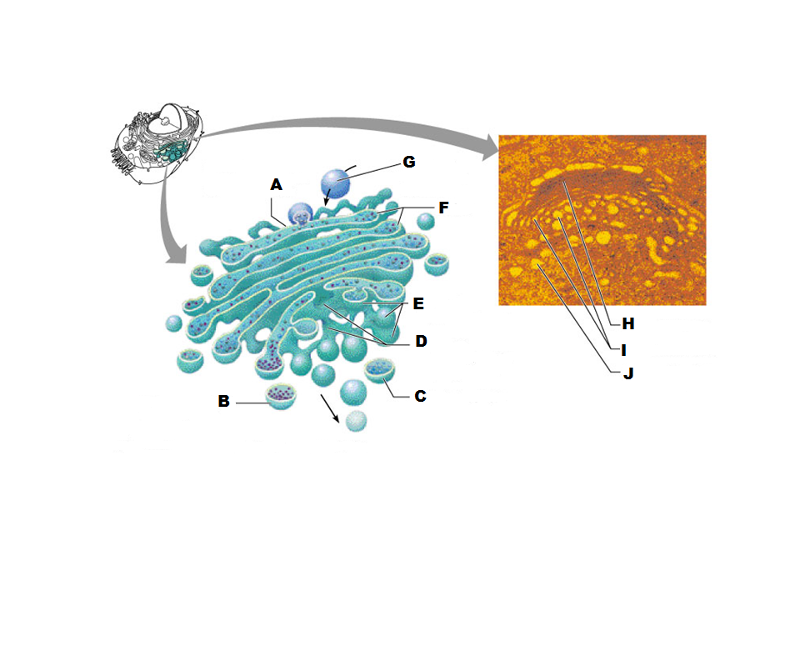
What is I in this picture?
New Vesicles forming
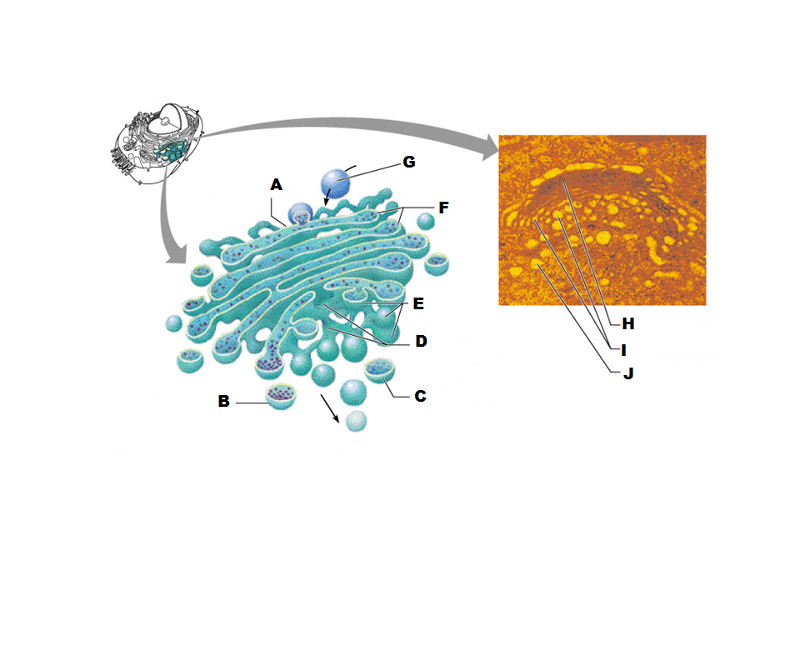
What is J in this picture?
Transport vesicle from the golgi
What does the Cis face do?
Receives proteins from the rough ER
What does the medial cisternae do?
Adds carbohydrates to proteins to form glycoproteins
Adds proteins to lipids to form lipoproteins
What does the trans face do?
Modifies the proteins further and packages them in vesicles for transport
What contains proteins to be exported from the cell?
Secretory vesicles
What delivers proteins to the cell plasma membrane to be incorporated there?
Membrane vesicles
What carries proteins to another location in the cell other than the plasma membrane?
Transport Vesicles
How many different kinds of enzymes are their in lysosomes?
60
Lysosomes work best in what kind of environment?
acidic
What do lysosomes contain?
Digestive and hydrolytic enzymes
What do peroxisome's do?
Removes hydrogen from organic compounds such as fatty acids and amino acids
Oxidixes toxins such as alcohol
What does peroxisomes contain?
Oxidases and catalases
Where do you find more mitochondria cells?
Muscle cells, liver and kidney
Cells with large energy needs
Mitochondria do what kind of replicating?
self-replicating
What kind of DNA do Mitochondria have?
their own distinct kind
How many genes do Mitochondria have and what pattern is the DNA?
37 genes and the DNA is circular
Where does Mitochondrial DNA come from?
mother
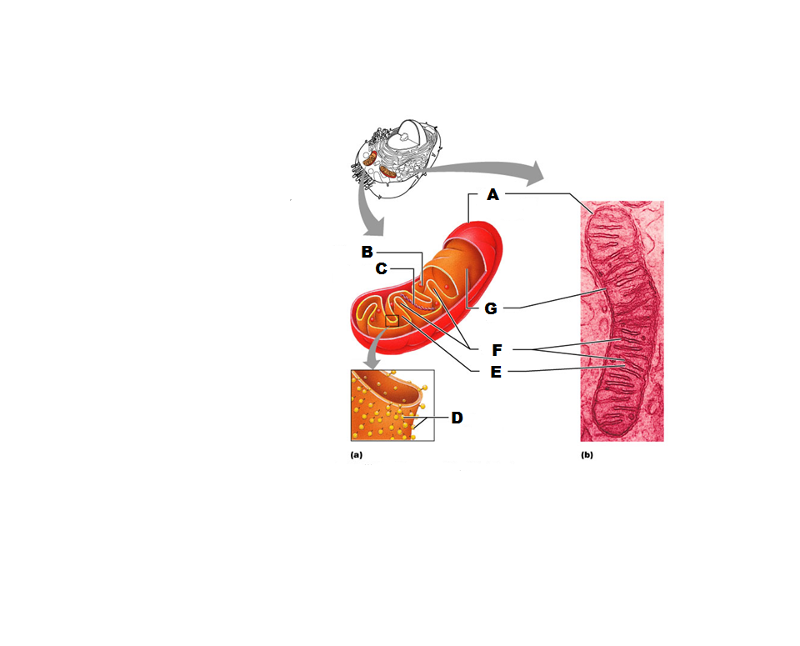
What is A in this picture?
Outer mitochondrial membrane
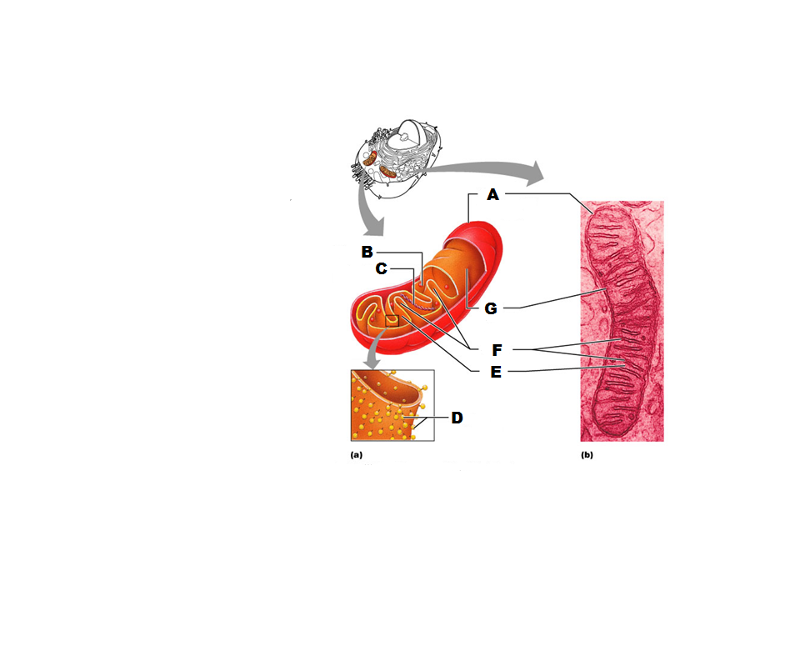
What is B in this picture?
Ribosome
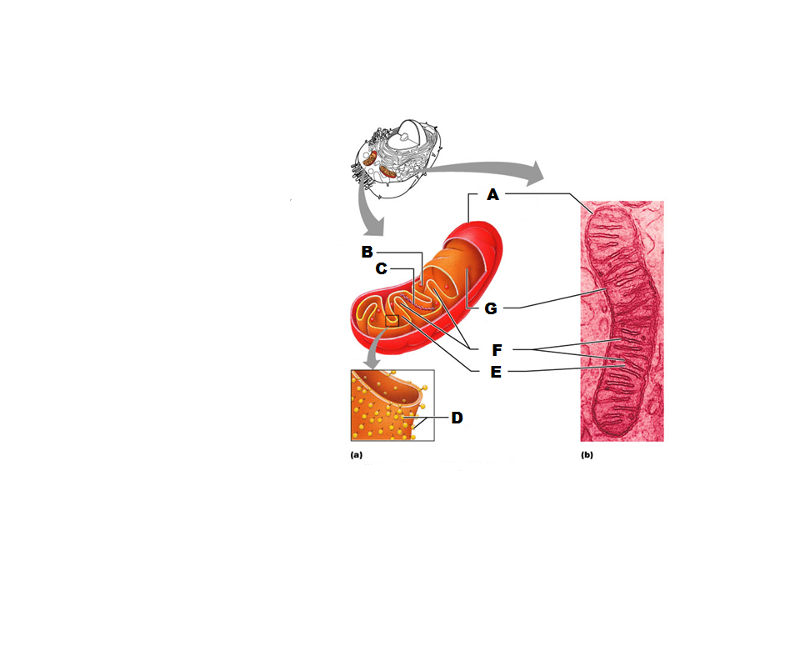
What is C in this picture?
Mitochondrial DNA
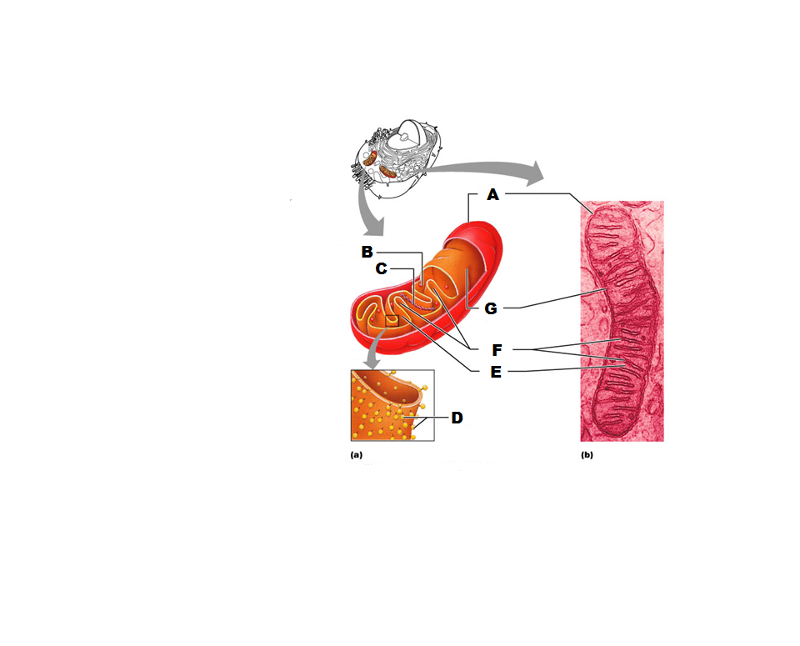
What is D in this picture?
Enzymes
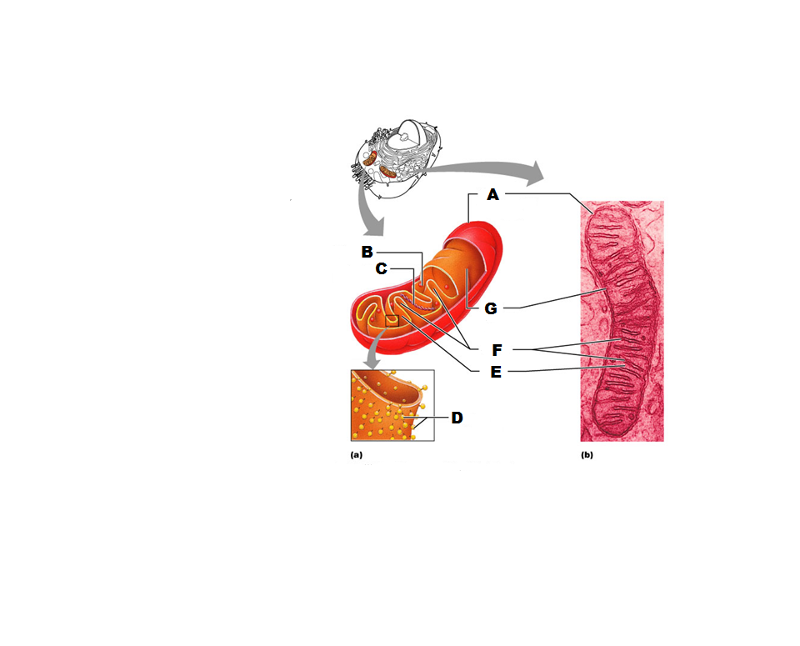
What is E in this picture?
Matrix
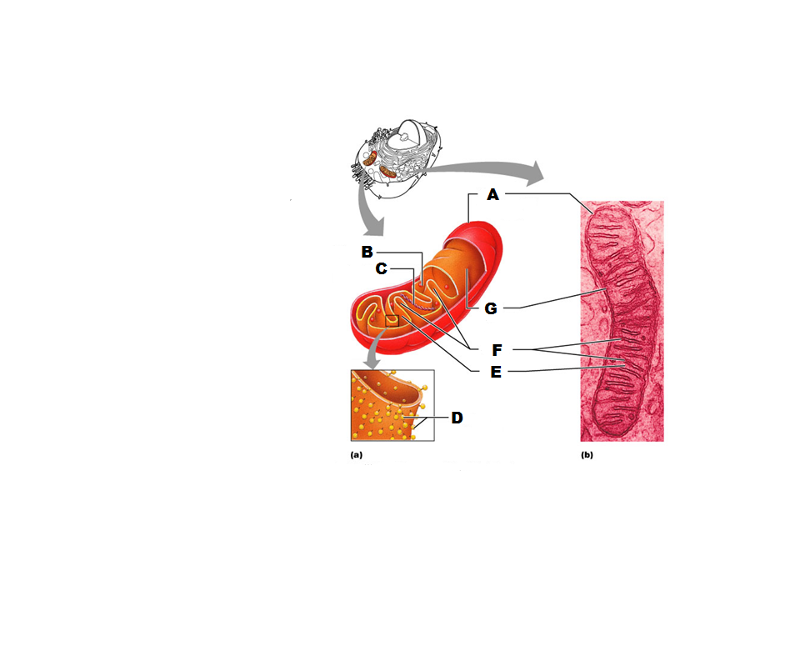
What is F in this picture?
Cristae
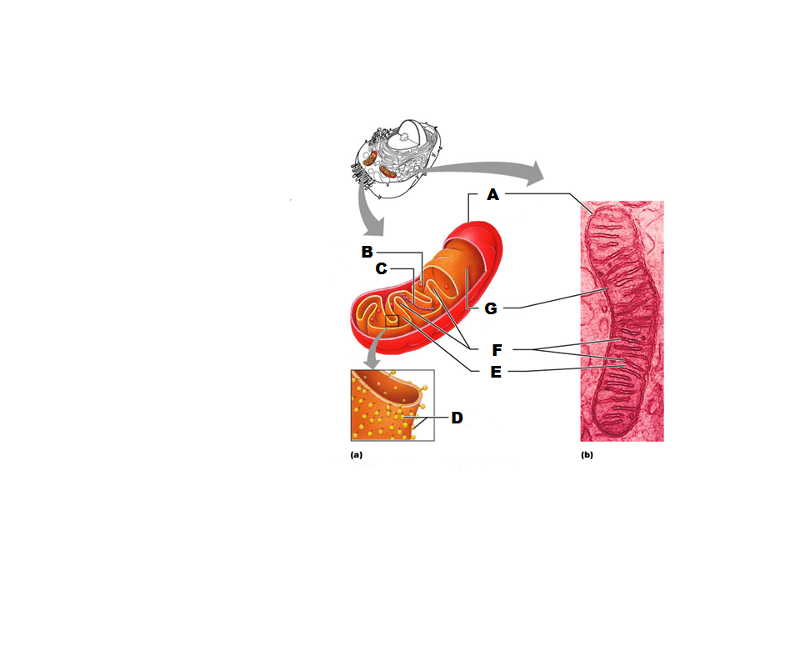
What is G in this picture?
Inner mitochondrial membrane
What detoxifies toxins such as alcohol in liver cells
Smooth ER
What synthesizes fatty acids and steroids such as Estrogen and testosterone
Smooth ER
Structural framework for cell shape and for movement of organelles within the cell, chromosomes during mitosis and phagocytosis
Cytoskeleton
What forms the mitotic spindle?
Centrioles
What is the centrosome?
Cellular location of the centrioles
How many clusters of triplets do centrioles have?
9
How many centrioles do each cell have and how are they located?
2 pairs perpendicular to each other
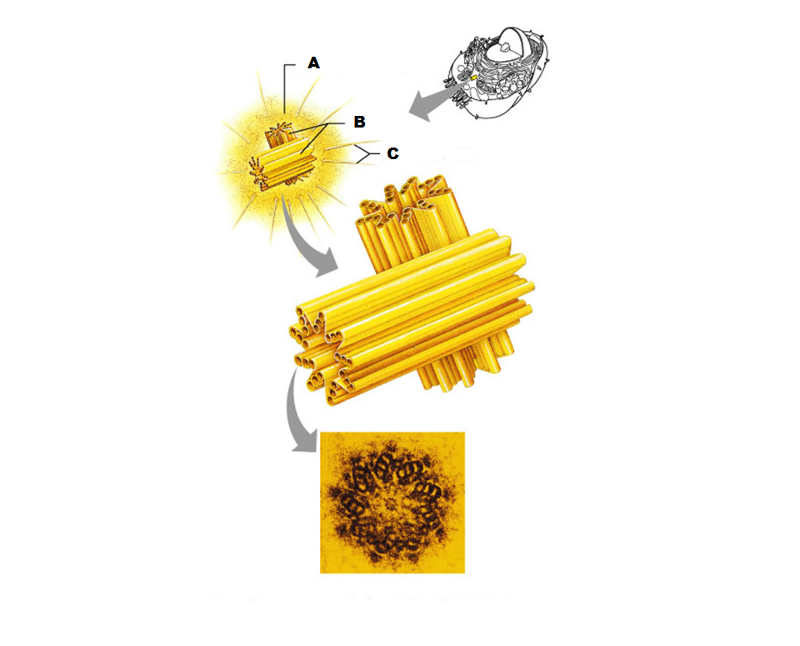
What is A in this picture?
Centrosome matrix
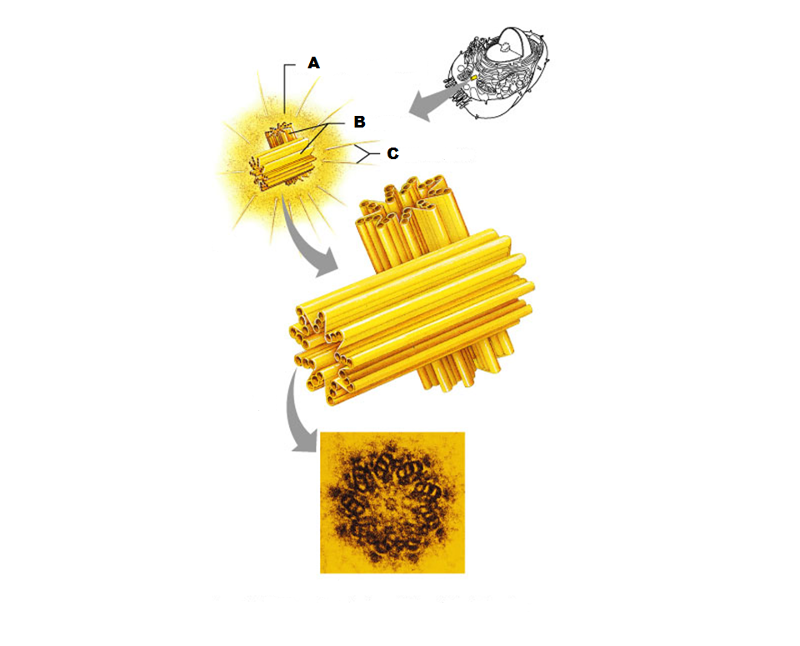
What is B in this picture?
Centrioles
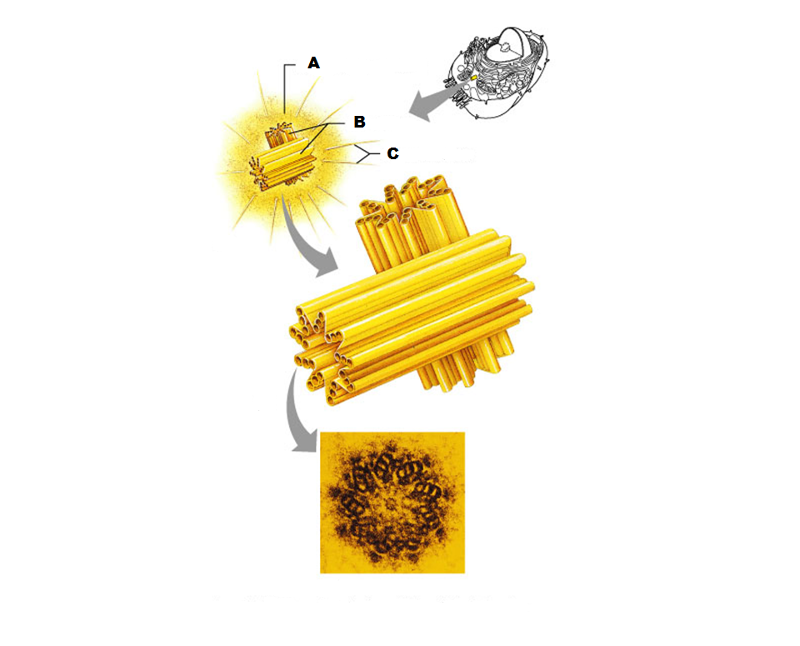
What is C in this picture?
Microtubules
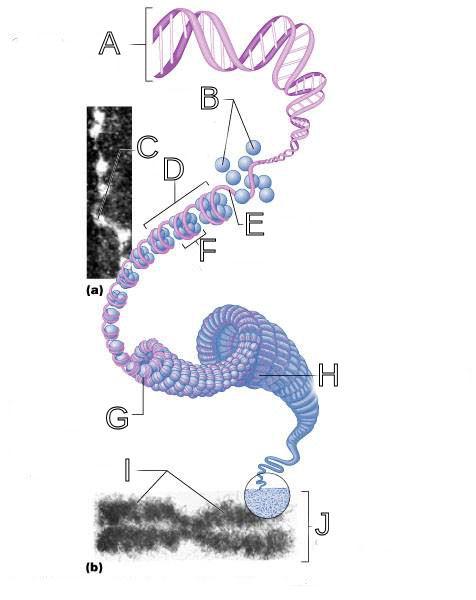
What is A labeled in this picture?
DNA double helix
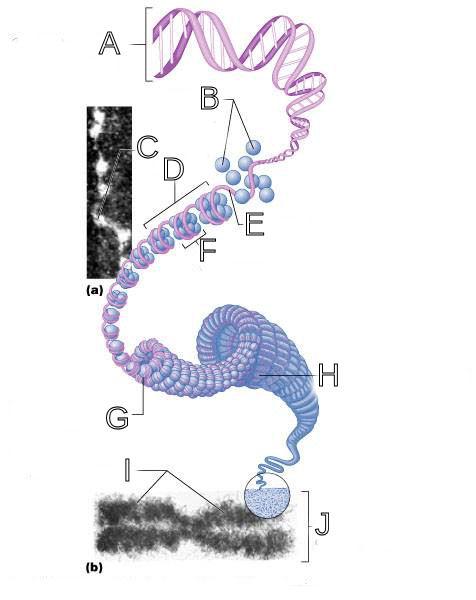
What is B labeled in this picture?
Histones
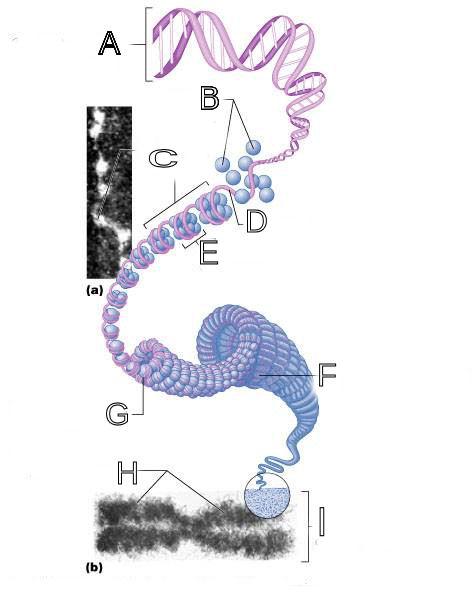
What is C labeled in this picture?
Chromatid " beads on a string"
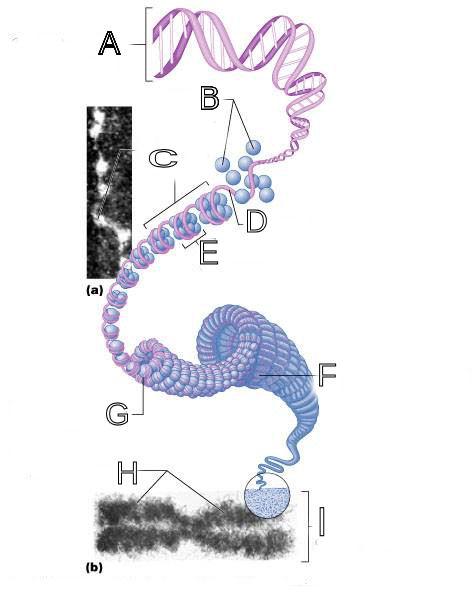
What is D labeled in this picture?
Linker DNA
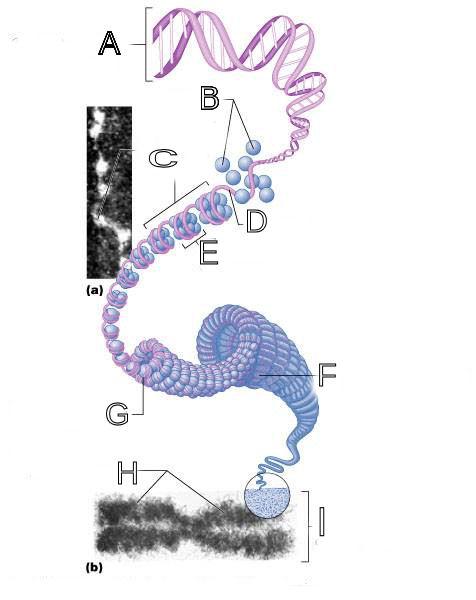
What is E labeled in this picture?
Nucleosomes
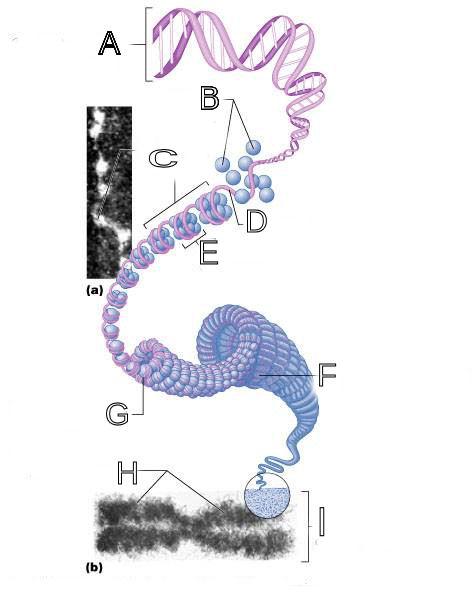
What is F labeled in this picture?
Super coiled structure
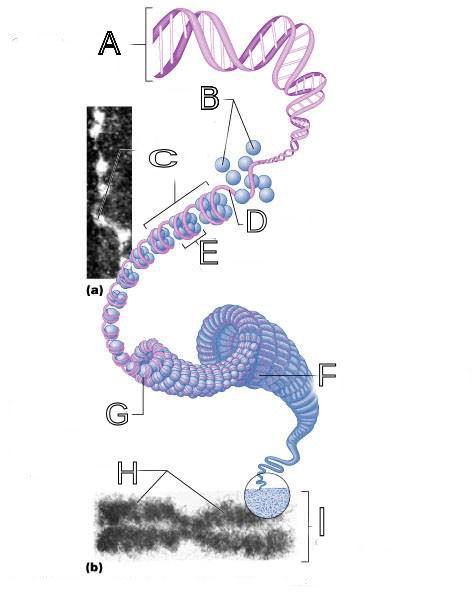
What is G labeled in this picture?
Tight Helical fiber
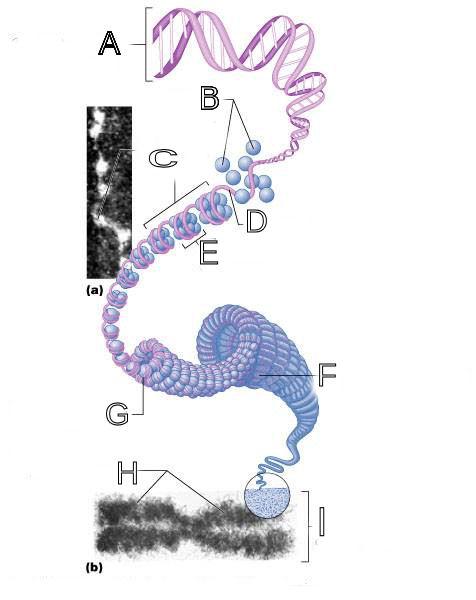
What is H labeled in this picture?
Chromatid
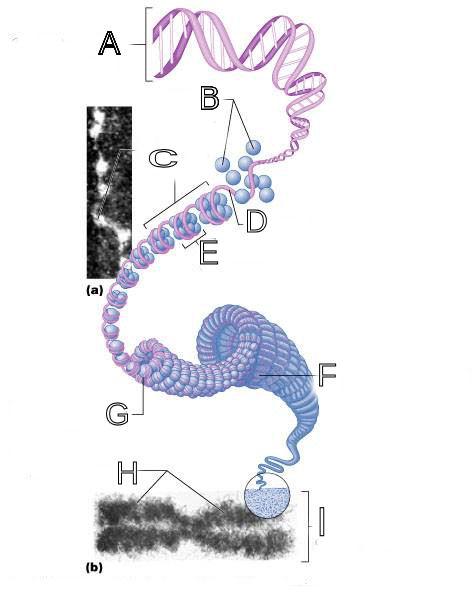
What is I labeled in this picture?
Metaphase chromosome
DNA base pairs are:
Adinene to _________
Guanine to _________
Adinene to Thymine
Guanine to Cytosine
RNA base pairs are:
Adinene to _______
Guanine to ______
Adinene to Thymine
Guanine to Cytosine
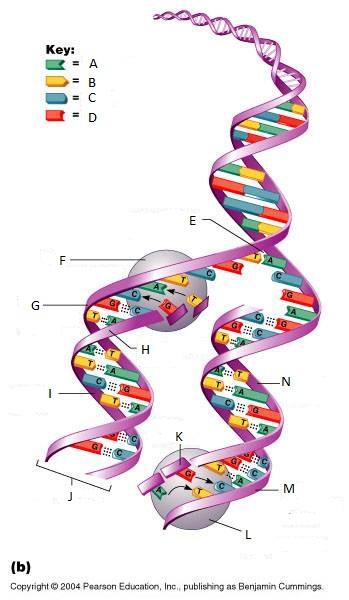
What is A in this picture?
Adenine
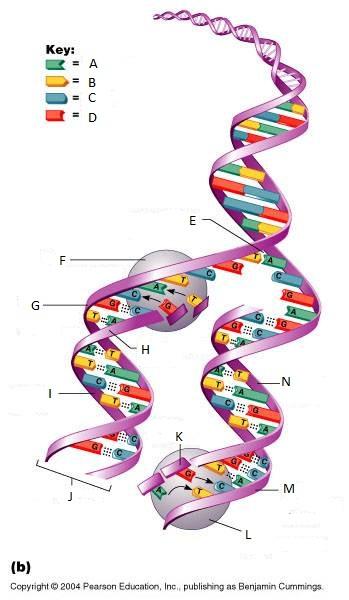
What is B in this picture?
Thymine
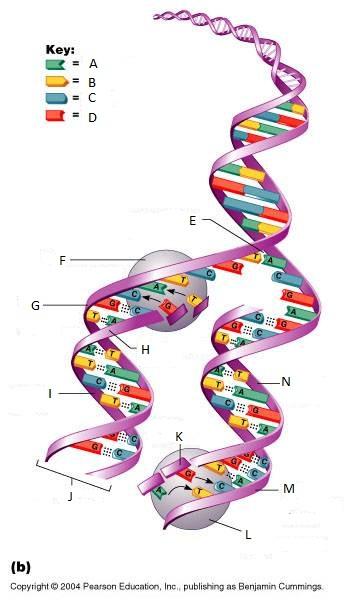
What is C in this picture?
Cytosine
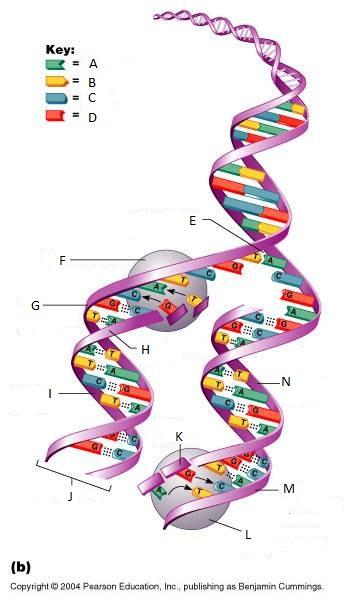
What is D in this picture?
Guanine
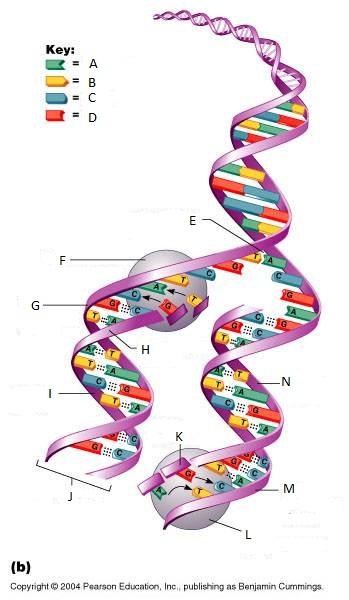
What is E in this picture?
Replication fork
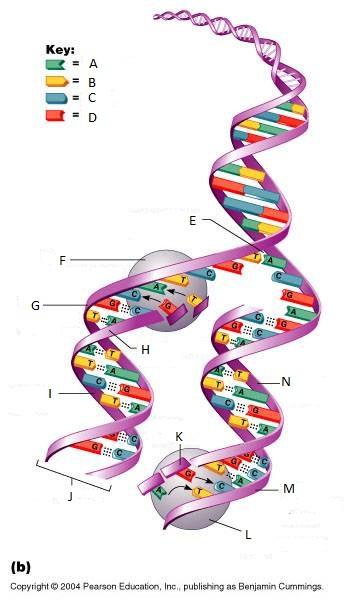
What is F in this picture?
DNA Polymerase III
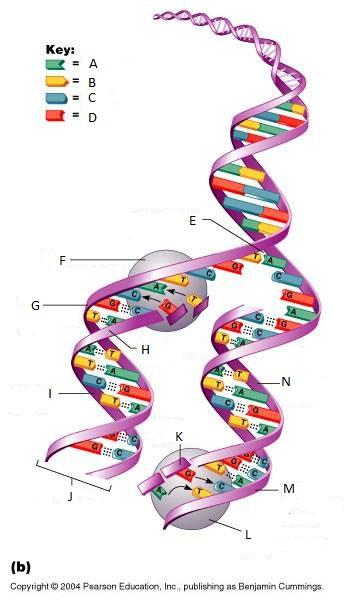
What is G in this picture?
Old template strand
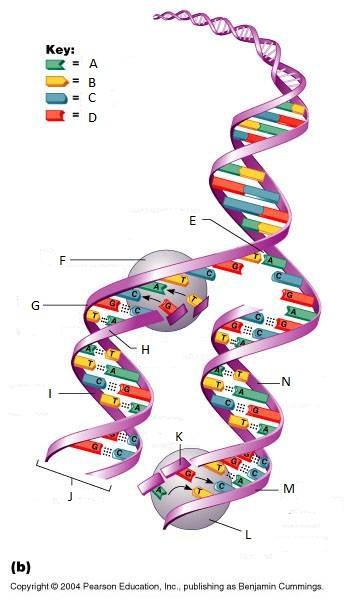
What is H in this picture?
Newly made strand
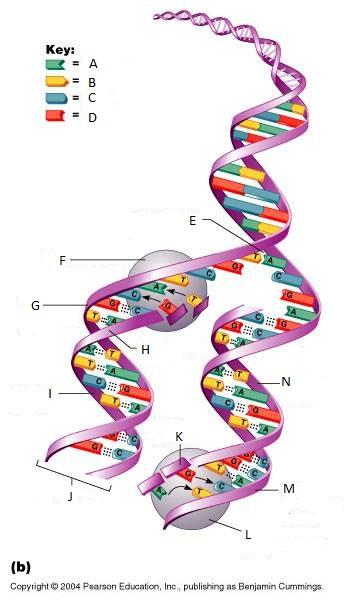
What is I in this picture?
Leading strand
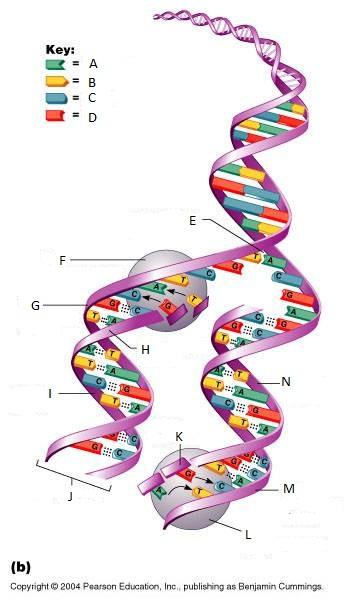
What is J in this picture?
DNA One chromatid
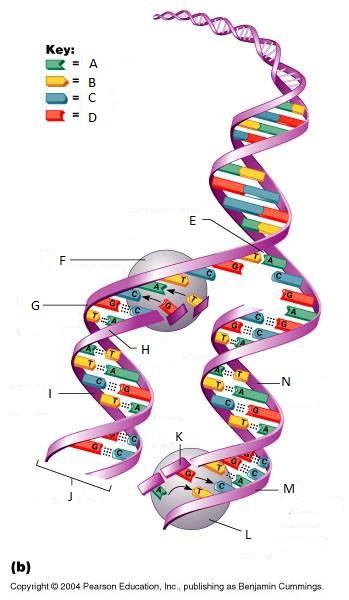
What is K in this picture?
New strand forming
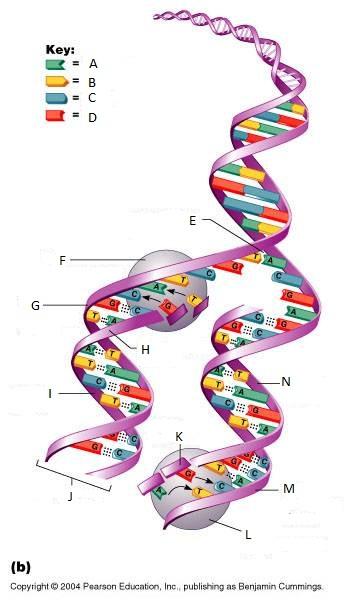
What is L in this picture?
DNA Polymerase III
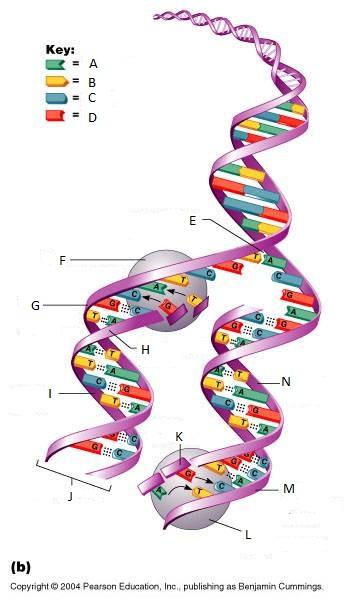
What is M in this picture?
Old template strand
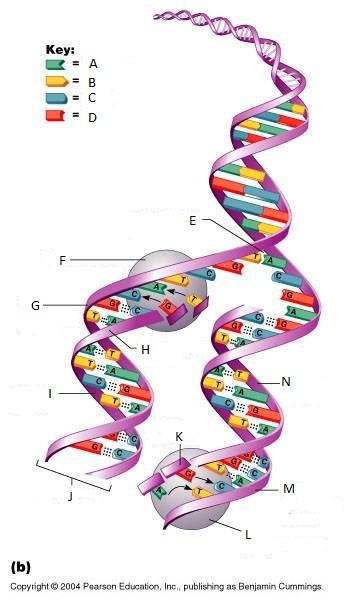
What is N in this picture?
Lagging strand